Imagine a world where machines don’t just follow orders but proactively decide what needs to be done. These machines adapt, reason, and act with autonomy, driven by goals rather than mere commands. This isn’t a distant sci-fi future; it’s the reality shaping our world through agentic AI.
Table of Contents
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI represents a groundbreaking leap in artificial intelligence, shifting from passive, task-specific systems to dynamic, goal-driven agents capable of independent decision-making. The term “agentic” stems from the word “agent,” implying an entity capable of acting with purpose. These AI systems don’t merely follow rules or respond to instructions—they actively pursue objectives, adapting to new contexts and challenges without constant human intervention.
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI:
- Autonomy: Operates independently, reducing reliance on human input.
- Goal-oriented: Focuses on achieving specific outcomes rather than executing predefined tasks.
- Adaptability: Learns and adjusts to new information or environments in real-time.
- Decision-Making: Evaluates scenarios, weighs options, and selects the best course of action.
For example, an agentic AI system in e-commerce might predict trends, adjust pricing, and recommend inventory changes to maximize profits—all autonomously.
Here is a simple Explanation 👇
How Does Agentic AI Work?
Agentic AI operates as a sophisticated system capable of autonomous decision-making and goal-directed behavior. Unlike traditional AI, which often requires human supervision and predefined instructions, agentic AI adapts dynamically to its environment and learns from its interactions. Its workings can be understood through several core processes, which are interconnected to enable a seamless and intelligent operation. Here’s an in-depth breakdown:
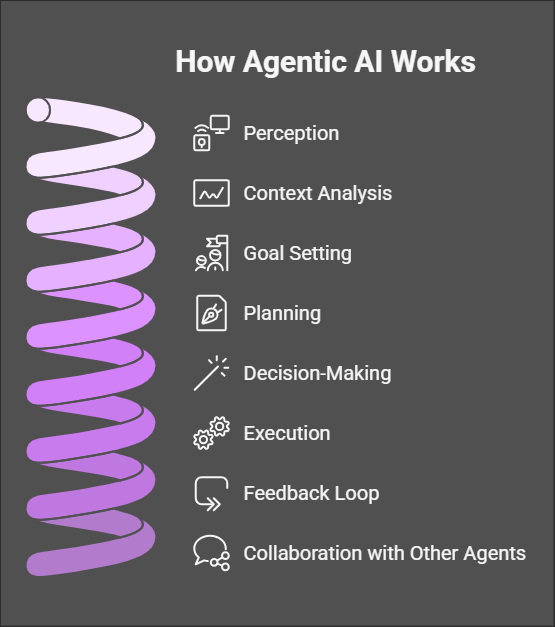
1. Perception
Agentic AI begins by perceiving its surroundings through data collection. This is achieved using various input sources, including sensors, APIs, and integrated data streams.
- Example: In an autonomous vehicle, perception involves gathering data from LiDAR, cameras, and GPS to detect obstacles, road signs, and traffic patterns.
- Technology Involved: Computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), and sensor fusion techniques allow the AI to interpret data accurately.
2. Context Analysis
Once data is collected, the AI system analyzes it to understand the context. This step involves identifying patterns, detecting anomalies, and recognizing key variables.
- Example: A customer service AI chatbot processes language inputs to determine user sentiment and intent.
- Key Techniques: Machine learning models, semantic analysis, and probabilistic reasoning enable accurate context comprehension.
3. Goal Setting
Agentic AI distinguishes itself by its ability to set goals autonomously. These goals are often defined based on its programming, mission priorities, or learned behaviors.
- Example: In a financial advisory application, the AI might set a goal to minimize risk while maximizing returns for a user’s portfolio.
- Core Feature: This step allows the AI to align its actions with the desired outcomes, moving beyond reactive behavior.
4. Planning
The system uses advanced algorithms to devise strategies for achieving its objectives. Planning involves evaluating possible actions, predicting outcomes, and selecting the most effective course of action.
- Example: In a smart factory, agentic AI can plan the optimal sequence of tasks to minimize downtime and maximize productivity.
- Methodologies Used: Reinforcement learning, decision trees, and Monte Carlo simulations are common approaches for strategic planning.
5. Decision-Making
Based on the plan, agentic AI makes decisions in real-time, even in unpredictable situations. This ability to think on its feet differentiates it from static, rule-based AI systems and highlights the evolving capabilities of an AI intelligent agent that can adapt and respond dynamically to changing environments.
