Launching a product, entering a new market, or improving operational efficiency—business research is the foundation for success in these ventures. It transforms uncertainty into clarity and intuition into informed decisions. But what exactly does it entail, and how can you use it effectively?
Table of Contents
This guide will explore the ins and outs of business research: its types, methods, tools, challenges, and applications. By the end, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to harness its power for your business.
What is Business Research?
Business research is the systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to answer critical business questions. It focuses on understanding markets, customer behavior, competitors, and operational efficiencies.
At its core, business research enables companies to:
- Make data-driven decisions.
- Identify opportunities and mitigate risks.
- Stay competitive in evolving markets.
For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses that relied on market research to adapt their models (e.g., embracing e-commerce) thrived, while those that ignored insights struggled to survive.
Types of Business Research
Understanding the types of business research is essential for selecting the right approach to gain actionable insights. Broadly, business research can be categorized into qualitative and quantitative methods. Each category has distinct methodologies that serve different purposes, depending on the questions being asked and the nature of the data required.
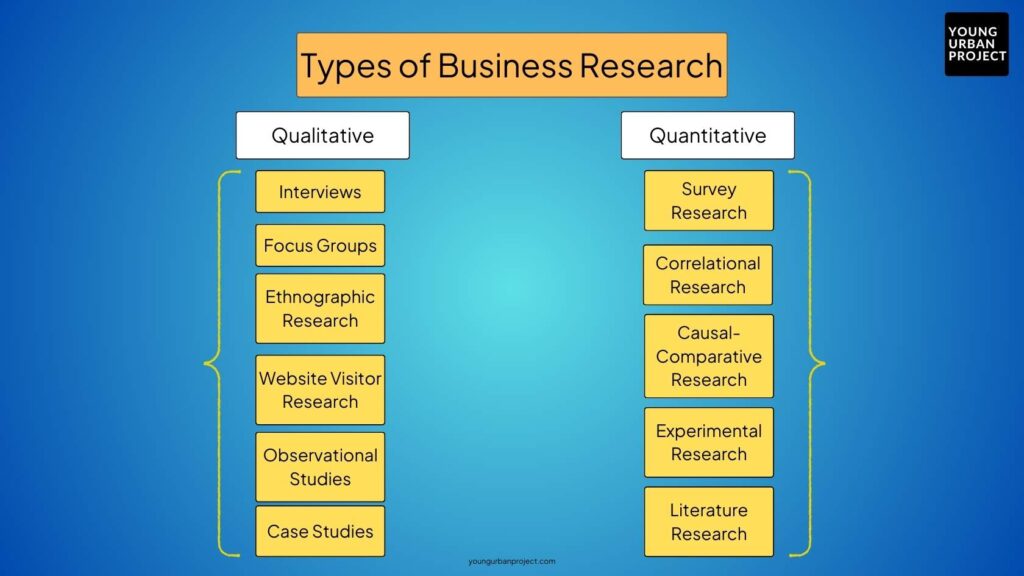
- Qualitative Research
Qualitative research focuses on understanding the deeper motivations, emotions, and behaviors of individuals. It’s often used in exploratory phases to uncover insights that may not be immediately apparent through numerical data. The richness of qualitative research lies in its ability to capture the nuances of human behavior and perception.
Key Methods in Qualitative Research
Interviews
Interviews are one-on-one conversations where the researcher delves into the subject’s thoughts, opinions, and experiences. These are often semi-structured, combining open-ended questions with the flexibility to explore emerging themes. For example, a retail company might interview customers to understand how they perceive the brand and its offerings.
Focus Groups
A focus group brings together a small group of individuals to discuss a particular topic. Guided by a moderator, participants share their views, offering varied perspectives. This method is particularly useful for testing new product ideas or marketing strategies. For instance, a tech company planning to hire Android developers might gather users to evaluate a new app interface, ensuring the design aligns with user expectations before moving into full-scale development.
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research involves immersing the researcher in the subject’s environment to observe behaviors and interactions in their natural context. This method is invaluable for industries like retail, where understanding the customer journey in-store can lead to strategic insights.
Website Visitor Research
In digital contexts, understanding visitor behavior on websites provides insights into user engagement and content preferences. Tools like heatmaps and session recordings are often used to gather qualitative data on how users interact with a website.
