Yu might have seen a tech gadget cost a fortune when it first hits the market, only to become more affordable a few months later. That’s no accident. Companies aren’t just raising prices for the sake of it—they’re using a deliberate pricing strategy designed to extract maximum value from early adopters. This approach, known as the skimming pricing strategy, is the business world’s equivalent of “taking the cream off the top.”
Brands use skimming to attract high-paying customers at first, then progressively make the product more accessible to a wider, more price-sensitive audience.
In this blog, we’ll dive deep into how this strategy works, why companies like Apple have mastered it, and how you can leverage it to maximize profits for your business. Whether you’re an entrepreneur or an experienced marketer, understanding the art and science behind skimming pricing can make all the difference in launching a successful product.
Table of Contents
What is Skimming Pricing Strategy?
The skimming pricing strategy is a pricing technique where businesses initially set a high price for a product or service when it’s first introduced to the market. Over time, the price is gradually reduced as demand from early adopters diminishes, allowing the company to capture additional segments of more price-sensitive consumers.
The term “skimming” refers to “skimming the cream off the top,” or in this case, extracting the maximum revenue from the most willing customers. This is usually applied to products that are innovative, have a perceived high value, or are in industries with little competition at launch.
The Benefits of a Skimming Pricing Strategy
- Maximizing Early Profits
By targeting the highest-paying customers first, businesses can quickly recoup their initial development or marketing costs. This is particularly beneficial for industries that require heavy investment in research and development, such as technology or pharmaceuticals. - Brand Perception and Exclusivity
A higher price tag at launch can create a sense of exclusivity and prestige. Many consumers associate higher prices with higher quality, which can help to enhance a brand’s image. - Early Adoption by Enthusiasts
Early adopters, often referred to as “tech enthusiasts” or “first movers,” are usually less price-sensitive. They are willing to pay a premium for the latest technology or innovation, allowing businesses to maximize profit margins in the early phases of a product launch. - Allows for Future Price Flexibility
As demand from early adopters tapers off, the business can lower the price to appeal to more budget-conscious consumers. This gradual reduction makes it easier to adjust pricing without significant backlash or devaluing the product too quickly.
How Does the Skimming Pricing Strategy Work?
The skimming pricing strategy works in phases:
- Launch Phase: The product is introduced at a high price. During this phase, the goal is to capture the segment of the market that values innovation, uniqueness, or quality over cost. This group is willing to pay more for early access or exclusivity.
- Growth Phase: As competitors begin to enter the market, the initial demand from high-paying customers slows down. To keep momentum, companies lower the price slightly to attract a wider consumer base that might have been priced out at launch.
- Maturity Phase: By the time a product reaches this stage, it is no longer new or exclusive. The price is lowered further to compete with other similar products, allowing the business to capture the largest possible audience and extend the product’s lifecycle.
Key Factors to Consider Before Using a Skimming Pricing Strategy
Not every product is suited for a skimming pricing strategy. Here are the critical factors to evaluate:
- Product Innovation
A skimming pricing strategy is best suited for products that are innovative, unique, or have some form of technological advancement. The uniqueness of the product justifies the initial high price. - Market Demand and Consumer Segmentation
Companies should assess whether there is a segment of the market willing to pay a premium for the product. If the market is price-sensitive or there’s strong competition, skimming may not be the most effective strategy. - Initial Market Competition
Skimming works best when there is limited competition at the time of product launch. If competitors are offering similar products at lower prices, it becomes challenging to maintain a high price. - Cost Recovery
Products that involve substantial development or marketing costs, such as new technology or pharmaceuticals, benefit from skimming as it allows for faster cost recovery during the early stages of product release. - Price Elasticity
Businesses need to assess the price elasticity of their product—how sensitive the demand is to changes in price. Skimming is more effective when the product’s demand isn’t highly price-sensitive initially, allowing for higher initial pricing.

Skimming Pricing Strategy vs. Penetration Pricing
When selecting a pricing strategy, it’s essential to understand the key differences between skimming pricing strategy and penetration pricing strategy.
- Skimming Pricing: High prices are set initially, then lowered over time.
- Penetration Pricing: Low prices are set initially to quickly gain market share, with prices gradually increasing.
While skimming focuses on maximizing short-term profits from early adopters, penetration aims to build long-term customer loyalty and market dominance by undercutting competitors. Both strategies have their place depending on the nature of the product and the competitive landscape.
Also Read: 10 Creative Product Launch Ideas
Advantages of Skimming Pricing Strategy
- Faster Return on Investment (ROI)
The high initial price tag means that companies can start recouping their investment faster, particularly useful for products that require significant R&D or marketing budgets. - Higher Profit Margins in Early Phases
The willingness of early adopters to pay more enables businesses to enjoy high profit margins at the start of the product lifecycle. - Prestige Pricing
Setting a higher price can often lead to perceptions of exclusivity and superior quality, adding a prestige factor to the product, which in turn can drive demand among certain consumer segments. - Market Flexibility
Once the early phase is over, the company has room to lower the price to remain competitive, adapting the product to different market segments over time.
Disadvantages of Skimming Pricing Strategy
- Limited Market Reach Initially
The high price point may limit the product’s market reach, alienating price-sensitive customers who might wait for a price drop before purchasing. - Encouraging Competitors
The high profitability in the early stages can attract competitors, who may develop similar products and offer them at lower prices. - Risk of Price Drop Perception
If prices are lowered too quickly or frequently, consumers might perceive the product as losing value. This can erode brand loyalty and consumer trust. - Potential for Backlash
Early adopters who paid the initial high price may feel alienated or upset when they see the price drop, particularly if it happens too soon after launch.
