When we think of a company’s success, we often think of the flagship products that put it on the map. But, behind every popular product is a strategic lineup called the product mix, a carefully crafted array of products designed to appeal to different customer needs and expand market reach. By understanding and optimizing your product mix, you can significantly increase revenue, build a loyal customer base, and outperform competitors.
Table of Contents
In this guide, we’ll explore the concept of product mix, exploring its importance, dimensions, components, and strategies. We’ll also cover practical examples, analysis techniques, and insights into studying competitors’ product mixes to help you develop a competitive advantage. Let’s get started!
What is Product Mix?
A product mix refers to all the products a company offers to its customers. It includes different categories of products, each with multiple options. Some products may be closely related, while others serve different needs. A well-balanced product mix helps a business attract a wider audience, meet diverse customer preferences, and increase sales.
Imagine you’re running a tech company. If you offer smartphones, laptops, and smartwatches, each of these categories would be a product line, but together, they make up the product mix. A company’s product mix reflects its identity and positioning within the market; a well-curated mix aligns with brand values, appeals to different consumer groups, and allows for flexible responses to changing market demands.
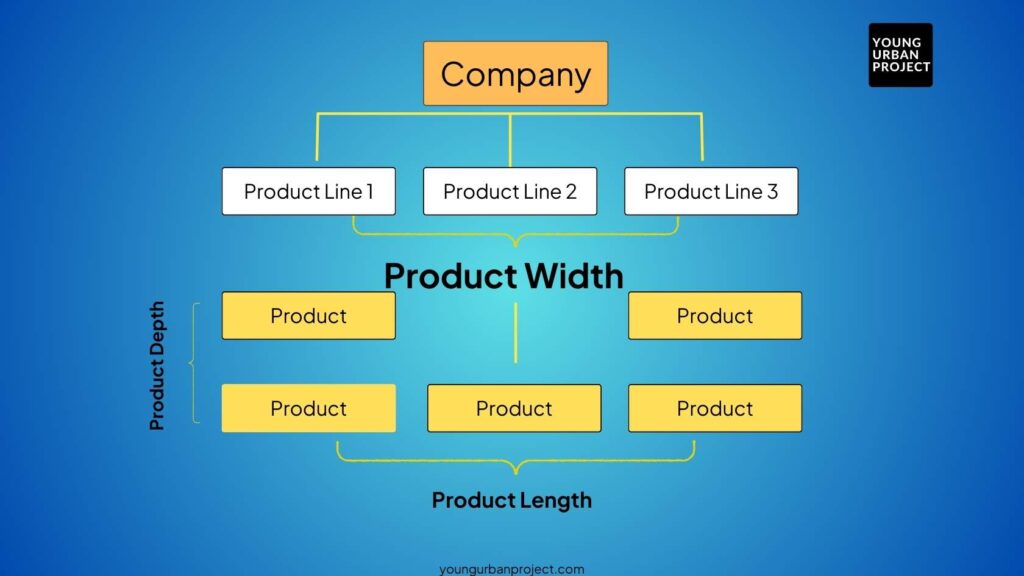
Here’s an illustration of a Product Mix
Importance of Product Mix
A strategically designed product mix is essential to an organization’s success.
1. Meeting Diverse Customer Needs
A diverse product mix allows businesses to cater to different customer preferences, budgets, and requirements. For example, Apple’s product mix includes various price points, from affordable iPhones to premium laptops, appealing to multiple demographics.
2. Increasing Market Share
By offering a wide array of products, companies can capture a broader market share. Coca-Cola, for instance, has a vast product mix that spans sodas, juices, and water, allowing it to reach a global audience with diverse beverage preferences.
3. Enhancing Brand Recognition and Loyalty
A well-curated product mix strengthens brand identity and fosters customer loyalty. When customers trust a brand’s quality across products, they are more likely to purchase from different lines, increasing the chances of repeat business.
4. Generating Cross-Selling and Upselling Opportunities
A robust product mix facilitates cross-selling and upselling. For instance, an electronics store that sells both laptops and accessories can cross-sell items such as cases or software, boosting overall revenue.
5. Adaptability to Market Changes
Market demands can change swiftly, and a diversified product mix allows companies to pivot more easily. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, many companies expanded their product mix to include essentials like sanitizers and PPE to adapt to new market needs.
6. Optimizing Profitability
Not every product line will be a best-seller, but a balanced mix allows higher-margin products to subsidize lower-margin or experimental lines. This helps companies maintain profitability while experimenting with new offerings.
