Pricing can make or break a business. Set your price too high, and customers may walk away. Set it too low, and you might struggle to make a profit. So, how do businesses strike the right balance? The answer lies in the price mix. It shapes how businesses set and adjust their prices to attract customers and maximize profits.
Table of Contents
So, in this guide, we’ll explore the importance of price mix, the factors influencing pricing decisions, common pricing strategies, and mistakes to avoid. By the end, you’ll understand how pricing is more than just a number—it’s a powerful tool for business growth.
What Is Price Mix?🤔
Price Mix is the way businesses decide the price of their products or services. A company cannot just pick any price; they must think about many things before setting it. These include costs, customer demand, competition, and business goals.
Price mix is an important part of the marketing mix, along with product, place, and promotion. It helps a business attract customers, compete in the market, and earn profits. If the price is too high, customers may not buy the product. If it is too low, the company may not make enough profit. That is why businesses use different pricing strategies to find the right balance.
A good price mix keeps customers happy while ensuring the company stays profitable. Price mix also helps in building a strong brand. Understanding the price mix is essential for any business that wants to succeed in a competitive market.
Also read: What is Product Mix?
Why Price Mix is Important❓

1. It Controls Customer Demand
Price affects buying decisions. If the price is high, fewer people may buy. If it is low, more people may purchase, but profits may decrease. Businesses adjust prices to find the right balance. Discounts, offers, and seasonal pricing also help in managing demand. A well-planned price mix keeps both sales and profits steady.
2. It Decides Business Profits
The right price helps a business make a good profit. A high price brings more profit per item but may reduce the number of buyers. A low price increases sales but lowers earnings per unit. Businesses must choose prices that cover costs and make enough profit. Proper pricing ensures long-term business success and growth.
3. It Boosts Product Sales
Sales promotions use pricing strategies to attract customers. Discounts, bundled offers, and seasonal price cuts encourage people to buy more. Limited-time deals create urgency and boost sales. A smart price mix makes promotions more effective. It helps businesses get new customers while keeping old ones happy. This leads to higher overall sales.
4. It Shapes First Impressions
People judge a product by its price. If it is too cheap, they may think it is low quality. If it is expensive, they expect it to be premium. The price should match the product’s quality and target customers. A good pricing strategy builds trust. It helps customers feel they are getting value for money.
5. It’s Easy to Adjust
Unlike product quality or branding, businesses can change prices quickly. They can lower prices to attract buyers or increase them to boost profits. Companies adjust prices based on competition, demand, and market conditions. This flexibility helps them stay competitive. A smart price mix allows businesses to respond fast to market changes.

Check out: Our 8-week Product Marketing Course
6. It Helps in Price Comparison
Customers always compare prices before buying. They check if a product is worth the cost. If a business sets the right price, it stands out from competitors. Pricing also decides the target audience. Low prices attract budget shoppers, while high prices appeal to premium buyers. A well-planned price mix makes a business more competitive.
7. It Builds Brand Image
Price affects a brand’s image. Expensive products are seen as high-quality and exclusive. Cheap products may seem affordable but not premium. Businesses use pricing to build their brand reputation. Luxury brands set high prices to maintain exclusivity. Budget brands keep prices low to attract more customers. A good price mix strengthens brand positioning.
8. It Keeps Businesses Competitive
Pricing is a powerful tool in competition. If a business offers better prices, it attracts more customers. Some businesses use low prices to gain market share. Others set premium prices to show higher value. Competitor-based pricing ensures a business stays relevant. A well-balanced price mix keeps a business strong in the market.
9. It Covers Business Costs
A business must cover costs to survive. This includes production, marketing, salaries, and more. If the price is too low, the business may struggle to recover these costs. If it is too high, customers may not buy. A good price mix ensures costs are covered while keeping prices attractive. This balance keeps the business profitable.
10. It Builds Customer Trust
Customers trust fair pricing. If they feel a product is worth the price, they return to buy again. Sudden high price increases can drive customers away. Frequent price drops may make them wait for discounts. A stable and fair price mix builds customer loyalty. It helps businesses keep customers for the long term.
Also read: What is Promotion Mix?
