Marketing isn’t about throwing ads at random people and hoping for the best. It’s about speaking directly to the right people. People who actually care about what you offer. But how do you find them? That’s where market segmentation comes in.
Table of Contents
By dividing your audience into smaller, more specific groups, you can craft messages that truly resonate. But with so many types of market segmentation, how do you know which one to use? Let’s break it down step by step.
What is Market Segmentation?
At its core, market segmentation is the process of breaking a large customer base into customer segments with common traits. These segments could be based on demographic segmentation, behaviors, interests, location, and more.
By doing this, businesses can:

Without market segmentation, you’re basically throwing spaghetti at the wall and hoping something sticks. With it, you’re delivering messages that actually matter to the people receiving them.
Also read: What is Segmentation in Marketing and What are its Types?
Why is a Market Segmentation Strategy Important?
Think about two companies:
1️⃣ Company A blasts the same generic ad to everyone.
2️⃣ Company B customizes its messaging based on different customer personas, customizing content for young professionals, retirees, and college students.
Who’s more likely to see better results? Company B.
A well-thought-out market segmentation strategy helps businesses:

Types of Market Segmentation
1. Demographic Segmentation
What It Is:
Demographic segmentation categorizes people based on objective traits like age, gender, income, education, and occupation.
Why It Works:
It helps businesses create targeted products and marketing messages for different groups.
Key Factors in Demographic Segmentation:
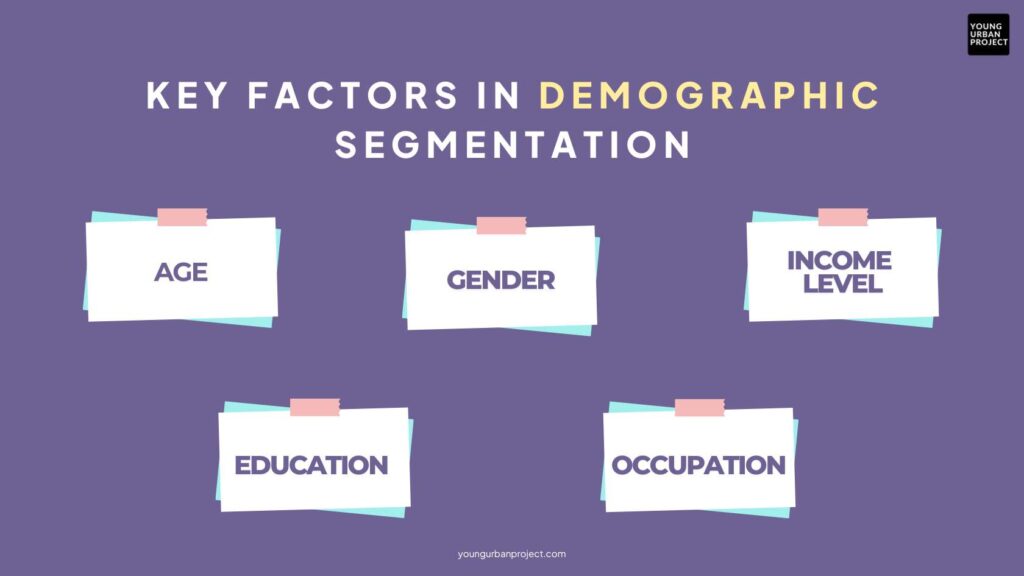
- Age – A toy brand targets kids, while a retirement plan is marketed to seniors.
- Gender – Skincare companies create separate products for men and women.
- Income Level – Luxury brands target high-income customers, while budget-friendly stores focus on cost-conscious shoppers.
- Education – A coding boot camp markets itself to college students and career switchers.
- Occupation – A B2B software company might target IT managers rather than entry-level employees.
✅ Example: A high-end car brand like Tesla markets its electric vehicles to high-income professionals, while Toyota promotes budget-friendly models to middle-class families.
2. Psychographic Segmentation
What It Is:
Unlike demographics, psychographic segmentation focuses on people’s interests, values, and motivations.
Why It Works:
It helps brands understand why customers make certain decisions.