- Example: An AI system managing renewable energy might decide to switch to stored battery power during peak demand to avoid grid overload.
- Considerations: Factors like resource constraints, risks, and potential rewards are evaluated before taking action.
6. Execution
After determining the optimal strategy, the AI executes its chosen actions. Execution can involve physical actions (as in robotics) or virtual operations (such as sending notifications or adjusting algorithms).
- Example: A delivery drone navigates to a specific location, avoiding obstacles and adapting to changing weather conditions.
- Key Traits: Precision, speed, and reliability are hallmarks of effective execution.
7. Feedback Loop
A crucial aspect of agentic AI is its ability to learn from its actions. After execution, the system analyzes the results and incorporates this feedback to refine future decisions.
- Example: A marketing AI system tracks the performance of an ad campaign and adjusts targeting criteria based on audience engagement metrics.
- Learning Mechanisms: Supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning enable continuous improvement.
8. Collaboration with Other Agents
In multi-agent systems, agentic AI also works collaboratively with other agents to achieve shared objectives. Communication protocols and shared knowledge bases are used to ensure effective cooperation.
- Example: In a swarm of drones performing a search-and-rescue mission, each drone shares real-time data with others to cover more ground efficiently.
- Core Concept: This interaction amplifies the capabilities of the system, making it greater than the sum of its parts.
9. Ethical and Safety Frameworks
To ensure reliability, agentic AI often operates within ethical and safety constraints. These frameworks guide the AI in making decisions that align with societal values and regulations.
- Example: In healthcare, agentic AI prioritizes patient privacy and adheres to compliance standards like HIPAA.
Tools Used: Rule-based governance models, ethical AI guidelines, and compliance frameworks.
Also read: 45+ Best AI Tools for Digital Marketing to improve productivity and drive results
Types of Agents in an Agentic AI
Agentic AI systems consist of various types of agents, each tailored to fulfill specific roles and contribute to the system’s overall intelligence. These agents are designed to perform tasks that align with their unique capabilities, enabling agentic architectures to handle complex, multifaceted challenges effectively. Here’s an in-depth look at the key types of agents.
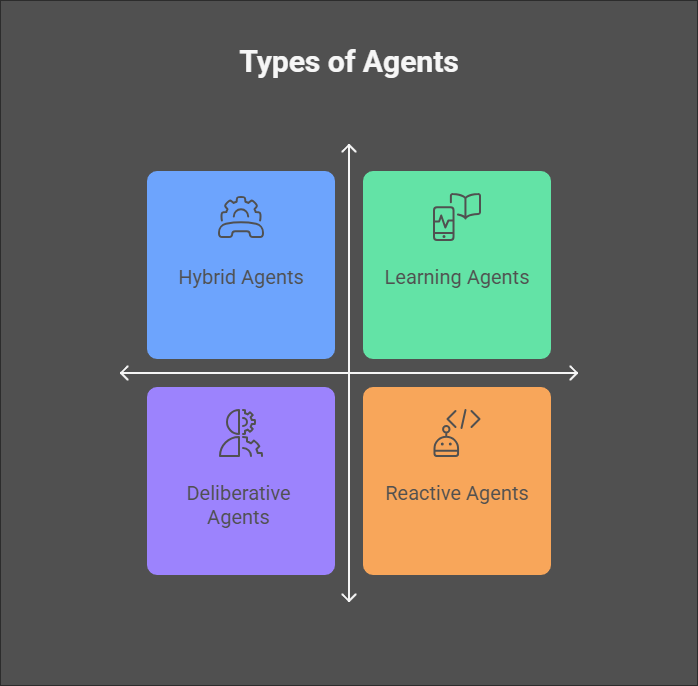
1. Reactive Agents
Reactive agents function by responding to stimuli from their environment without engaging in advanced planning or reasoning. They operate based on predefined rules or behaviors, which makes them efficient for straightforward, repetitive tasks.
How They Work
- They rely on sensor inputs to perceive their environment and trigger an immediate action based on those inputs.
- They do not possess memory or the ability to learn from past experiences, focusing solely on current stimuli.
Example
- Chatbots: Many basic customer service chatbots fall into this category. For instance, a chatbot that provides predefined answers to common queries such as “What are your business hours?” or “Where can I track my order?”