Observational Studies
Observation allows researchers to study subjects without direct interaction, ensuring that behaviors are as natural as possible. For example, observing consumer behavior in a shopping mall can help businesses determine ideal store locations.
Case Studies
Case studies are in-depth explorations of a specific instance, such as a business’s market entry strategy. They provide comprehensive insights that can be generalized or adapted for similar scenarios.
- Quantitative Research
Quantitative research emphasizes numerical data and statistical analysis. This method is particularly effective for validating hypotheses, measuring trends, and forecasting outcomes. Unlike qualitative methods, quantitative research relies on structured tools like surveys and experiments to gather measurable data.
Key Methods in Quantitative Research
Survey Research
Surveys are among the most commonly used quantitative tools. By asking structured questions to a sample population, surveys collect data on preferences, behaviors, or opinions. For instance, a hotel chain might use customer satisfaction surveys to assess the quality of its services.
Correlational Research
Correlational studies examine relationships between two or more variables to determine whether they are related. For example, a retailer might explore the relationship between promotional emails and sales to optimize marketing efforts.
Causal-Comparative Research
This type of research investigates cause-and-effect relationships by comparing different groups. For example, a company might study how implementing remote work policies affects employee productivity compared to traditional office setups.
Experimental Research
Experimental research is highly controlled and seeks to determine causation by manipulating independent variables while observing their effect on dependent variables. For instance, an online retailer might run A/B tests to compare the effectiveness of two different website designs.
Literature Research
Literature research involves reviewing existing studies, reports, and academic papers to gather insights. While not as interactive as other methods, it provides a foundation for understanding industry trends and theoretical frameworks.

The Intersection of Qualitative and Quantitative Research
While qualitative and quantitative research are distinct, they are not mutually exclusive. Many businesses adopt a mixed-methods approach, combining the depth of qualitative insights with the precision of quantitative data. For example, a company launching a new product might first conduct focus groups to explore customer needs (qualitative) and then follow up with surveys to quantify demand (quantitative).
Choosing the Right Type of Research
The choice between qualitative and quantitative research depends on the business question at hand. Qualitative research is best for exploratory phases, while quantitative research is ideal for validation and measurement. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each type ensures a well-rounded approach to business decision-making.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Business Research
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Drives data-backed decisions | Can be time-consuming |
| Enhances customer-centric strategies | High costs for comprehensive studies |
| Reduces risks in market entry | Potential biases in data collection |
| Identifies emerging trends | Requires skilled professionals |
| Builds competitive advantage | Insights may become obsolete quickly |
Challenges in Business Research
Business research is an indispensable tool for decision-making, but it is not without its hurdles. From logistical difficulties to ethical dilemmas, researchers face numerous challenges that can affect the accuracy, reliability, and timeliness of their findings. Below is an in-depth exploration of these challenges, categorized for clarity.
1. Data-Related Challenges
- Data Availability
Accessing reliable and relevant data can be difficult, particularly in industries with limited digital footprints or where data privacy laws restrict availability. Small businesses and startups often struggle with finding comprehensive datasets. - Data Accuracy and Quality
Poor data quality can distort findings. This includes errors in data collection, outdated information, or biases in the source. Cleaning and verifying data before analysis can be time-consuming and resource-intensive. - Data Overload
Businesses now have access to enormous amounts of data, which can be overwhelming. Extracting actionable insights from this sea of information requires advanced analytical skills and tools, which not all organizations possess.
2. Technological Challenges
- Tool Selection
The sheer number of tools available for business research can be overwhelming. Choosing the right tools for data collection, analysis, and visualization that align with research objectives is a critical challenge. - Keeping Up with Innovations
The landscape of research tools evolves rapidly. Staying updated with emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics is crucial but difficult for many businesses. - Integration Issues
Many organizations use multiple tools for research, leading to compatibility issues. Integrating these tools seamlessly and ensuring a unified workflow is often challenging.
3. Methodological Challenges
- Defining the Scope
Narrowing down the research scope to answer specific business questions effectively can be complex. A broad focus may dilute findings, while a narrow focus may overlook key insights. - Choosing the Right Methodology
Selecting the most suitable research methodology—quantitative, qualitative, or mixed—requires expertise. A mismatch can lead to irrelevant or incomplete results. - Ensuring Validity and Reliability
Researchers must ensure their methods consistently produce accurate and reproducible results. Achieving high validity and reliability is particularly difficult in qualitative research.