Factors Affecting The Pricing Decision👀
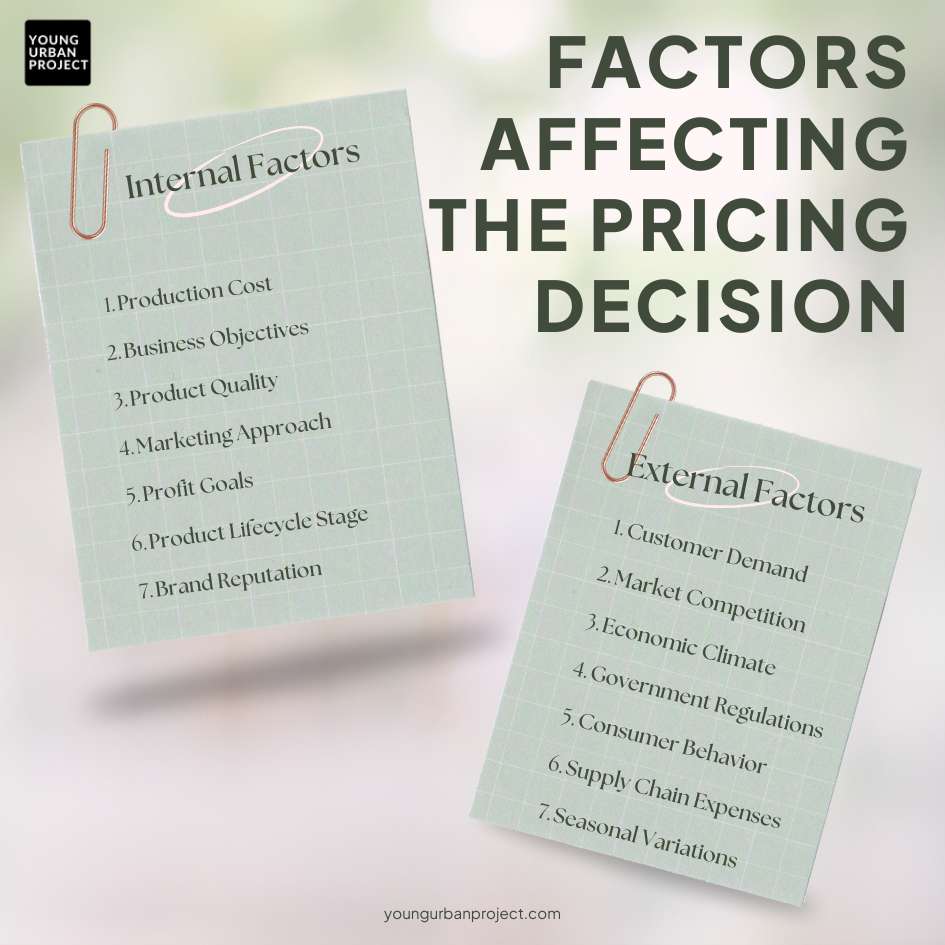
Setting the right price for a product or service is not easy. Businesses must think about many things before deciding on a price. These things are called factors affecting pricing decisions. They are divided into two types: internal factors (things inside the business) and external factors (things outside the business).
Internal Factors👇
Internal factors come from within the company. These factors are under the business’s control.
1. Cost of Production – The price must cover the cost of making the product. If costs are high, the price will also be high. If costs are low, the company can set a lower price.
2. Business Goals – Some companies want high profits, while others focus on attracting more customers with lower prices. The pricing decision depends on these goals.
3. Product Quality – High-quality products usually have higher prices, while low-quality products are cheaper.
4. Marketing Strategy – The price should match the company’s overall marketing plan. For example, if a company wants to show its product as premium, it will set a high price.
5. Profit Margin – Businesses decide how much profit they want from each sale. A higher profit margin means a higher price.
6. Product Lifecycle – A new product may have a high price at first, and then the price may go down over time.
7. Brand Image – Well-known brands can charge higher prices because people trust them. New brands may have to set lower prices to attract buyers.
External Factors👇
External factors come from outside the company. These factors are not under the business’s control.
1. Market Demand – If many people want a product, the company can set a higher price. If demand is low, the price must be lower.
2. Competition – If many companies sell the same product, they must keep their prices competitive. If a company has no competitors, it can charge a higher price.
3. Economic Conditions – In times of economic growth, people spend more, and businesses can charge higher prices. In a recession, companies may have to lower their prices.
4. Government Policies – Taxes, import duties, and price regulations set by the government can affect pricing decisions.
5. Customer Preferences – Different customers have different spending habits. Some are willing to pay more for quality, while others look for the cheapest option.