- Thermostats: A thermostat that turns the heating on when the temperature drops below a set point is a classic example of a reactive agent.
Advantages
- Simple design and quick responses.
- Reliable for well-defined tasks.
Limitations
- Lack of adaptability and strategic thinking.
2. Deliberative Agents
Deliberative agents are equipped with advanced reasoning capabilities, allowing them to analyze situations, predict potential outcomes, and make informed decisions based on logical planning. They take a goal-oriented approach and often use symbolic reasoning to navigate complex scenarios.
How They Work
- These agents assess their environment and develop a detailed plan to achieve a specific objective.
- They consider multiple variables and weigh the pros and cons of possible actions before executing a decision.
Example
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars are an excellent example of deliberative agents. They analyze traffic conditions, anticipate the movements of other vehicles, and plan routes to reach their destination safely and efficiently.
- Virtual Assistants: High-level AI assistants like Siri or Alexa, when tasked with creating a detailed schedule or managing a shopping list based on preferences and constraints, demonstrate deliberative capabilities.
Advantages
- Highly intelligent and capable of tackling complex tasks.
- Can adapt to dynamic environments.
Limitations
- Slower response times due to extensive reasoning.
- Requires significant computational power.
3. Hybrid Agents
Hybrid agents combine the instant responsiveness of reactive agents with the advanced reasoning of deliberative agents. They leverage the strengths of both approaches, making them versatile and effective in diverse scenarios.
How They Work
- These agents use a dual-layer approach:
- A reactive layer handles immediate responses to external stimuli.
- A deliberative layer engages in strategic planning and decision-making.
Example
- Robotic Vacuum Cleaners: Devices like the Roomba utilize a hybrid approach. They react to obstacles in real time (reactive) while also planning the most efficient cleaning route (deliberative).
- Intelligent Drones: A drone performing a search-and-rescue mission reacts to sudden weather changes while simultaneously strategizing the most effective search patterns.
Advantages
- Balance between speed and intelligence.
- Effective for tasks requiring both immediate action and strategic planning.
Limitations
- More complex to design and implement.
4. Learning Agents
Learning agents represent the pinnacle of agentic AI, as they can adapt and improve over time through experience. These agents employ machine learning techniques to refine their performance, making them suitable for dynamic and unpredictable environments.
How They Work
- These agents collect feedback from their actions and use it to enhance their decision-making processes.
- They often employ supervised learning, unsupervised learning, or reinforcement learning models to identify patterns and optimize behaviors.
Example
- Recommendation Systems: Platforms like Netflix or Spotify use learning agents to suggest movies or music based on user preferences and engagement history.
- Smart Financial Advisors: Robo-advisors in the financial sector analyze market trends and user investment behaviors to provide personalized recommendations.
Advantages
- Continuous improvement through learning.
- Adaptable to new and unforeseen circumstances.
Limitations
- Requires large volumes of data for effective learning.
- Risk of unintended biases in the learning process.

How These Agents Work Together
In an agentic architecture, these agents often function collaboratively to achieve a common goal. Each agent type contributes its unique strengths to the system:
- Reactive agents handle immediate responses and real-time adjustments.
- Deliberative agents focus on long-term planning and decision-making.
- Hybrid agents bridge the gap between instant reactions and strategic reasoning.
- Learning agents enhance the system’s overall performance by continuously refining their operations.
Example: Smart City Management
In a smart city infrastructure:
- Reactive agents manage real-time traffic signals.
- Deliberative agents optimize energy distribution based on usage patterns.
- Hybrid agents ensure seamless coordination between emergency response systems and daily operations.
- Learning agents improve systems over time, identifying inefficiencies and optimizing resource allocation.
Agentic AI vs Traditional AI vs Generative AI
| Aspect | Agentic AI | Traditional AI | Generative AI |
| Core Functionality | Autonomous decision-making and goal-oriented behavior. | Rule-based systems or specific task execution. | Creating new content like text, images, or music. |
| Architecture | Multi-agent systems with reactive, deliberative, and learning agents. | Linear or deterministic algorithms. | Neural networks, often deep learning models. |
| Learning Capability | Learns and adapts via feedback and interaction. | Limited learning; focuses on fixed patterns. | Trains on data to improve generative outputs. |
| Adaptability | High; responds to dynamic, real-world scenarios. | Low; struggles with changing environments | Moderate; adapts based on training data scope. |
| Applications | Autonomous vehicles, smart cities, robotics. | Data analysis, rule-based automation. | Text-to-image generation, chatbots, and content creation. |
| Key Example | Smart financial advisors optimizing investments. | Spam filters or diagnostic systems. | ChatGPT, MidJourney, or DALL·E. |
Also read: Modern Marketing Concepts: Meaning, Importance and Types
Single-Agent System
In a single-agent system, one AI agent operates independently to achieve a specific goal. These systems are typically simpler and are well-suited for tasks requiring focused, linear problem-solving.