4. Ethical Challenges
- Privacy and Confidentiality
Protecting participants’ personal and confidential information is a growing challenge, particularly with stricter data protection regulations such as GDPR. - Informed Consent
Ensuring participants fully understand and agree to the terms of the research can be challenging, especially in cross-cultural or online contexts. - Bias and Misrepresentation
Avoiding researcher and participant bias is a significant ethical hurdle. Unintentional misrepresentation of findings can also harm stakeholders.
5. Resource Challenges
- Budget Constraints
Conducting comprehensive business research often requires substantial financial resources. Small businesses may struggle to allocate sufficient funds for tools, personnel, and technology. - Time Constraints
Tight deadlines can compromise the depth and quality of research. Many businesses need quick insights, which may lead to oversimplified analyses. - Skilled Personnel
Finding qualified researchers with expertise in data collection, analysis, and interpretation can be difficult, particularly in niche industries or smaller markets.
6. Cultural and Environmental Challenges
- Cross-Cultural Research
When conducting research across different regions or countries, cultural differences can complicate data collection and interpretation. Factors like language barriers, cultural norms, and legal restrictions must be considered. - Changing Market Dynamics
Businesses operate in rapidly evolving environments. Research findings can quickly become obsolete due to sudden shifts in consumer preferences, technology, or competition.
7. Practical Challenges in Execution
- Reaching Target Audiences
Identifying and engaging the right respondents for surveys or interviews can be difficult. Many potential participants may be unwilling to share insights or may provide inaccurate information. - Managing Research Bias
Both researchers and respondents may bring unconscious biases that skew results. Ensuring objectivity in qualitative and quantitative research remains a persistent challenge. - Stakeholder Alignment
Aligning the expectations and objectives of all stakeholders involved in the research process can be complex, especially in large organizations.
8. External Challenges
- Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Adhering to local and international laws during data collection, particularly in heavily regulated industries like healthcare or finance, adds complexity. - Competition
Competitors may conduct parallel research, influencing market dynamics and potentially rendering findings less impactful.
Economic and Political Factors
External economic or political instability can disrupt research processes and skew results. For instance, sudden economic downturns or new trade regulations can alter market conditions overnight.
Strategies to Overcome Business Research Challenges
Addressing the challenges in business research requires a combination of strategic planning, leveraging modern technology, and fostering collaboration. Below is a comprehensive guide on overcoming these challenges effectively:
1. Invest in Training and Skill Development
One of the foundational steps in overcoming research challenges is equipping teams with the right skills. Research methodologies and data analysis tools are evolving, and continuous learning ensures teams remain capable of handling new demands.
- Workshops and Certifications: Organizations can provide access to industry-recognized certifications in areas like data analysis, statistical software, and qualitative research methods.
- On-the-Job Training: Pairing experienced researchers with newer team members fosters mentorship and practical learning.
- Cross-Functional Skills: Training in communication, presentation, and stakeholder management helps bridge gaps between research teams and decision-makers.
2. Utilize Advanced Technology and Automation
Technological tools can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of business research.
- AI and Machine Learning: These technologies enable researchers to analyze large datasets faster and uncover patterns that might go unnoticed through traditional methods. Tools like IBM Watson and Google AI are popular for predictive analytics.
- Data Cleaning Software: Automated data-cleaning tools like OpenRefine or Talend ensure datasets are accurate and ready for analysis.
- Survey Platforms: Tools like Qualtrics and SurveyMonkey simplify designing and distributing surveys to target respondents while providing analytics dashboards.
3. Build a Robust Ethical Framework
Ensuring ethical practices during research builds trust and minimizes risks associated with legal or reputational harm.
- Compliance with Laws: Familiarize teams with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, which govern data usage and privacy.
- Transparency: Inform participants about how their data will be used, and ensure that consent forms are detailed and easy to understand.
- Bias Management: Train researchers to recognize and reduce unconscious biases during data collection and analysis.
4. Focus on Strategic Tool Selection
With the abundance of tools available, it’s essential to select the ones best suited for your business research objectives.
- Criteria for Selection: Evaluate tools based on usability, scalability, compatibility with existing systems, and cost-effectiveness.