6. Supply Chain Costs – If the cost of raw materials, transportation, or labor goes up, businesses may need to raise their prices.
7. Seasonal Changes – Prices of some products change with the seasons. For example, winter clothes may be more expensive during cold months and cheaper in the summer.
The Pricing Strategies
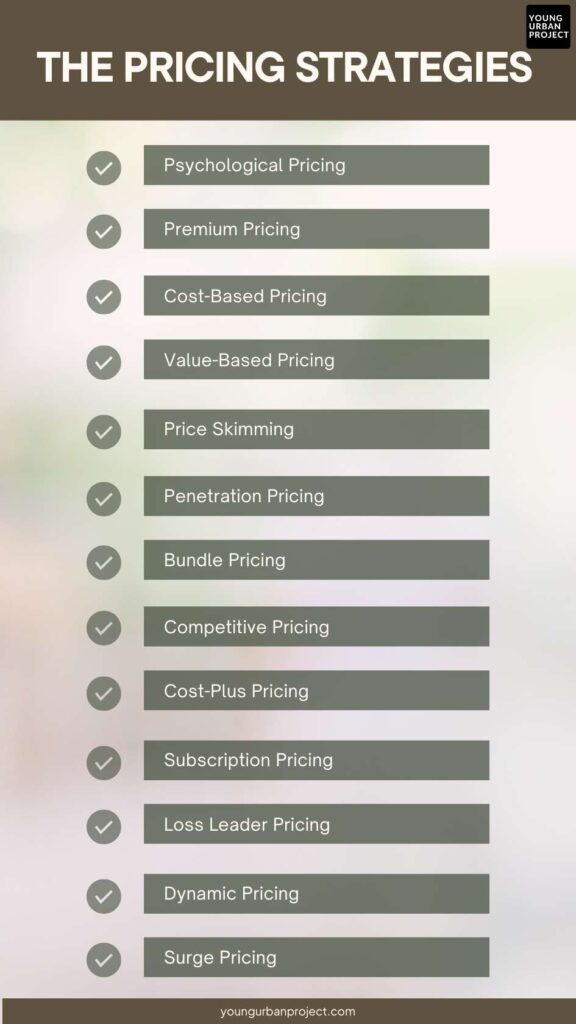
1. Psychological Pricing
This strategy uses pricing tricks to make products seem cheaper than they actually are. Businesses adjust prices to influence customer perception.
🔹 Example: A product priced at $9.99 instead of $10.00 seems like a better deal, even though the difference is only one cent.
📌 Why use it?
- Encourages impulse buying.
- Makes prices seem more attractive.
Problem: Customers may feel misled if they recognize the tactic.
2. Premium Pricing
A business sets high prices to show that the product is luxurious or high-quality. This strategy works for brands that focus on exclusivity.
🔹 Example: Rolex watches are very expensive because they are seen as luxury products.
📌 Why use it?
- Builds a strong brand image.
- Attracts high-income customers.
Problem: Customers must believe the product is worth the high price.
3. Cost-Based Pricing
The company calculates the total cost of production and then adds a profit margin. This method is widely used and easy to follow.
🔹 Example: If it costs $10 to make a product and the company wants a $5 profit, the selling price will be $15.
📌 Why use it?
- Ensures costs are covered.
- Simple to apply.
Problem: Does not consider market demand or competitor prices.
4. Value-Based Pricing
In this strategy, businesses set the price based on how much customers think the product is worth. The focus is on perceived value.
🔹 Example: Apple charges high prices for iPhones because people believe they are high-quality and innovative.
📌 Why use it?
- Customers feel they are paying for quality.
- Works well for unique or premium products.
Problem: Requires strong branding and market research.
5. Price Skimming
Price skimming is when a company starts with a high price for a new product and gradually reduces it over time. This helps recover investment costs quickly.
🔹 Example: New iPhones are very expensive at launch, but the price drops after a few months.
📌 Why use it?
- Maximizes profits in the early stages.
- Attracts early adopters willing to pay more.
Problem: The high initial price may discourage budget-conscious buyers.
6. Penetration Pricing
Penetration pricing is when a business starts with a very low price to attract customers and gain market share. Once the brand is established, the price is increased.
🔹 Example: A new streaming service offers a free or very cheap subscription at first. Later, it raises the price.
📌 Why use it?
- Quickly attracts customers.
- Helps businesses compete with larger brands.