Also read: 10 Creative Product Launch Ideas: Make Your Next Launch a Success
Dimensions of Product Mix
Understanding the types of product mix is crucial to shaping a strategy.
Here’s a closer look at the four dimensions that define a company’s product mix:
✅1. Width
The width of a product mix refers to the number of different product lines a company offers. Each product line is a group of related products that fulfill similar functions or are targeted at similar markets.
Example:
Consider Procter & Gamble (P&G), which has a wide product mix. It offers multiple product lines in categories such as personal care, household cleaning, health, and grooming. For instance:
- Personal Care: Pantene, Olay, Head & Shoulders
- Cleaning: Tide, Ariel, Gain
- Grooming: Gillette, Braun
- Health: Vicks, Pepto-Bismol
Each of these categories represents a distinct product line, making P&G’s product mix wide. This diversity allows P&G to serve multiple markets and meet a broad range of customer needs.
✅2. Length
The length of a product mix is the total number of individual products within the company’s product lines. It is calculated by adding up all the products across all product lines.
Example:
Let’s look at Apple Inc. for a clear example of product mix length. Apple has several product lines, and each line has multiple products, such as:
- iPhones: iPhone 14, iPhone 13, iPhone SE
- iPads: iPad Pro, iPad Air, iPad Mini
- Mac: MacBook Pro, MacBook Air, iMac
- Wearables and Accessories: Apple Watch, AirPods, AirTag
In this example, the length of Apple’s product mix is the total number of models across all these lines. Suppose Apple offers 5 iPhone models, 3 iPad models, 3 Mac models, and 4 wearables. Then, Apple’s product mix length would be 5 + 3 + 3 + 4 = 15. Length shows the full array of options a customer has when considering Apple products.
✅3. Depth
The depth of a product mix refers to the variety of versions available within each product line. This includes variations in size, color, features, or any other differentiating factors that give customers more choices within a specific product line.
Example:
Let’s consider Coca-Cola as an example of product mix depth. Within the Coca-Cola product line, you’ll find several versions:
- Classic Coca-Cola
- Diet Coke
- Coca-Cola Zero Sugar
- Coca-Cola Cherry
- Coca-Cola Vanilla
Each of these variations represents a different version of the same core product, catering to different preferences, such as sugar-free options or unique flavors. In this case, the depth of Coca-Cola’s product line is high, as it offers multiple versions of its cola product. This depth allows Coca-Cola to capture more customers by addressing varied tastes and health preferences.
✅4. Consistency
The consistency of a product mix measures how closely related the various product lines are in terms of use, production, distribution, or target market. High consistency means the product lines are closely related, while low consistency indicates a diverse mix of unrelated products.
Example:
Unilever has a less consistent product mix compared to specialized companies. Unilever’s portfolio includes:
- Personal Care: Dove, Axe, Sunsilk
- Food and Beverages: Knorr, Lipton, Ben & Jerry’s
- Home Care: Surf, Domestos, Cif
While Unilever’s product lines are related to everyday consumer needs, they cover vastly different categories, from personal care to food items to household cleaning. This makes Unilever’s product mix less consistent than a company like Apple, whose products all fall under the umbrella of consumer electronics.
In contrast, Nike has a high consistency in its product mix because all its product lines (shoes, apparel, accessories) are related to sports and fitness.
Also read: What Is Product Classification in Marketing: Types and Importance
Product Mix Strategies
A product mix strategy refers to the approach a company uses to manage and grow its range of products, services, and brand offerings. The ultimate goal of any product mix strategy is to ensure that the right mix of products is available to meet market demand, maximize profitability, and support long-term business growth. Companies use different strategies based on their business goals, market conditions, and consumer preferences.
In this section, we’ll explore the most effective product mix strategies, including their components, examples, benefits, and how to implement them successfully.
Key Components
To understand how a product mix strategy works, it’s crucial to consider the following components that shape it:
1. Market Research and Consumer Insight
A strong product mix strategy starts with understanding your customer. Market research helps businesses identify consumer preferences, pain points, and unmet needs. Whether you’re focusing on specific demographics, such as millennials or eco-conscious consumers, thorough research lays the foundation for a tailored product mix.
2. Brand Identity and Positioning
The strategy must align with the brand’s identity. A well-planned product mix enhances a brand’s position in the market. For instance, luxury brands like Rolex or Louis Vuitton focus on high-quality, exclusive products, whereas brands like Unilever offer a range of affordable to premium products across various categories.