- Integrated Platforms: Use platforms like Salesforce or HubSpot that offer data collection, analysis, and reporting capabilities in one ecosystem, reducing integration issues.
- Free or Open-Source Alternatives: For budget-constrained projects, tools like R and Python for statistical analysis or Tableau Public for data visualization can be highly effective.
5. Foster Cross-Departmental Collaboration
Research often impacts multiple stakeholders, from marketing to product development. Effective collaboration ensures alignment and maximizes the utility of insights.
- Regular Updates: Schedule cross-functional meetings to discuss research progress, challenges, and preliminary findings.
- Shared Goals: Define shared objectives to ensure all departments see the research’s value and contribute accordingly.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Engage stakeholders early in the research process to set realistic expectations and build trust.
6. Adopt Agile Research Practices
Traditional research methods can be slow and cumbersome. Agile research practices emphasize flexibility, speed, and iterative improvements.
- Short Iterations: Break down the research process into smaller, manageable phases, allowing for frequent reviews and adjustments.
- Feedback Loops: Incorporate feedback from stakeholders after each phase to refine objectives and methodologies.
- Rapid Prototyping: Use quick pilots or simulations to test hypotheses before committing to large-scale studies.
7. Allocate Resources Efficiently
Resource constraints, whether financial, time-based, or personnel-related, can hinder the research process. Proper allocation ensures that priorities are met without overextending budgets or timelines.
- Budget Planning: Set realistic budgets based on the scope of the research and include contingencies for unexpected costs.
- Outsourcing: For specialized tasks like advanced statistical modeling or focus group moderation, consider hiring external experts.
- Time Management Tools: Use software like Trello or Asana to track research milestones and deadlines.
8. Leverage External Expertise
Not all organizations have the in-house expertise required for complex research projects. Partnering with external agencies or consultants can fill these gaps.
- Research Agencies: Established firms like Nielsen or Gartner specialize in providing actionable business insights.
- Academic Partnerships: Collaborate with universities for access to academic expertise and resources at lower costs.
- Freelance Experts: Platforms like Upwork offer access to skilled researchers for specific projects.
9. Address Cross-Cultural and Market-Specific Challenges
For businesses operating across borders, understanding local nuances is vital.
- Localized Research Teams: Hire local researchers familiar with the cultural and regulatory environment.
- Cultural Training: Educate teams on cultural norms and practices to avoid misinterpretation of findings.
- Translation and Adaptation: Use professional translation services to ensure survey questions and research materials are culturally relevant.
10. Continuously Update Research Practices
The dynamic nature of markets and industries necessitates staying updated with emerging trends and best practices in research.
- Industry Reports: Regularly review publications from organizations like McKinsey, Deloitte, or the World Economic Forum.
- Professional Networks: Join research associations or online communities like ESOMAR or LinkedIn groups to stay informed.
- Adopt New Models: Be open to adopting new research paradigms, such as behavioral economics or sentiment analysis, which may provide richer insights.
11. Enhance Communication of Findings
The value of research is realized only when its insights are effectively communicated to decision-makers.
- Visual Storytelling: Use visual tools like infographics, dashboards, and presentations to make data more digestible.
- Actionable Insights: Focus on providing clear, actionable recommendations rather than overwhelming stakeholders with raw data.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Create channels for stakeholders to discuss and challenge findings, ensuring mutual understanding and buy-in.
How to Conduct Business Research
Conducting effective business research is a structured process that combines planning, execution, and analysis. Here’s a comprehensive step-by-step guide to ensure that your research yields actionable and reliable results.

1. Define the Research Objective
Before diving into data collection, establish a clear objective. A well-defined goal helps focus your efforts and ensures alignment with your business needs.
- Ask Specific Questions: What problem are you solving? Are you exploring customer preferences, evaluating competitors, or assessing market trends?
- Align with Stakeholders: Collaborate with stakeholders to identify priorities and set measurable outcomes.
- Create SMART Goals: Objectives should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
Example: If launching a new product, the objective might be to assess customer demand in specific demographics.
2. Identify the Type of Research
Choosing the right type of research—qualitative or quantitative—is critical.
- Qualitative Research: Use for exploring ideas, opinions, or behaviors in-depth. Techniques include interviews, focus groups, and observational studies.
- Quantitative Research: Ideal for gathering numerical data to identify trends or patterns. Methods include surveys, experiments, and statistical analysis.