Problem: The company may face losses in the beginning.
7. Bundle Pricing
Businesses sell multiple products together at a lower price than if bought separately. This strategy increases the total amount customers spend.
🔹 Example: Fast-food chains sell a burger, fries, and soda as a combo meal at a lower price than buying each item individually.
📌 Why use it?
- Encourages customers to buy more.
- Increases perceived value.
Problem: Customers may not want all items in the bundle.
8. Competitive Pricing
A company sets its price based on competitors’ prices. This ensures that their prices are neither too high nor too low compared to the market.
🔹 Example: If McDonald’s sells a burger for $5, Burger King may sell a similar burger for $4.90 to attract customers.
📌 Why use it?
- Helps stay competitive in the market.
- Reduces the risk of pricing too high or too low.
Problem: Does not consider product uniqueness or brand value.
9. Cost-Plus Pricing
A simple method where a business adds a fixed percentage to the cost of production to determine the selling price.
🔹 Example: If it costs $100 to make a product and the company adds a 20% markup, the selling price will be $120.
📌 Why use it?
- Guarantees a steady profit margin.
- Easy to calculate and apply.
Problem: Does not consider customer demand or competitor pricing.
10. Subscription Pricing
A business charges a recurring fee for customers to access a product or service over time.
🔹 Example: Netflix charges a monthly fee instead of a one-time purchase.
📌 Why use it?
- Creates a steady income stream.
- Builds long-term customer relationships.
Problem: Customers may cancel subscriptions if they don’t see enough value.
11. Loss Leader Pricing
Businesses sell one product at a very low price, sometimes at a loss, to attract customers who will then buy other products.
🔹 Example: Supermarkets sell bread or milk at a very low price so that customers visit the store and buy other expensive products.
📌 Why use it?
- Attracts customers to the business.
- Encourages additional purchases.
Problem: If customers only buy the discounted product, the business may lose money.
12. Dynamic Pricing
Businesses change prices based on demand, season, or customer behavior. This strategy is common in travel and e-commerce.
🔹 Example: Airline ticket prices increase during holidays and decrease during off-seasons.
📌 Why use it?
- Maximizes profits during peak demand.
- Helps businesses respond to market changes.
Problem: Frequent price changes may frustrate customers.
13. Surge Pricing
This strategy increases prices when demand is high. Businesses use it to balance supply and demand while maximizing revenue. It is common in ride-sharing, airlines, and event ticketing.
🔹 Example: Uber raises fares during rush hours, bad weather, or major events. This encourages more drivers to be available while ensuring customers can still get a ride.
📌 Why use it?
- Ensures availability during peak times.
- Encourages service providers to work when demand is high.
Problem:
- Customers may feel frustrated when prices surge.
- Can create negative brand perception if used excessively.
Price Mix Examples
1. Xiaomi – Penetration Pricing Strategy (Penetration Pricing)

A great example of price mix is Xiaomi, a Chinese electronics company, entered the smartphone market by offering high-quality phones at very low prices compared to Samsung and Apple. They kept their profit margins low to attract customers and gain market share. Once they built a strong customer base, they gradually increased prices for newer models.
📌 Why does this work?
- Attracts budget-conscious customers.
- Helps Xiaomi compete with big brands at lower prices.
Problem: The company must sell a high volume of products to make profits.
2. Rolex – Exclusivity Pricing (Luxury Pricing)

Rolex uses exclusivity pricing, keeping prices very high to maintain brand equity. They also limit production to create a sense of scarcity, increasing demand among wealthy customers.
📌 Why does this work?
- Attracts elite customers who see Rolex as a status symbol.
- Limited availability creates a sense of urgency to buy.
Problem: The brand loses middle-class customers who can’t afford it.
3. Uber – Dynamic Pricing Strategy (Surge Pricing)

Uber uses dynamic pricing, meaning fares increase when demand is high (such as during rush hours, bad weather, or major events). This encourages more drivers to be available while ensuring customers can always get a ride.
📌 Why does this work?
- Maximizes revenue when demand is high.
- Helps balance supply and demand in real-time.
Problem: Customers complain when surge prices are too high.
4. Netflix – Subscription Pricing Strategy (Subscription Pricing)

Another very famous example of price mix is Netflix, which charges a monthly fee instead of charging per movie. This model ensures recurring revenue and keeps customers engaged with regular content updates.
📌 Why does this work?