Key Factors in Psychographic Segmentation:
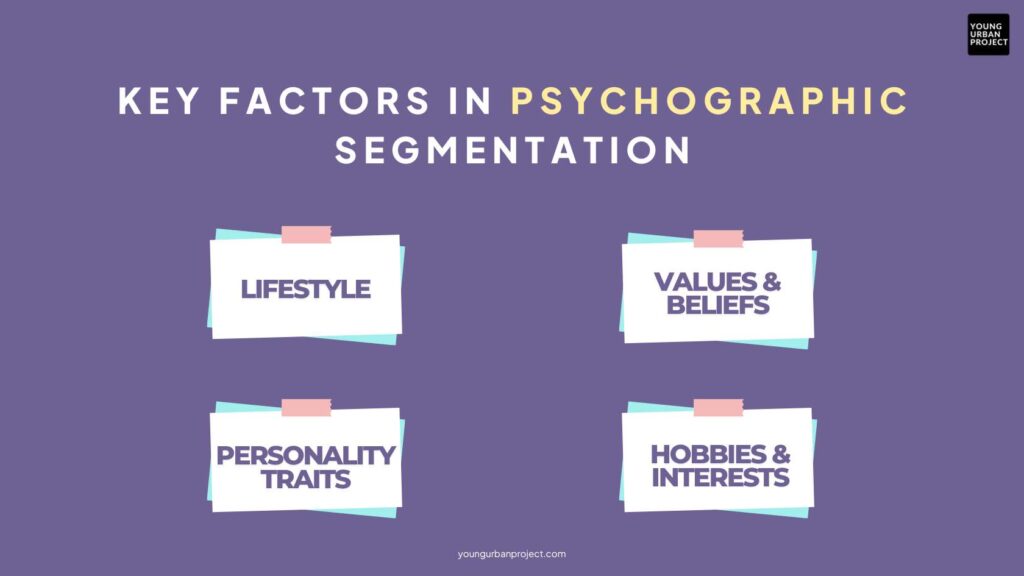
- Lifestyle – An organic food brand targets health-conscious consumers.
- Values & Beliefs – A sustainable fashion brand appeals to environmentally conscious buyers.
- Personality Traits – A tech company might market differently to early adopters vs. those resistant to change.
- Hobbies & Interests – A travel agency might focus on adventure seekers vs. luxury vacationers.
✅ Example: Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign speaks to people who value perseverance and self-improvement, making it a perfect example of psychographic segmentation.
3. Geographic Segmentation
What It Is:
Geographic segmentation divides customers based on their location.
Why It Works:
Location affects climate, culture, and lifestyle, all of which impact purchasing behavior.
Key Factors in Geographic Segmentation:
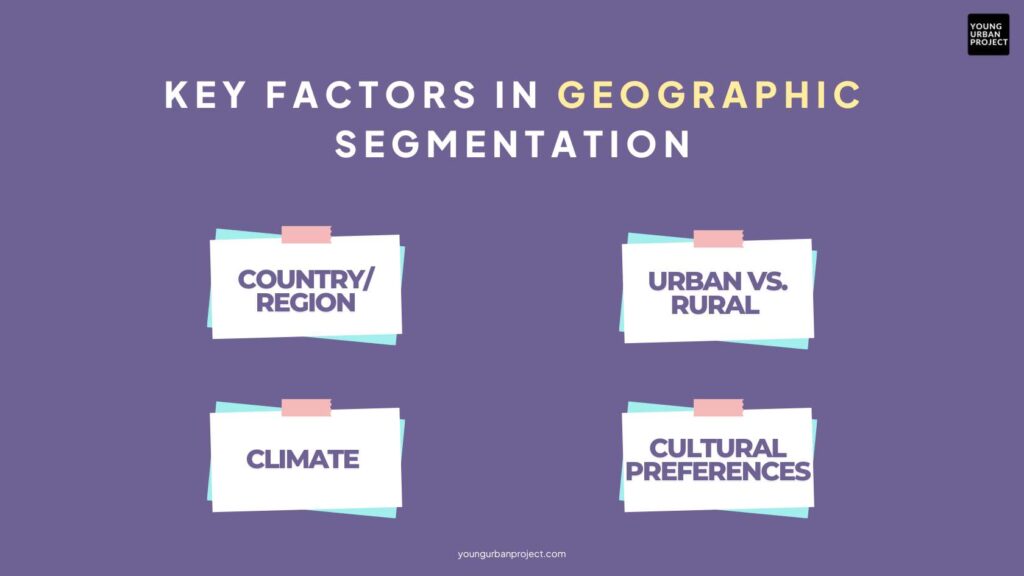
- Country/Region – A fast-food brand adjusts its menu based on local preferences.
- Urban vs. Rural – A luxury fashion brand targets urban shoppers, while a tractor company focuses on rural buyers.
- Climate – A winter jacket company promotes its products in colder regions.
- Cultural Preferences – A beverage company may adjust flavors based on local tastes.
✅ Example: McDonald’s customizes its menu worldwide—offering McSpicy Paneer in India and Teriyaki Burgers in Japan.