3. Product Life Cycle Management
A product mix must account for the life cycle of each product in the mix. Products evolve through the introduction, growth, maturity, and decline stages. Managing these stages is vital. Products in the growth or maturity phase may require more marketing effort, while declining products may need to be phased out or replaced with new offerings.
Also read: Building a Product Launch Plan for New Product Marketers: Step-by-Step
4. Pricing Strategy
Price alignment with each product is a key consideration in any product mix. The pricing of each product affects how the product fits into the overall mix. For example, offering premium products alongside budget options can create cross-selling opportunities, but you must ensure the pricing strategy doesn’t undermine the brand.
5. Distribution Channels
A product mix strategy includes the evaluation of which distribution channels are most effective for each product. Some products might perform best through online channels, while others need physical retail presence. Tailoring the strategy to each product’s distribution needs can enhance reach and sales performance.

👀 Checkout our Product Marketing Course
Types of Product Mix Strategies
There are several strategies that businesses use to optimize their offerings. The strategy a company chooses depends on its goals, market conditions, and resources. Here are some of the most common types:
1. Expansion Strategy
An expansion strategy involves increasing the width or depth of a company’s product mix. The goal is to capture new customers, meet the diverse needs of existing customers, or enter new markets. There are two key types of expansion strategies:
- Product Line Extension: Adding more variations to an existing product line to cater to different consumer preferences. For instance, Coca-Cola introduced Diet Coke and Coca-Cola Zero as product line extensions to appeal to health-conscious consumers.
- New Product Development: Launching entirely new products that are distinct from the existing product lines. For example, Nike expanding from selling just sports shoes to launching sports apparel, fitness trackers, and accessories.
Benefits of Expansion Strategy:
- It allows companies to target new customer segments.
- Enhances brand visibility across different market segments.
- Increases the overall revenue potential by introducing new products.
Also Read: Importance of Marketing Mix
2. Contraction Strategy
A contraction strategy focuses on reducing the product mix by eliminating products that no longer perform well or do not align with the company’s overall goals. Contraction is a critical move for businesses facing saturated markets or declining demand.
- Product Line Pruning: This is the process of discontinuing certain products from a line that are underperforming, outdated, or irrelevant to customer needs. For example, a smartphone brand might stop producing older models to focus on its newer, more popular devices.
- Divesting or Selling Products: If a product line doesn’t align with the brand’s core business objectives, it may be sold off to another company or discontinued entirely.
Benefits of Contraction Strategy:
- Helps businesses focus on their most profitable products.
- Reduces operational complexity and cost by cutting out non-performing products.
- Allows businesses to reallocate resources to more lucrative and promising product lines.
Also Read: What Is Marketing Mix?
3. Deepening Strategy
The deepening strategy involves adding more variations within an existing product line. By expanding the depth of a product line, companies can meet niche market needs, provide more choices to their customers, and improve customer satisfaction.
For example, a cosmetics brand might offer multiple shades and formulations of foundation to appeal to different skin tones, types, and preferences. Another example is a car manufacturer offering various models with different features, such as hybrid, electric, or gasoline engines.
Benefits of Deepening Strategy:
- Provides customers with more tailored options and choices.
- Increases brand loyalty, as customers find more products that suit their specific needs.
- Enhances market penetration in niche segments.
4. Brand Extension Strategy
Brand extension is the process of using an established brand name to launch a new product in a different category or market. This strategy works well when a brand has strong equity and customer trust.
For example, Apple, initially known for its computers, expanded into consumer electronics like the iPhone, iPad, and Apple Watch. The success of these products was due, in part, to the trust consumers had in the Apple brand. Similarly, companies like Virgin have extended their brand into areas like airlines, mobile services, and even space tourism.
Benefits of Brand Extension Strategy:
- It leverages the established brand equity, making new product introductions easier and faster.
- Helps the brand diversify into different markets, reducing dependency on one product line.
- Facilitates cross-selling opportunities by bringing related products under the same brand.
Also Read: Importance of Brand Positioning
5. Diversification Strategy
Diversification is one of the most ambitious product mix strategies, involving the introduction of new products in entirely new categories. This strategy is often used to mitigate risk or expand into new markets that are unrelated to the company’s existing products.
For instance, Amazon, initially an online bookstore, diversified into electronics, cloud computing, and even grocery delivery services through its acquisition of Whole Foods. Similarly, Apple diversified from being a computer maker to providing a variety of services like music streaming and financial services through Apple Pay.
Benefits of Diversification Strategy:
- Reduces risks by spreading the business across various markets.
