What’s the secret behind products that become household names? Some companies launch their products with unmatched precision, instantly capturing their target audience’s hearts. How do they do it? Their secret is an efficient product marketing framework that guides every step of their strategy.
Table of Contents
This blog will give you an in-depth understanding of the product marketing framework. You’ll understand what it is, why it’s a game-changer, and how to use it effectively. Along the way, we’ll explore actionable steps and insider tips to help you craft a framework that drives your marketing efforts and maximizes impact.
What Exactly Is Product Marketing?
Before we unpack the framework, let’s clarify product marketing. It’s the strategic process of bringing a product or service to market, positioning it effectively, and driving demand. Unlike general marketing, which focuses broadly on brand awareness, product marketing zeros in on connecting the product to its target audience.
A product marketer serves as the bridge between the product development team and the marketing team, ensuring everything from market research to the product launch is aligned with the needs of the target market.
Key responsibilities of product marketing include:
- Defining the target audience
- Crafting the message and value proposition
- Creating strategies for a successful product launch
- Enabling sales teams with tools and insights
- Monitoring performance post-launch
Now, let’s move on to what you came here for: the product marketing framework.
What Is a Product Marketing Framework?
A product marketing framework is a structured blueprint that outlines the steps, product marketing strategies, and processes required to bring a product or service to market successfully. It makes sure that every phase of your marketing efforts is data-driven, intentional, and geared toward achieving measurable outcomes.
Think of it as a roadmap that guides your marketing team through the complexities of product positioning, messaging, promotion, and beyond. A strong framework doesn’t just align internal teams—it also ensures that your marketing campaign resonates deeply with the target market.

Why is a Product Marketing Framework Important?
A well-structured product marketing framework is the backbone of any successful marketing campaign. It doesn’t just bring order to chaos; it transforms your marketing efforts into a cohesive, results-driven strategy. Without a clear framework, even the most promising product or service can get lost in the noise of a competitive marketplace. Let’s explore why this framework is a non-negotiable asset for businesses:
1. Alignment Across Teams
A well-defined framework ensures that all teams—product development, sales, marketing, and customer success—are on the same page. Misalignment leads to fragmented efforts, wasted resources, and missed opportunities.
Example: Imagine a scenario where the marketing team promotes a feature that hasn’t been fully developed by the product team. This misstep confuses potential customers and erodes trust. With a solid product marketing framework, such disconnects are avoided as all teams operate with a shared understanding of goals, timelines, and deliverables.
2. Data-Driven Decision Making
One of the biggest advantages of a product marketing framework is its reliance on data at every stage. From market research to performance measurement, a structured approach ensures that decisions are based on insights rather than assumptions.
Example: Before launching their new iPhone models, Apple conducts meticulous market research to understand consumer preferences, identify gaps in competitors’ offerings, and predict demand. This data-driven approach allows them to refine their product positioning and tailor their messaging effectively.
3. Optimized Use of Resources
Without a framework, marketing teams often find themselves reinventing the wheel for every campaign. This leads to inefficiencies and drains both time and money. A structured product marketing framework provides a reusable playbook that streamlines workflows and maximizes resource utilization.
Example: Companies like HubSpot have pre-defined frameworks that guide their marketing and product launch processes. This consistency enables them to execute campaigns faster and with greater impact.
4. Clear and Consistent Messaging
One of the cornerstones of a strong framework is well-defined positioning and messaging. It ensures that your brand speaks with a unified voice across all touchpoints, whether it’s a website, social media post, or sales pitch.
Example: Coca-Cola has mastered consistent messaging with its timeless themes of happiness and togetherness. Their marketing strategies ensure that every campaign reinforces their core message, creating a deep emotional connection with their audience.
5. Improved Go-to-Market Efficiency
Launching a product without a clear go-to-market strategy is like setting sail without a compass. A product marketing framework ensures that every aspect of the launch—from pricing and promotion to distribution—is meticulously planned and executed.
Example: When Zoom launched its video conferencing tool, their framework included a free trial strategy, targeted content for different audience segments, and partnerships with key influencers. This systematic approach allowed them to penetrate the market quickly and gain significant traction.
6. Enhanced Customer Experience
A great framework doesn’t just focus on acquiring customers; it prioritizes their entire journey. From the first touchpoint to post-purchase support, it ensures that every interaction adds value and strengthens loyalty.