Also read: What is Positioning in Marketing
4. Behavioral Segmentation
What It Is:
Use behavioral segmentation to classify customers based on their purchasing habits and interactions with your brand.
Why It Works:
It helps predict what customers will do next.
Key Factors in Behavioral Segmentation:

- Purchase History – A coffee brand offers loyalty rewards to frequent buyers.
- Usage Frequency – A streaming service creates separate plans for casual and binge-watchers.
- Brand Loyalty – Apple targets long-time customers differently from first-time buyers.
- Benefits Sought – Some customers want premium features, while others prioritize affordability.
✅ Example: Amazon personalizes product recommendations based on previous shopping behavior, an excellent example of behavioral segmentation.
5. Technographic Segmentation
What It Is:
This type of market segmentation focuses on how customers interact with technology.
Why It Works:
It helps tech brands target the right audience.
Key Factors in Technographic Segmentation:
- Device Preference – A mobile gaming company prioritizes smartphone users over desktop users.
- Software Usage – A SaaS company markets differently to advanced vs. beginner users.
- Tech-Savviness – A smartwatch brand targets fitness enthusiasts with advanced tracking needs.
✅ Example: Adobe offers Photoshop in different versions, one for professionals, another for beginners.
6. Firmographic Segmentation
What It Is:
Firmographic segmentation is used in the B2B market to categorize businesses based on key attributes.
Why It Works:
It helps companies tailor their offerings to different business needs.
Key Factors in Firmographic Segmentation:
- Industry – A cybersecurity firm markets to banks differently than to eCommerce stores.
- Company Size – Enterprise software is priced higher for large corporations.
- Revenue – A consulting firm offers premium services to high-revenue businesses.
✅ Example: LinkedIn sells different advertising solutions based on company size and industry.
7. Transactional Segmentation
What It Is:
This method segments customers based on their spending habits.
Why It Works:
It helps brands create offers tailored to purchase frequency and spending levels.
Key Factors in Transactional Segmentation:
- High-Spending vs. Low-Spending Customers – A luxury hotel offers premium rewards to frequent travelers.
- Loyalty-Based Offers – A retailer gives discounts to returning customers.
✅ Example: Airlines use transactional segmentation to create different loyalty tiers for frequent and occasional flyers.
8. Generational Segmentation
What It Is:
Generational segmentation focuses on groups born in specific time periods.
Why It Works:
Each generation has unique values and buying behaviors.
Key Factors in Generational Segmentation:
- Gen Z (Born 1997-2012) – Prefers short-form videos and influencer marketing.
- Millennials (Born 1981-1996) – Values experiences and brands with purpose.
- Gen X (Born 1965-1980) – Prefers practical solutions and traditional marketing.
- Baby Boomers (Born 1946-1964) – Focuses on quality and brand loyalty.
✅ Example: Snapchat targets Gen Z with interactive filters, while Facebook remains popular among Gen X and Boomers.
9. Value Segmentation
What It Is:
This segmentation groups customers based on the value they seek in a product.
Why It Works:
Different people have different priorities—some want luxury, others want affordability.
✅ Example: Rolex targets premium customers, while Timex appeals to budget-conscious buyers.
10. Lifestage Segmentation
What It Is:
It categorizes consumers based on life transitions.
Why It Works:
Life changes impact purchasing behavior.
Key Factors in Lifestage Segmentation:
- College Students – Need budget-friendly solutions.
- New Parents – Seek baby products.
- Retirees – Look for travel or healthcare plans.
✅ Example: Pampers targets new parents, while AARP focuses on retirees.
11. Seasonal Segmentation
What It Is:
This segmentation adapts marketing to seasonal trends.
Why It Works:
People buy different things at different times of the year.
✅ Example: Retailers promote coats in winter and swimsuits in summer.
12. Persona Segmentation
What It Is:
It combines multiple segmentation types to create detailed customer personas.
✅ Example: An online fitness brand may have:
Casual Exercisers – Prefer simple home workouts.
Serious Athletes – Want advanced training programs.
How to Pick the Right Market Segmentation Type
Choosing the right segmentation type isn’t just about picking one at random; it requires a strategic approach. Here’s how you can use market segmentation effectively:
1. Gain Insights into Your Existing Customers
Before you can segment your audience, you need to understand your current customer base.
How to do it:
Analyze your website and social media data to see who engages with your brand.
Check purchase history to identify trends in buying behavior.
Gather customer feedback to understand their needs and pain points.
✅ Example: A SaaS company notices that most of its high-value customers come from tech startups. This insight could lead them to focus on firmographic segmentation.
2. Build Detailed Buyer Personas
A buyer persona is a semi-fictional representation of your target audience based on real data.