- Opens new revenue streams and business opportunities.
- Strengthens the company’s market position by allowing it to dominate multiple sectors.
Also Read: What is Promotion Mix
Implementing Product Mix Strategies
A successful product mix strategy requires careful planning and execution.
Here are some steps to help you effectively implement your strategy:
1. Conduct Market Research
Before implementing any product mix strategy, it’s essential to understand your target audience, competitors, and market trends. Consumer research will guide your decisions on expanding, contracting, or deepening your product mix.
2. Evaluate Your Current Mix
Regularly assess your product mix to identify opportunities for optimization. Look at each product’s sales performance, customer feedback, and profitability. This will help you determine whether certain products need to be phased out or whether you should introduce new variations.
3. Align with Business Goals
Every product mix strategy should align with your overarching business objectives. If your goal is to increase market share, an expansion strategy with line extensions might be the way to go. If you’re aiming to improve profitability, a contraction strategy could be more effective.
4. Monitor Results and Adjust
Once the strategy is in place, continuously monitor its success. Track sales, customer responses, and market conditions to determine if any adjustments are necessary. The product mix should remain flexible to adapt to changes in the market or consumer preferences
Also Read: What Is Price Mix?
Benefits of a Well-Planned Product Mix Strategy
A well-planned product mix strategy offers numerous advantages to a business, enabling it to meet customer needs more effectively, maximize profits, and strengthen its brand positioning. Here are some key benefits:
1. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
A carefully structured product mix strategy helps ensure that a business offers products that meet diverse customer needs, preferences, and budgets. By providing a well-thought-out variety, the company can cater to different consumer segments, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty. For instance, offering various sizes, colors, or flavors within a product line allows customers to find products that best match their preferences, enhancing their overall experience.
2. Increased Market Reach and Revenue Streams
A comprehensive product mix can expand a company’s reach by targeting different segments of the market. With multiple product lines and options within each, businesses can appeal to a wider audience, from budget-conscious consumers to premium buyers. By tapping into diverse markets, a company not only broadens its customer base but also diversifies its revenue streams, reducing dependency on a single product line for income.
3. Better Competitive Advantage
A well-planned product mix allows businesses to stand out in competitive markets by offering unique options that competitors may not provide. By understanding the needs of their target audience and filling product gaps, companies can strengthen their position in the marketplace. For example, a company that offers eco-friendly, sustainable product alternatives within its product mix may attract customers looking for environmentally conscious choices, setting it apart from competitors.
4. Higher Profit Margins
Strategic product mix planning enables businesses to introduce premium products or variations with higher profit margins. By differentiating products based on quality, features, or branding, a company can offer products at different price points. Premium versions of products typically yield higher profit margins, allowing businesses to maximize profitability while giving customers the option to “upgrade.”
5. Optimized Resource Utilization
A well-balanced product mix ensures that a company uses its resources efficiently. By planning its product offerings, a business can streamline production, reduce inventory costs, and optimize supply chain processes. For instance, by offering multiple variations within the same product line, a company can often leverage shared production techniques, ingredients, or materials, which reduces costs and increases operational efficiency.
6. Stronger Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
A thoughtfully designed product mix that aligns with a brand’s mission and values reinforces brand identity, making it more memorable and trustworthy to customers. When a company consistently delivers products that reflect its brand promise, it builds stronger emotional connections with its audience. This brand consistency encourages repeat purchases and customer loyalty, as customers are more likely to stick with a brand they trust.
7. Increased Opportunities for Cross-Selling and Upselling
With a well-planned product mix, businesses can more effectively implement cross-selling and upselling strategies. For instance, a consumer purchasing a phone might also buy accessories like cases, chargers, or headphones, all of which can be included within the product mix. Upselling opportunities also arise when there are higher-end versions of the same product line, enabling customers to move up to more premium offerings. This approach maximizes sales opportunities and boosts average transaction value.
8. Adaptability to Market Changes
A diverse product mix makes it easier for companies to respond to shifts in consumer demand, industry trends, and economic changes. For example, if a particular product line becomes less profitable due to changing market preferences, a company with a broader product mix can pivot resources toward other, more promising products. This adaptability is crucial in maintaining resilience and relevance over the long term.
9. Reduced Business Risk
By diversifying its product offerings, a business can spread its risk across multiple lines and variations. If one product line underperforms, other successful lines can help sustain the company’s revenue and protect it from a significant loss. This approach also helps safeguard a company from market fluctuations and seasonal demand changes, providing a buffer against economic uncertainties.