Example: Amazon’s customer-centric approach is built on a well-oiled framework that ensures seamless browsing, personalized recommendations, efficient order fulfillment, and responsive customer support. This holistic experience keeps customers coming back.
7. Measurable Results
A structured product marketing framework sets clear goals and defines key performance indicators (KPIs) for every stage of the process. This not only allows you to track progress but also provides insights to refine future marketing strategies.
Example: Nike uses its framework to measure the impact of campaigns like “Just Do It.” Metrics such as website traffic, engagement rates, and sales data help them determine ROI and optimize future campaigns.
8. Competitive Advantage
In today’s crowded marketplace, having a structured approach can be a game-changer. It enables you to move faster, pivot effectively, and outmaneuver competitors who lack a cohesive plan.
Example: Netflix’s marketing team uses its framework to stay ahead in the streaming wars. Their data-driven approach helps them identify trending genres, tailor promotions, and retain subscribers better than competitors.
Also read: 20 Product Marketing Books
The Stages of Product Marketing Framework
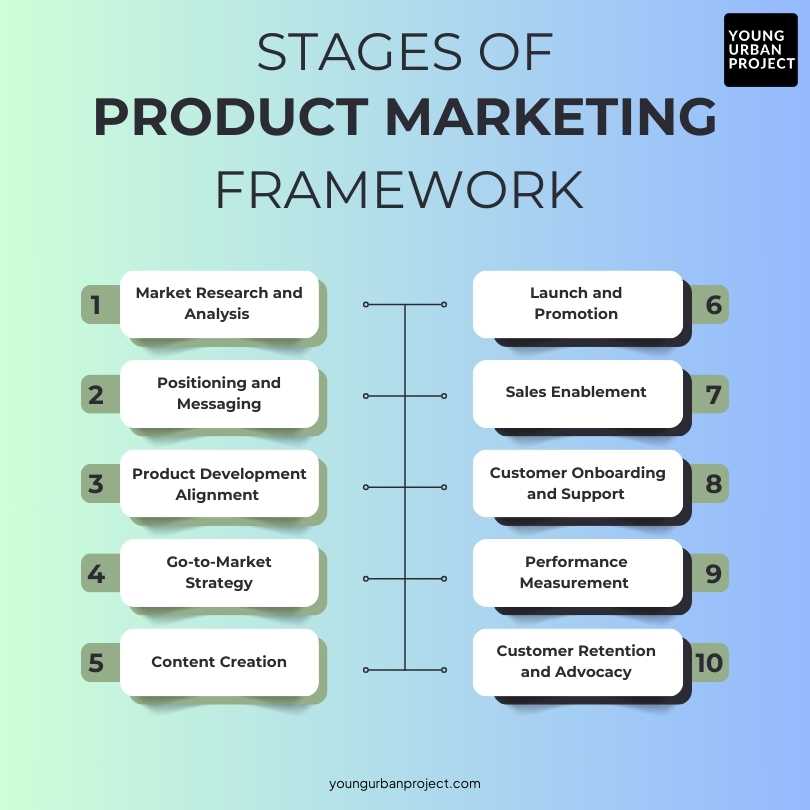
A well-defined product marketing framework is a step-by-step guide that ensures your marketing efforts are intentional, cohesive, and effective. These stages are the backbone of bringing any product or service to market successfully, helping you align with your target market, optimize messaging, and achieve your business objectives. Let’s explore each stage in detail with actionable insights and examples to bring the process to life.
1. Market Research and Analysis
Everything starts with understanding your audience and the market landscape. This stage lays the foundation for your entire marketing plan and involves gathering key insights into:
- Customer Needs and Pain Points
Identify what challenges your target audience faces and how your product can solve them.
Example: When Slack entered the market, they focused heavily on the pain point of team communication inefficiencies and positioned their product as a simple, centralized solution. - Competitor Strengths and Weaknesses
Analyze competitors to uncover gaps in their offerings or weaknesses in their messaging. This helps you refine your product positioning.
Example: Spotify leveraged market research to understand what made Apple Music strong (integration with devices) and weak (lack of personalization). Spotify then built a framework emphasizing user-curated playlists and discovery algorithms. - Market Opportunities
Use research to spot untapped opportunities or trends you can capitalize on.