How to do it:
Identify demographics (age, income, education, job title).
Define their motivations, pain points, and decision-making processes.
Analyze their online behavior—what platforms they use and how they interact with content.
✅ Example: A fitness brand creates two buyer personas:
1️⃣ “Busy Professionals” – Age 30-45, looking for quick home workouts.
2️⃣ “Serious Athletes” – Age 20-35, interested in advanced training programs.
This allows them to use psychographic segmentation effectively.
3. Identify Potential Target Markets
Once you understand your current customers, look for new customer segments that align with your business goals.
How to do it:
Use market research to identify untapped opportunities.
Check competitors—who are they targeting?
Look for gaps in the market where customer needs aren’t being met.
✅ Example: A local bakery notices that there’s a demand for vegan products in their area. By using geographic segmentation, they can tailor their offerings to this new market segment.
4. Conduct Research on Your Chosen Segments
Now that you have potential segments, it’s time to validate them with deeper research.
How to do it:
Conduct surveys and interviews with customers in your chosen segment.
Use tools like Google Analytics, Facebook Audience Insights, and market reports.
Look at industry trends and competitor data.
✅ Example: A travel agency finds that Gen Z travelers prefer budget-friendly, experience-based trips, while Millennials prioritize luxury and comfort. This insight helps them refine their generational segmentation approach.
5. Validate Your Strategy Through Testing
Not every market segmentation process will be successful on the first try. You need to test and optimize.
How to do it:
Run A/B tests on different marketing messages for each segment.
Launch pilot campaigns to see which segments respond best.
Measure key performance indicators (KPIs) like engagement, conversion rates, and ROI.
✅ Example: A skincare brand tests two ad versions—one emphasizing anti-aging benefits for Boomers and another promoting vegan ingredients for Gen Z. The results help them refine their marketing campaign strategy.
6. Choose the Right Segmentation Method (or Combine Multiple Ones)
There’s no rule saying you must pick just one type of market segmentation—many businesses use a combination for effective marketing.
How to do it:
If selling in different locations → Use geographic segmentation.
If targeting specific behaviors → Use behavioral segmentation.
If focusing on lifestyle and values → Use psychographic segmentation.
✅ Example: A premium coffee brand combines:
Behavioral segmentation – Targeting frequent coffee buyers.
Demographic segmentation – Marketing higher-priced products to high-income earners.
Geographic segmentation – Promoting iced coffee in hot climates.
This mix leads to a more targeted marketing approach.
7. Ensure Your Segmentation Aligns with Your Business Goals
Your segmentation should help achieve long-term business objectives—not just short-term sales.
How to do it:
If your goal is brand loyalty → Use behavioral segmentation to reward frequent buyers.
If your goal is market expansion → Use geographic segmentation to identify new regions.
If your goal is better ad targeting → Use firmographic segmentation for B2B marketing.
✅ Example: Netflix’s goal is to increase engagement. They use behavioral segmentation to personalize content recommendations based on viewing history.
8. Continuously Monitor and Adapt Your Segmentation Strategy
Customer segments evolve over time, so your market segmentation strategy should too.
How to do it:
Regularly analyze data to spot changes in customer behavior.
Adapt your strategy based on market trends and technological advancements.
Gather feedback and improve your customer experience.
✅ Example: A retail brand initially targets Millennials but notices Gen Z is now a key market segment. They adjust their social media strategy to focus more on TikTok and Instagram.
Best Practices for Market Segmentation
Even the best market segmentation strategy can fail if not implemented correctly. Here are 8 essential best practices to help you use market segmentation effectively and get the best results.

1. Evolve with Your Market 🚀
Consumer behavior isn’t static—it changes with time, trends, and technology. If you stick to outdated customer segments, your marketing efforts will lose effectiveness.
How to do it:
Regularly review market research and industry trends.
Update your customer personas based on new data.
Monitor feedback and engagement to spot shifts in preferences.
✅ Example:
A clothing brand initially targets Millennials, but after tracking purchases, they notice Gen Z is driving most of their sales. They shift their marketing messages to focus on TikTok and Instagram-friendly ads.
2. Keep It Manageable—Don’t Over-Segment 🎯
It’s tempting to create highly specific customer segments, but too many will make it hard to scale your business.
How to do it:
Stick to 4-6 strong market segments instead of dozens.
Focus on segments that have enough potential customers to justify marketing to them.
Avoid unnecessary complexity—if two segments behave the same way, merge them.
✅ Example:
A SaaS company starts with 12 micro-segments for their B2B market, but managing unique strategies for each is inefficient. Instead, they consolidate them into firmographic segmentation (small businesses vs. enterprises) for better targeting.