10. Improved Inventory Management and Forecasting
With a clearly defined product mix strategy, a company can forecast demand for each product line more accurately, making inventory management more efficient. A structured approach to the product mix helps balance supply and demand, reducing stockouts or overstocking, which can be costly. Improved inventory planning leads to better cash flow management, minimizes waste, and ensures that the most popular products are always available for customers.
11. Innovation and Growth Opportunities
An organized product mix strategy allows a business to identify opportunities for product innovation. By regularly analyzing the performance of each product line and understanding customer feedback, companies can spot gaps in the market and invest in developing new products that meet emerging needs. This focus on innovation fosters growth and keeps the brand relevant in the minds of consumers.
12. Alignment with Strategic Business Goals
A well-defined product mix aligns with a company’s overall strategic goals, supporting its long-term vision and mission. By strategically choosing product lines and variations that reflect the brand’s identity, values, and growth objectives, companies can maintain a cohesive direction. This alignment ensures that each product contributes to achieving business milestones, whether that’s expanding into new markets, increasing profitability, or enhancing customer satisfaction.
Also Read: What is Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM)?
Difference Between Product Line and Product Mix
| Aspect | Product Line | Product Mix |
| Definition | A group of related products under a single brand, serving a specific purpose or market. | The complete assortment of product lines a company offers. |
| Scope | Narrow; focuses on products within a particular category. | Broad; includes all product lines and product categories offered by the company. |
| Example | Apple’s iPhone models (iPhone 13, iPhone 14, etc.). | Apple’s total offerings, including iPhones, iPads, Macs, accessories, and services. |
| Purpose | To fulfill specific needs within a targeted market segment. | To cater to multiple customer needs and market segments. |
| Flexibility | Easier to modify by adding new variations within the category. | More complex to adjust due to the need for balance and consistency across different lines. |
How to Perform a Product Mix Analysis
Conducting a product mix analysis helps businesses understand their product portfolio’s effectiveness, profitability, and market positioning. Here’s a step-by-step approach to performing an insightful product mix analysis:
1. Identify and Categorize Products
- List all products, grouping them by product lines and categories. Note key product attributes, such as price points, target audience, and unique features.
- Categorizing products enables you to see how each product line fits within the overall product mix and whether any gaps exist in meeting customer needs.
2. Measure Sales and Profitability Metrics
- Analyze revenue, profit margins, and sales volume for each product line and individual product. This will help determine which products drive profitability and which may need adjustment or removal.
- Use metrics like gross margin, net margin, and profit per unit sold to evaluate financial performance and see which products add the most value.
3. Assess Product Performance Using KPIs
- Select key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate each product’s success. KPIs could include units sold, average customer ratings, repeat purchase rates, and return rates.
- Compare each product’s performance against these metrics to determine strengths, weaknesses, and trends.
4. Evaluate Customer Demand and Feedback
- Analyze customer feedback, reviews, and survey results to understand customer satisfaction levels. Product demand and satisfaction levels are critical to determining if your product mix aligns with market needs.
- Look for patterns in customer preferences, which can help you identify which products to prioritize or potentially enhance.
5. Analyze Product Line Cannibalization
- Assess whether new or existing products in your mix are competing against each other for sales. When similar products target the same audience, they can reduce each other’s effectiveness.
- Adjust your product lines to ensure they complement each other rather than compete, maximizing each product’s profitability.
6. Compare with Competitors’ Product Mix
- Analyzing competitors’ offerings can give insight into market standards and gaps. See if there are products they offer that your business doesn’t and vice versa.
- This competitive assessment can reveal potential areas for differentiation or opportunities to fill unmet customer needs.
7. Use the 80/20 Rule (Pareto Analysis)
- Identify the top 20% of products that generate 80% of your revenue. Focusing on these high-performing items helps prioritize where to allocate resources for growth.
- Conversely, consider reducing or improving the 20% of products that underperform, helping streamline inventory and increase profitability.
8. Review and Adjust Regularly
- Conduct product mix analysis regularly to adapt to evolving customer needs, market trends, and competitor strategies. This keeps your product mix optimized for maximum impact and ensures relevance over time.
How to Analyze a Competitor’s Product Mix
Understanding a competitor’s product mix can provide valuable insights into their strategy, strengths, and potential vulnerabilities. Here’s a step-by-step guide to analyzing a competitor’s product mix:
1. Identify Competitors and Gather Product Information
- List primary competitors in your industry, focusing on those targeting similar audiences. Visit their websites, online stores, and social media profiles to collect data on their product lines, categories, and individual products.