Selecting the right approach depends on your research goals. For example, understanding customer motivations might require qualitative research, while measuring satisfaction rates might require quantitative methods.
3. Develop a Research Plan
A detailed research plan acts as a roadmap, guiding your process.
- Define the Scope: Specify the target market, industry, or competitors.
- Select Research Methods: Decide on techniques like surveys, interviews, or secondary data analysis.
- Set a Timeline: Break the process into phases, such as data collection, analysis, and reporting, with clear deadlines.
- Allocate Resources: Identify team members, budget, and tools required for the research.
Example: A company studying e-commerce trends might plan to collect customer feedback through surveys and supplement it with market reports.
4. Collect Data
The data collection stage involves gathering information that directly addresses your research objectives.
Primary Research
- Surveys: Design structured questionnaires using tools like SurveyMonkey or Google Forms. Keep questions concise and relevant.
- Interviews: Conduct one-on-one or group interviews for in-depth insights. Use open-ended questions to encourage detailed responses.
- Focus Groups: Bring together diverse participants to discuss a specific topic and identify shared perspectives.
- Observations: Monitor customer behavior in real-world settings, such as shopping habits or product usage.
Secondary Research
- Industry Reports: Access market insights from organizations like Gartner, Statista, or IBISWorld.
- Government Data: Utilize publicly available resources like census data or trade statistics.
- Academic Journals: Refer to peer-reviewed studies for reliable data and methodologies.
5. Analyze and Interpret Data
After collecting data, the next step is to organize and analyze it to uncover patterns and insights.
- Data Cleaning: Eliminate incomplete, duplicate, or inaccurate data to improve quality. Tools like OpenRefine can automate this process.
- Statistical Analysis: Use software like Excel, SPSS, or Python to calculate averages, correlations, or trends.
- Thematic Analysis: For qualitative data, identify recurring themes and sentiments.
- Visualization: Present data using charts, graphs, or dashboards to make it understandable and actionable. Tools like Tableau or Power BI are useful for visualization.
Example: A retail business might discover that its target audience spends more during seasonal sales, prompting it to adjust marketing strategies.
6. Draw Conclusions and Make Recommendations
The ultimate purpose of research is to provide actionable insights that drive decisions.
- Summarize Findings: Highlight key trends, anomalies, and correlations that align with your research objectives.
- Provide Context: Relate findings to broader industry trends or organizational goals.
- Offer Recommendations: Suggest specific actions, such as launching a product, optimizing pricing, or entering a new market.
- Anticipate Risks: Highlight potential challenges or limitations based on your findings.
7. Report and Communicate Results
Effectively communicating your research findings ensures that stakeholders can act on them.
- Create Clear Reports: Include an executive summary, detailed analysis, and visual aids.
- Tailor to Your Audience: Simplify technical jargon for non-researchers and provide actionable insights for decision-makers.
- Present Findings: Use presentations or dashboards for real-time discussion and collaboration.
Example: A B2B company might prepare a report showing competitors’ pricing strategies and recommend adjustments to remain competitive.
8. Implement Findings
Research is only valuable when its insights are applied effectively.
- Develop Strategies: Align findings with marketing, sales, or operational strategies.
- Monitor Outcomes: Track the impact of implemented changes using KPIs or metrics.
- Iterate and Improve: Use post-implementation feedback to refine research and processes.
9. Maintain Ethical Standards
Throughout the process, ensure your research adheres to ethical guidelines.
- Privacy Compliance: Protect participant data in line with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Transparency: Clearly explain the purpose of the research and obtain informed consent.
- Avoid Manipulation: Report findings objectively without cherry-picking favorable results.
10. Conduct Ongoing Research
Markets and customer preferences evolve constantly. Establishing an ongoing research process ensures your business remains informed and adaptable.
- Track Market Trends: Regularly update research to reflect new trends or disruptions.
- Customer Feedback Loops: Continuously collect and analyze customer feedback for iterative improvements.
- Competitor Monitoring: Use tools like SEMrush or SimilarWeb to keep an eye on competitors’ strategies.
Conclusion
Business research is a critical investment for organizations aiming to stay ahead in competitive markets. By leveraging robust methods, cutting-edge tools, and actionable insights, companies can transform data into a strategic advantage, ensuring success in today’s dynamic business environment.