Examples of Single-Agent Systems:
- Autonomous Drones: A drone conducting inspections or deliveries on its own.
- Personal Assistants: AI like Siri or Alexa responding to user queries and commands.
Strengths of Single-Agent Systems:
- Straightforward to design and manage.
- Ideal for applications with limited complexity.
Multi-Agent System
A multi-agent system (MAS) involves multiple AI agents working collaboratively or competitively to achieve goals. These systems are often more complex, as agents must communicate and coordinate their actions.
Examples of Multi-Agent Systems:
- Smart Cities: Traffic management systems where multiple agents optimize routes and reduce congestion.
- Stock Trading Platforms: Agents predicting market trends and executing trades based on shared data.
Key Advantages of Multi-Agent Systems:
- Scalability: Can handle larger and more complex tasks.
- Redundancy: If one agent fails, others can take over.
Collaboration: Agents can pool resources and share insights for better outcomes.
Also read: Main Goal of Generative AI
Uses of Agentic AI
Agentic AI is driving profound transformations across multiple industries by enhancing operational efficiency, reducing human error, and fostering innovation. By integrating autonomous decision-making and learning capabilities, agentic AI optimizes workflows, empowers predictive analytics, and supports personalized services in real-time. Here are some of its most impactful applications:
1. Healthcare
The healthcare sector is benefiting greatly from agentic AI’s ability to enhance diagnostics, streamline patient care, and provide valuable insights.
- Automating Patient Diagnostics & Treatment Recommendations: Agentic AI systems can process vast amounts of medical data, including patient history, lab results, and symptoms, to diagnose conditions and suggest personalized treatment plans autonomously. This helps reduce the burden on healthcare professionals while providing patients with accurate, data-driven care.
- Monitoring Patient Vitals in Real-Time with Wearables: Devices like smartwatches and health trackers powered by agentic AI can continuously monitor vital signs (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure) and alert healthcare providers to any anomalies, enabling immediate intervention when necessary.
- Predicting Disease Outbreaks: By analyzing patterns in healthcare data, environmental conditions, and social behavior, agentic AI can predict potential disease outbreaks or health risks, allowing governments and healthcare organizations to prepare and respond proactively.
2. Logistics
Agentic AI transforms logistics by optimizing supply chains, automating repetitive tasks, and reducing operational costs.
- Autonomous Inventory Tracking: With AI-powered sensors and robotic systems, agentic AI can autonomously track inventory levels in warehouses, ensuring real-time updates and minimizing human error. This helps reduce stockouts, excess inventory, and delays.
- Real-Time Optimization of Delivery Routes: Agentic AI can evaluate traffic conditions, weather patterns, and delivery priorities to calculate the most efficient delivery routes autonomously. This results in cost savings, faster deliveries, and improved customer satisfaction.
Example: Companies like Amazon use AI-powered robots and drones to optimize warehouse management and delivery routes, significantly improving operational efficiency.
3. Finance
In finance, agentic AI is enhancing security, automating investments, and personalizing financial advice.
- Identifying Fraudulent Transactions: Agentic AI systems can detect unusual patterns in financial transactions and flag them as potential fraud. These systems learn from historical data to improve their ability to identify suspicious activities in real-time.
- Personalizing Investment Strategies: AI-powered robo-advisors use agentic capabilities to analyze an individual’s financial goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions. Based on this analysis, they autonomously suggest tailored investment strategies that can adjust as market dynamics shift.
4. Education
Agentic AI is reshaping the educational landscape by providing personalized learning experiences and streamlining administrative tasks.
- Designing Adaptive Learning Platforms: Agentic AI can evaluate each student’s learning style, strengths, and weaknesses to design personalized learning paths that cater to individual needs, promoting better engagement and outcomes.