- Explore how they present their product mix: product descriptions, unique features, target demographics, and pricing structure. This can reveal their approach to meeting market demands.
2. Examine the Breadth and Depth of Their Product Mix
- Evaluate the breadth (number of product lines) and depth (variety within each product line) of each competitor’s product mix. A broad mix suggests they’re targeting a diverse market, while a narrower focus could indicate specialization.
- Identify whether they have a balanced product mix or emphasize certain categories more heavily. This can reveal their priorities and areas of expertise.
3. Analyze Their Product Positioning and Target Market
- Review each product’s features, quality, and price point to determine positioning (e.g., premium, budget-friendly, niche-focused). Positioning analysis can provide insight into the customer segments they’re prioritizing.
- Look at how their products are marketed on different channels, such as through targeted messaging, influencer partnerships, or promotional campaigns. This helps gauge who they aim to reach and how they differentiate.
4. Identify Product Mix Gaps and Opportunities
- Assess if there are any product lines or variations competitors don’t offer that could be profitable for your business. For instance, if a competitor lacks eco-friendly options, consider adding sustainable products to your mix to capture this audience.
- Also, look for over-saturation in a competitor’s product lines. For example, if they have several similar products within one line, they may be over-relying on that segment, creating an opportunity for your business to diversify.
5. Evaluate Their Product Mix Strategy and Adaptability
- Track any changes in your competitor’s product mix, such as recent launches, discontinued products, or shifts in promotional focus. Frequent product launches may suggest an aggressive growth strategy, while cuts might indicate a focus on streamlining.
- Analyze their adaptability to market trends, such as new technology, consumer preferences, or sustainability trends. By observing how quickly they pivot or innovate, you can identify their agility in responding to market demands.
6. Leverage Tools for Competitive Analysis
- Use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and SpyFu to assess competitors’ online presence and SEO strategies related to their product mix. These tools reveal which product pages drive the most traffic and the keywords they target, offering insight into their strengths.
- Social media listening tools like Brandwatch or Sprout Social can also help track customer sentiment toward competitor products, giving you insights into perceived weaknesses and customer preferences.
7. Benchmark and Differentiate Your Product Mix
- Use the insights gathered to benchmark your own product mix against competitors’ strengths and weaknesses. Identify areas where you can differentiate—whether in product features, pricing, or customer experience.
- Look for ways to position your product mix more attractively by filling any gaps in the market or enhancing aspects that align with customer demand better than competitors.
Analyzing a competitor’s product mix can uncover opportunities for innovation, reveal strengths to emulate, and help identify market gaps your business can exploit. A thorough competitor analysis provides a roadmap for strategically shaping your product mix for competitive advantage.
Conclusion
A well-designed product mix strategy is a powerful tool for any business aiming for long-term success. By strategically expanding, contracting, deepening, or diversifying product lines, companies can cater to a broad audience, enhance brand loyalty, and increase their market presence. Regular assessment and refinement of the product mix ensure that companies stay competitive, meet customer needs, and align with evolving market trends.
By using the strategies outlined above, businesses can position themselves to not only survive in competitive markets but thrive and grow, creating a portfolio of products that resonates deeply with their target audience.
FAQs: What Is Product Mix
1. What is a product mix in marketing?
A product mix, also known as a product assortment, refers to the complete range of products and product lines a company offers to its customers. It includes all variations in product lines, categories, and individual items, covering aspects such as price, functionality, and target market.
2. Why is having a well-planned product mix strategy important?
A well-planned product mix strategy allows a business to maximize profitability, cater to diverse customer needs, strengthen brand loyalty, and remain competitive. It helps companies balance their offerings across different market segments, minimizing risk by not relying on a single product line.
3. What is the difference between a product line and a product mix?
A product line is a group of related products under one brand that fulfills a specific customer need, while the product mix encompasses all product lines and individual products offered by a company. The product mix provides a broader view of a company’s complete assortment of offerings.
4. How do companies decide which product mix strategy to use?
Companies typically base their product mix strategy on market research, customer feedback, competitive analysis, and internal capabilities. Strategies might include expanding existing lines, diversifying products, or focusing on high-performing items, depending on goals like increasing market share or entering new markets.
5. How can you perform a product mix analysis?
A product mix analysis involves assessing each product’s profitability, customer demand, and alignment with company goals. It includes tracking sales data, analyzing customer feedback, evaluating competitors’ offerings, and identifying any gaps or opportunities to optimize the mix for better performance.