A robust research phase ensures your marketing campaign connects with the right audience and resonates with their needs.
2. Positioning and Messaging
Positioning answers the “why” behind your product, while messaging communicates that “why” effectively to your audience. This stage is about:
- Crafting a Unique Value Proposition (UVP)
Highlight what makes your product different and why it’s the best solution for your audience.
Example: Tesla’s positioning isn’t just about electric cars; it’s about innovation, sustainability, and luxury, all in one package. - Tailoring Messaging for Your Target Market
Your message should speak directly to your audience’s needs and aspirations.
An effective product positioning strategy ensures that when people encounter your product, they immediately understand its relevance and value.
3. Product Development Alignment
Marketing and product development should work hand in hand to create a product that truly meets customer needs. This stage involves:
- Collaborating with the Product Development Team
Provide insights from market research to guide feature development.
Example: Airbnb’s marketing team noticed a growing demand for unique stays, prompting the product team to introduce categories like treehouses and tiny homes. - Highlighting Benefits Over Features
Focus on how features translate into benefits for the user.
This alignment strengthens your framework and ensures your product or service delivers what customers expect.
4. Go-to-Market Strategy
Your go-to-market strategy defines how you’ll introduce your product to your target audience. Key elements include:
- Choosing the Right Channels
Decide whether to focus on social media, email marketing, paid ads, or offline events based on your audience’s preferences. - Defining Tactics for Engagement
Create campaigns that build anticipation and drive early interest.
A solid go-to-market strategy ensures a smooth and impactful product launch.
5. Content Creation
Content is the bridge between your message and your audience. It educates, engages, and converts potential customers.
- Developing a Content Plan
Include diverse formats like blogs, videos, infographics, and case studies to reach different audience segments. - Aligning Content with Your Positioning
Every piece of content should reflect your product positioning and unique value.
Example: HubSpot uses blogs, eBooks, and templates to attract marketers and demonstrate the value of its CRM tools.
Engaging content is a cornerstone of effective marketing strategies and ensures your product is seen as the ideal solution.
6. Launch and Promotion
The product launch is the culmination of all your planning and preparation. To make it successful:
- Coordinate Efforts Across Teams
Align marketing, sales, and customer support to ensure a cohesive launch experience. - Target Promotions to Specific Audiences
Use segmented campaigns to address different needs within your target market.
Example: Apple’s iPhone launches focus on aspirational marketing, leveraging both hype and exclusivity.
A well-orchestrated launch sets the tone for your product’s journey in the market.
Also read: 10 Creative Product Launch Ideas
7. Sales Enablement
Your sales team needs the right tools and information to close deals effectively. This stage focuses on:
- Creating Sales Materials
Develop customer personas, objection-handling guides, and demo scripts. - Training the Sales Team
Ensure they understand the product inside and out, along with its positioning.
By equipping your sales team, you bridge the gap between marketing and sales, increasing the chances of conversion.
8. Customer Onboarding and Support
After the sale, your focus should shift to ensuring a seamless customer experience.
- Designing an Intuitive Onboarding Process
Provide step-by-step guides, tutorials, and resources to help users get started.
Example: Zoom’s onboarding emails and guides help users quickly understand the platform, leading to higher retention. - Offering Exceptional Support
Resolve customer queries promptly and effectively to build trust and satisfaction.
Satisfied customers are more likely to become advocates for your product or service.
9. Performance Measurement
No product marketing framework is complete without tracking its success. Measure:
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): How much you spend to gain a new customer.
- Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who stop using your product.
- ROI: The return on your marketing investments.
Analyzing these metrics provides insights to refine your marketing efforts and improve future campaigns.
10. Customer Retention and Advocacy
Your job doesn’t end with the first sale; long-term success depends on keeping customers happy.
- Engage Through Loyalty Programs
Reward repeat customers with discounts, perks, or exclusive access.
Example: Starbucks’ rewards program encourages repeat visits by offering points redeemable for free drinks. - Foster Advocacy
Encourage satisfied customers to spread the word through reviews, referrals, and testimonials.
Happy customers are your best marketers, reducing acquisition costs and boosting your brand’s credibility.