Also read: 15 Effective SAAS Marketing Strategies: An Ultimate Guide
3. Test & Optimize Your Segmentation Strategy 🛠
Not every segmentation approach will work as expected. Always test and refine based on real-world data.
How to do it:
Run A/B tests on different marketing messages for each target market.
Track conversion rates to see which customer segments perform best.
Adjust segmentation based on performance analytics.
✅ Example:
An email marketing platform targets freelancers and marketing teams separately. After testing, they find that behavioral segmentation (targeting based on email engagement patterns) works better than demographic segmentation alone.
4. Use Multiple Segmentation Methods 🔍
Relying on just one type of market segmentation can limit your marketing campaign. A combination of demographic segmentation, psychographic segmentation, and behavioral segmentation can lead to more precise targeting.
How to do it:
Combine geographic segmentation with psychographic segmentation to tailor local messaging.
Use behavioral segmentation alongside transactional segmentation for better personalization.
Adapt segmentation methods based on the customer experience you want to deliver.
✅ Example:
Spotify uses behavioral segmentation (listening habits), psychographic segmentation (music preferences), and demographic segmentation (age, location) to personalize playlists and ads for each user.
5. Align Segmentation with Business Goals 🎯
Your market segmentation strategy should help achieve key business objectives, such as increasing customer loyalty, improving engagement, or boosting revenue.
How to do it:
Define what success looks like—higher conversion rates, lower acquisition costs, or better retention.
Prioritize customer segments that drive profitability, not just engagement.
Ensure segmentation supports long-term brand positioning.
✅ Example:
A fitness app wants to improve retention. Instead of using only demographic segmentation, they use behavioral segmentation to target inactive users with personalized re-engagement emails.
6. Leverage Data for Smarter Segmentation 📊
Market segmentation is the process of using data to create customer personas—and the more data-driven it is, the more effective it becomes.
How to do it:
Use Google Analytics, CRM data, and social media insights.
Track past purchase history and customer experience feedback.
Apply AI and machine learning tools for predictive segmentation.
✅ Example:
Amazon analyzes transactional segmentation and behavioral segmentation to recommend products based on previous purchases and browsing history.
7. Personalize Your Marketing Messages 💡
Each customer segment should receive content and offers that feel tailor-made for them. Generic messaging won’t work.
How to do it:
Create customized email campaigns based on customer loyalty levels.
Use different ad creatives for different customer segments.
Develop landing pages that speak directly to each target audience.
✅ Example:
A cosmetics brand segments users into:
1️⃣ Eco-conscious buyers → Receives marketing about sustainable packaging.
2️⃣ Luxury buyers → Receives content about high-end skincare benefits.
This segmentation improves conversions and customer experience.
Also read: Retargeting vs Remarketing
8. Regularly Monitor and Adjust Your Segmentation Strategy 🔄
Your segmentation strategy is never “done.” Keep refining it based on new insights.
How to do it:
Set KPIs to measure success for each market segment.
Identify declining segments and shift focus if necessary.
Conduct quarterly market research to stay ahead of trends.
✅ Example:
Netflix constantly updates its behavioral segmentation model to suggest shows based on new user habits. If a viewer starts watching more documentaries, Netflix adapts its recommendations in real time.
Conclusion
Understanding types of market segmentation is key to building stronger connections with customers. Whether you’re using demographic segmentation, psychographic segmentation, or firmographic segmentation, the right strategy can supercharge your marketing campaign and drive results.
💡FAQs
1. What is market segmentation?
Market segmentation is when businesses break a large audience into smaller, more specific groups based on shared traits. This helps companies understand their customers better and create personalized marketing campaigns instead of using a one-size-fits-all approach.
2. What are the 4 basic types of market segmentation?
The four main types of market segmentation are:
1️⃣ Demographic segmentation – Who they are (age, gender, income, education).
2️⃣ Psychographic segmentation – Why they buy (lifestyle, values, interests).
3️⃣ Geographic segmentation – Where they are (country, city, climate).
4️⃣ Behavioral segmentation – How they act (shopping habits, brand loyalty, usage patterns).
Businesses often combine these methods to better target their audience and maximize results.
3. What are the advantages of market segmentation?
Market segmentation helps businesses in three big ways:
✔ More effective marketing – Instead of generic ads, you can send the right message to the right people.
✔ Better customer experience – Customers feel understood when you tailor products and marketing to their needs.
✔ Increased customer loyalty – When people relate to a brand, they stick around longer and buy more.
In short, market segmentation helps businesses grow by making marketing more personal and relevant. 🚀