- Ensures continuous revenue.
- Builds long-term customer loyalty.
Problem: Customers may cancel if prices rise or content declines.
5. Louis Vuitton – Value-Based Pricing Strategy (Value-Based Pricing)

Despite low production costs, Louis Vuitton handbags are priced high due to their luxury brand perception. Customers are willing to pay premium prices for exclusivity, craftsmanship, and status.
📌 Why does this work?
- Customers pay for exclusivity and status.
- Works well for high-end and luxury products.
Problem: Requires strong branding and brand marketing efforts.
Pricing Mistakes that A Seller Should Avoid
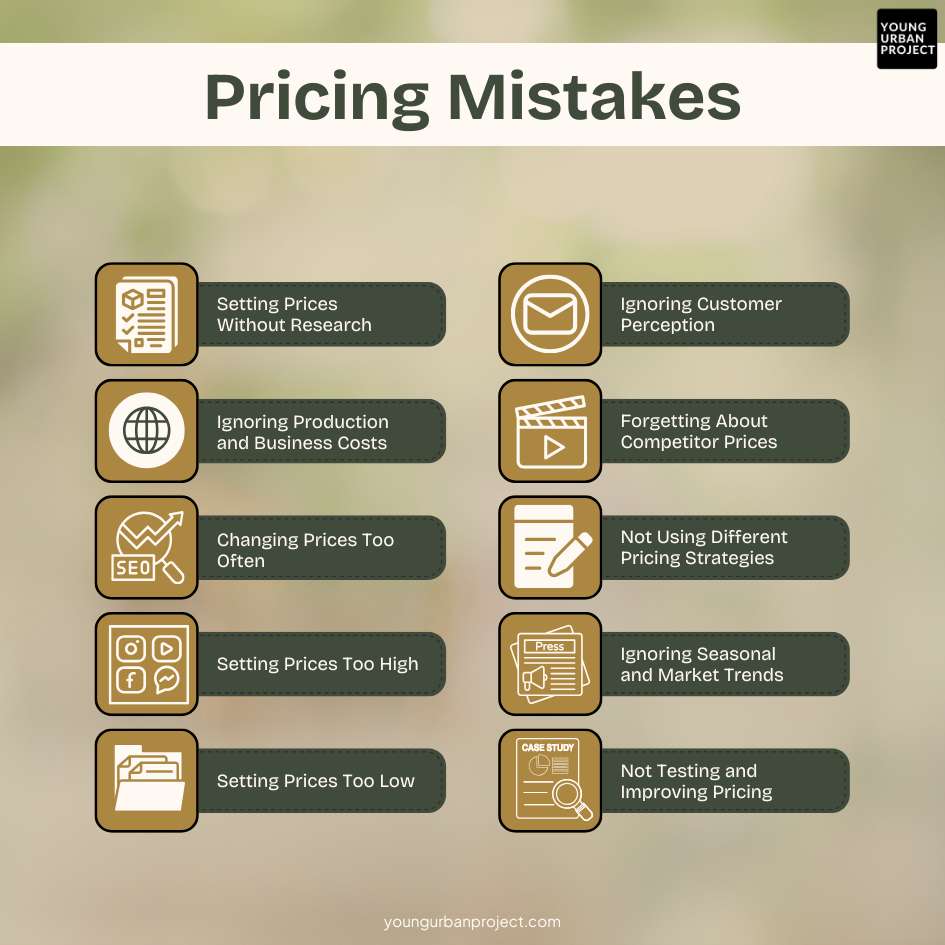
1. Setting Prices Without Research
Many sellers guess prices without checking the market. This can lead to setting prices too high or too low. Research helps sellers understand what customers are willing to pay. It also helps compare competitor prices. A good price should cover costs, attract customers, and bring profit. Proper business research prevents costly pricing mistakes.
2. Ignoring Production and Business Costs
Some sellers set low prices to attract buyers but forget to calculate costs. If a product costs more to make than its selling price, the business loses money. Pricing should always include production, marketing, delivery, and other expenses. A smart seller sets prices that bring profit while still being affordable for customers.
3. Changing Prices Too Often
If prices go up and down frequently, customers get confused. They may stop trusting the seller. Some may wait for discounts instead of buying at regular prices. While adjusting prices is important, it should be done carefully. Price changes should be based on demand, market conditions, and customer expectations, not random decisions.