Choosing the right marketing framework
Selecting the right marketing framework is like tailoring a suit—it has to fit the specific needs of your product or service, audience, and team to deliver optimal results. A poorly chosen framework can lead to inefficiencies, misaligned efforts, and missed opportunities, while the right one can supercharge your product marketing efforts and give your business a competitive edge. Here’s a deeper dive into the factors you should consider when making this critical decision:
1. Complexity of Your Product or Service
The complexity of what you’re marketing plays a significant role in determining the structure and depth of your framework.
- Simple Products
If you’re marketing a straightforward product, such as a fitness app or a reusable water bottle, your marketing efforts might center around building awareness, creating an emotional connection, and showcasing benefits. In this case, a streamlined framework focusing on content creation, social proof, and promotional campaigns could suffice.
Example: Take the case of a brand like Hydro Flask. Their framework likely revolves around emphasizing product design, sustainability, and everyday use through vibrant messaging and social media campaigns. - Complex Solutions
On the other hand, if you’re marketing a complex B2B SaaS product, your framework will need to incorporate stages like detailed market research, in-depth product positioning, long-term lead nurturing, and sales enablement. The aim is to break down the intricacies of the product or service and demonstrate its value to decision-makers.
2. Target Audience Needs
Your target audience should be at the center of your framework. A deep understanding of their preferences, challenges, and behaviors will help you choose a framework that resonates with them.
- Consumer Products
For mass-market products, your framework may need to focus on emotional storytelling, social proof, and visually engaging content. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok could play a pivotal role in reaching this audience.
Example: Dove’s Real Beauty campaign is built on a framework that focuses on emotional connections, addressing body image issues, and creating community engagement through storytelling and user-generated content. - Niche Markets or High-Involvement Products
If you’re targeting niche or high-involvement markets, such as healthcare professionals or enterprise IT managers, your marketing campaign should be highly educational and insight-driven. Your framework should prioritize webinars, in-depth guides, and expert consultations.
3. Marketing Team Size
The size of your marketing team can directly influence the type of framework you adopt.
- Smaller Teams
If your team is small, efficiency and simplicity are key. A lightweight framework that focuses on essential stages—like market research, basic content creation, and a lean go-to-market strategy—can help you achieve results without overloading your team.
Example: Startups like Canva initially used a minimal framework that focused on clear messaging, free trials, and user-generated testimonials to grow their user base. - Larger Teams
Larger teams can afford to adopt more detailed frameworks with multiple layers of collaboration. They can dedicate resources to advanced analytics, product positioning, and creating diverse campaigns targeting multiple customer segments.
4. Industry Dynamics
Different industries demand different approaches. Factors like competitive intensity, market maturity, and regulatory requirements can shape your choice of framework.
- Highly Regulated Industries
For industries like healthcare or finance, where compliance is crucial, your framework should integrate clear approval workflows, ensuring that all messaging adheres to regulations.
Example: Pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer follow detailed frameworks that include medical research validation, patient education, and strict compliance checks before any campaign goes live. - Fast-Paced Industries
In fast-moving industries like fashion or tech, you’ll need an agile framework that allows for quick pivots and rapid execution to capitalize on trends.
5. Business Objectives
Your ultimate goals should guide your framework selection. Are you trying to build brand awareness, generate leads, or increase customer retention?
- For Awareness: Choose a framework that emphasizes content creation, social media, and influencer marketing to reach a broad audience.
- For Lead Generation: Focus on frameworks that include targeted advertising, lead magnets, and nurturing sequences.
- For Retention and Advocacy: Incorporate frameworks that prioritize customer satisfaction, loyalty programs, and community-building initiatives.
6. Budget Constraints
Finally, consider the resources you have available. A smaller budget might require you to prioritize a framework with fewer stages or rely heavily on organic methods, while a larger budget opens up possibilities for advanced tools and multi-channel campaigns.
Conclusion
A winning product marketing framework is more than just a guide—it’s the foundation of successful marketing efforts. By following the steps above, you’ll create a framework that not only enhances your product launch but also drives long-term growth and customer satisfaction.
Remember: product marketing isn’t a sprint; it’s a marathon. With a strong framework, your marketing team will stay focused, your message will resonate, and your product or service will find its rightful place in the market.
So, whether you’re launching your first product or refining your approach, a solid product marketing framework is your key to success.