- Automating Administrative Tasks: Teachers and administrators benefit from agentic AI’s ability to automate repetitive tasks, such as grading assignments, scheduling, and managing student records. This allows educators to focus more on instruction and less on administrative burdens.
5. Manufacturing
In manufacturing, agentic AI improves operational efficiency, reduces downtime, and enhances overall productivity.
- Optimizing Production Lines: Agentic AI can monitor production line operations in real-time, identify bottlenecks, and suggest improvements to optimize throughput. AI systems can autonomously adjust machinery settings to ensure consistent product quality and minimize delays.
- Detecting & Resolving Equipment Malfunctions: By constantly monitoring machine performance and analyzing data patterns, agentic AI can predict when equipment will likely fail. It can then take preventative actions or autonomously alert maintenance teams before a failure occurs, reducing unplanned downtime.
6. Retail and E-Commerce
In retail and e-commerce, agentic AI is enhancing customer experiences, automating inventory management, and driving sales growth.
- Creating Hyper-Personalized Shopping Experiences: Agentic AI systems analyze customer behavior, preferences, and past purchase data to deliver personalized product recommendations and tailor marketing efforts. This improves conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
- Managing Inventory & Predicting Customer Demand: AI-powered systems can predict shifts in customer demand based on trends, seasonality, and market conditions. This allows retailers to autonomously adjust inventory levels, reducing waste and ensuring products are always available when customers need them.
7. Transportation
Transportation is another sector being radically transformed by agentic AI, especially with the rise of autonomous vehicles.
- Enabling Self-Driving Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles, powered by agentic AI, can navigate complex environments such as busy streets, adjusting their behavior based on traffic conditions, road signs, and potential obstacles. These vehicles make real-time decisions, allowing them to safely operate without human intervention.
Coordinating Fleets of Autonomous Vehicles: In public transportation, agentic AI can coordinate fleets of self-driving buses, taxis, or shuttles. By dynamically adjusting routes, pickup times, and vehicle allocation based on passenger demand and traffic conditions, agentic AI can improve efficiency and service availability.
Final Thoughts
The shift toward agentic AI represents a profound transformation in our interactions with technology. It’s not just about smarter systems but creating a world where technology anticipates, adapts, and acts purposefully.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business leader, or a curious learner, now is the time to understand and embrace the possibilities of agentic AI. The future isn’t just automated, it’s agentic. Are you ready to lead the charge?
FAQs: What is Agentic AI?
1. What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to autonomous, goal-oriented systems capable of perceiving their environment, making decisions, and taking actions to achieve specific objectives without continuous human intervention. Unlike traditional AI, which relies on predefined rules and lacks adaptability, Agentic AI can learn from interactions and adapt to new situations, making it more flexible and responsive.
2. How does Agentic AI differ from traditional AI?
Traditional AI operates based on predefined algorithms and lacks the ability to adapt to new situations without human input. In contrast, Agentic AI systems are designed to operate autonomously, making independent decisions, adapting to new situations, and pursuing predefined goals without requiring constant human oversight. This autonomy allows Agentic AI to perform complex tasks, solve problems creatively, and operate in dynamic settings.
3. What are the core characteristics of Agentic AI?
The core characteristics of Agentic AI include:
Autonomy: Operating independently without continuous human input.
Decision-Making Capabilities: Using advanced reasoning to evaluate factors and make informed choices.
Goal-Directed Behavior: Prioritizing and adjusting actions to achieve specific objectives.
These characteristics enable Agentic AI to solve complex problems, adapt to new conditions, and perform tasks with minimal intervention.
4. What are some key benefits of adopting Agentic AI in businesses?
Adopting Agentic AI in businesses offers several benefits, including:
Scalability: Handling increased workloads without significantly increasing resources. For example, in e-commerce, AI can manage spikes in demand by automating customer service and inventory management.
Cost Reduction: Automating tasks and optimizing processes to reduce operational costs.
Innovation Support: Fostering innovation by enabling new business models and services.
5. How do we regulate Agentic AI?
Regulating Agentic AI involves establishing guardrails that consider legal, regulatory, and compliance issues, as well as autonomy, security, and privacy. These guardrails place constraints on AI agents and can reduce the risk of AI agents misaligning with business goals. It’s essential to ensure that AI systems operate within ethical boundaries and align with human values.