Real-Life Example of Skimming Pricing Strategy
Apple iPhones
Apple is a master of the skimming pricing strategy. When a new iPhone is released, it is priced high, targeting enthusiasts and early adopters willing to pay a premium. As newer models are introduced, prices of older models drop, making them more accessible to a broader market.
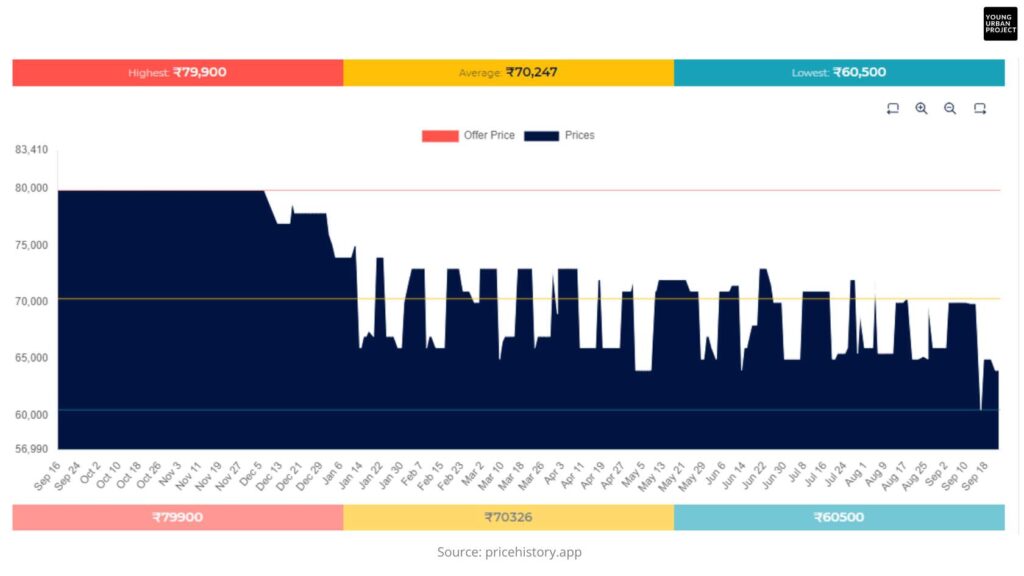
For example, this is the price history of Apple’s iPhone 15. Look how the price keeps reducing over time and ultimately reaches its lowest after the launch of new Apple iPhone 15.
When to Avoid the Skimming Pricing Strategy
While the skimming pricing strategy can be highly effective, there are situations where it may not be the best choice:
- Highly Competitive Markets: In industries with heavy competition, especially if competitors are offering similar products at lower prices, skimming may push customers toward alternatives.
- Price-Sensitive Markets: If the target market is primarily composed of price-sensitive consumers, skimming may reduce the product’s appeal, leading to lower initial sales.
- Short Product Lifecycle: For products with a short lifecycle, such as fashion items or seasonal goods, skimming may not be effective. The product may become obsolete or lose relevance before the business can lower the price and attract broader segments.
How to Implement a Skimming Pricing Strategy
- Market Research
Conduct extensive market research to identify early adopters and their willingness to pay a premium. Understanding consumer segments is essential to successfully implement the strategy. - Define Clear Pricing Stages
Establish a pricing plan with different stages, each targeting a specific market segment. Start with a high price and outline the conditions that will trigger price reductions (e.g., competitor pricing, sales slowdowns). - Create Product Value
Emphasize the product’s exclusivity and benefits to justify the high initial price. Strong branding and marketing are critical in convincing consumers that the product is worth the premium. - Monitor Competitor Activity
Keep a close eye on competitors to ensure your product maintains its competitive edge. Adjust your pricing strategy if competitors start offering similar products at lower prices.
Conclusion
The skimming pricing strategy is a powerful tool for businesses looking to maximize early profits and capture high-paying customers. It works best for innovative products in markets with limited competition, where early adopters are willing to pay a premium for new technology or exclusivity.
However, it’s important to use this strategy carefully, as it can limit initial market reach and attract competition. Understanding your market, competition, and consumer segments will help you determine if skimming is the right approach for your product. If executed well, it can lead to substantial early revenue gains, a stronger brand image, and a smooth transition to broader market segments.
FAQs: Skimming Pricing Strategy
What are the risks of a skimming pricing strategy?
While the skimming pricing strategy offers high initial profits, it comes with risks such as alienating price-sensitive customers, attracting competition, and facing backlash from early adopters when prices drop. Additionally, if the product doesn’t justify the high price in terms of perceived value, it can result in low initial sales.
Can small businesses use a skimming pricing strategy?
Yes, small businesses can use skimming, particularly if they are launching an innovative product or service with little competition. However, they must carefully plan their price reductions and ensure that their product justifies the high initial price to avoid customer dissatisfaction.
How does skimming pricing affect brand perception?
A skimming pricing strategy can enhance brand perception by positioning the product as premium or exclusive. However, if the price drops too quickly or if the product doesn’t live up to expectations, it can harm the brand’s reputation.
How long should a business maintain a high price before lowering it?
The duration of the high price phase depends on factors like market demand, competition, and product lifecycle. Typically, businesses maintain the high price until the initial demand from early adopters is satisfied, after which they gradually reduce the price to attract a broader audience.
What industries are best suited for a skimming pricing strategy?
Industries like technology, pharmaceuticals, and luxury goods often use skimming pricing. These sectors tend to have products with high research and development costs, limited initial competition, and consumers who are willing to pay a premium for early access or exclusive products.