4. Setting Prices Too High
If a product is too expensive, customers may not buy it. They might look for cheaper alternatives. Even if a product is high-quality, it needs to be reasonably priced. A seller should compare prices with competitors and understand what customers are willing to pay. High prices should match great value, features, or brand reputation.
Also read: What is ORM in Digital Marketing?
5. Setting Prices Too Low
Some sellers lower prices to attract more buyers, but this can reduce profits. Very low prices can also make customers think the product is poor quality. If a seller always offers discounts, customers may not buy at full price. It’s important to find a balance between affordability and making a profit.
6. Ignoring Customer Perception
Customers judge a product by its price. If a price is too cheap, they may think it’s low quality. If it’s too expensive, they expect premium value. Sellers should set prices that match customer expectations. A fair price makes the product attractive and helps build trust. Ignoring customer perception can harm sales and brand reputation.
7. Forgetting About Competitor Prices
Customers compare prices before buying. If a competitor sells the same product at a better price, customers may choose them instead. Sellers should always check competitor pricing and offer a better deal when possible. This doesn’t always mean lowering prices—it could mean adding value, better service, or unique features to justify the price.
8. Not Using Different Pricing Strategies
Sellers who use only one pricing method may lose opportunities. There are many pricing strategies, like bundle pricing, discounts, premium pricing, or psychological pricing. The right strategy depends on the product, market, and target customers. Mixing different strategies can help increase sales, attract more buyers, and keep the business competitive.
9. Ignoring Seasonal and Market Trends
Prices should change based on seasons and market trends. For example, winter clothes sell at higher prices in cold months but need discounts in summer. Sellers who don’t adjust prices for demand may lose sales. Paying attention to market trends helps in setting the right price at the right time.
10. Not Testing and Improving Pricing
Once a price is set, it should not stay the same forever. Sellers should test different prices to see what works best. Customer feedback, sales data, and market changes help improve pricing. If a price is too high or too low, adjustments should be made. Regularly improving pricing ensures long-term business success.
♻️Conclusion
Price mix is a very important part of the marketing mix. It helps businesses decide the best price for goods or services. A good price mix considers factors like production cost, customer demand, competition, and pricing strategies. If the price is too high, customers may not buy it. If it is too low, the business may not make a profit.
Businesses use different pricing strategies like cost-based pricing, value-based pricing, price skimming, and psychological pricing to attract customers. The right pricing decision helps in sales promotion, customer satisfaction, and profitability. It also helps businesses compete in the market.
A well-planned price mix increases sales volume and brand value. It also helps in price monitoring and product differentiation. Companies should always check their pricing objectives and market trends to stay competitive. Understanding the price mix is important for long-term success in any business.
💡FAQs: Price Mix
1. How does pricing affect consumer decisions?
Pricing plays a big role in how consumers choose products. A high price makes a product seem premium, while a low price attracts budget-conscious buyers. Psychological pricing, discounts, and offers influence buying behavior. If a product is costly, buyers might look for a budget-friendly option. A good price mix helps businesses attract the right customers and increase sales.
2. What should businesses consider when setting prices?
Businesses should consider many factors before deciding the price of a product. They must check production costs, competitor prices, customer demand, and market trends. Profit margins and pricing strategies also matter. If the price is too high, it may reduce sales. If it’s too low, the business may not earn enough profit. A balanced price helps attract customers and increase revenue.
3. What are the common pricing strategies?
There are many pricing strategies businesses use. Cost-based pricing adds a profit margin to the cost of production. Value-based pricing sets the price according to customer perception. Price skimming starts with a high price and lowers it over time. Penetration pricing offers low prices to attract customers. Psychological pricing uses tricks like $9.99 instead of $10 to influence buyers.
4. How can businesses manage their price mix effectively?
Businesses must adjust their price mix based on market conditions. They should monitor competitors, track customer behavior, and review costs regularly. Discounts, bundle pricing, and seasonal offers help attract customers. A flexible pricing strategy ensures steady sales. Businesses should also focus on value-based pricing to maintain customer trust and brand reputation.
5. How can pricing give businesses a competitive advantage?
A smart pricing strategy helps businesses stay ahead of competitors. Offering better prices, discounts, or bundles can attract more customers. Premium pricing creates a luxury brand image. Penetration pricing helps new businesses enter the market. Competitive pricing ensures a product stays relevant. A well-planned price mix keeps customers satisfied while maximizing profits.

