Performance marketing is a dynamic digital marketing approach that focuses on measurable outcomes, where advertisers pay for specific results rather than generic ad placements. This method ensures that marketing efforts are directly tied to business objectives, maximizing return on investment (ROI). In this blog, we’ll walk you through the steps in creating and executing an effective performance marketing strategy, from defining goals to optimizing campaigns.
What is Performance Marketing?
Performance marketing is a digital strategy where advertisers pay only for specific actions, such as clicks, leads, or sales. This results-driven approach ensures that marketing budgets are spent efficiently, with a clear focus on achieving tangible outcomes. Unlike traditional advertising, which often involves paying upfront for exposure, performance marketing ties costs directly to the campaign’s success.
If you are looking to understand how Performance Marketing works, this is going to be massively valuable for you.
At Young Urban Project, we place Performance Marketing at the center of Paid Advertising, Data Analytics, and Experimentation. We leverage it for customer acquisition and retention and we are big fans of this skill.
Also Read: Biggest Performance Marketing Challenges
How Performance Marketing Works
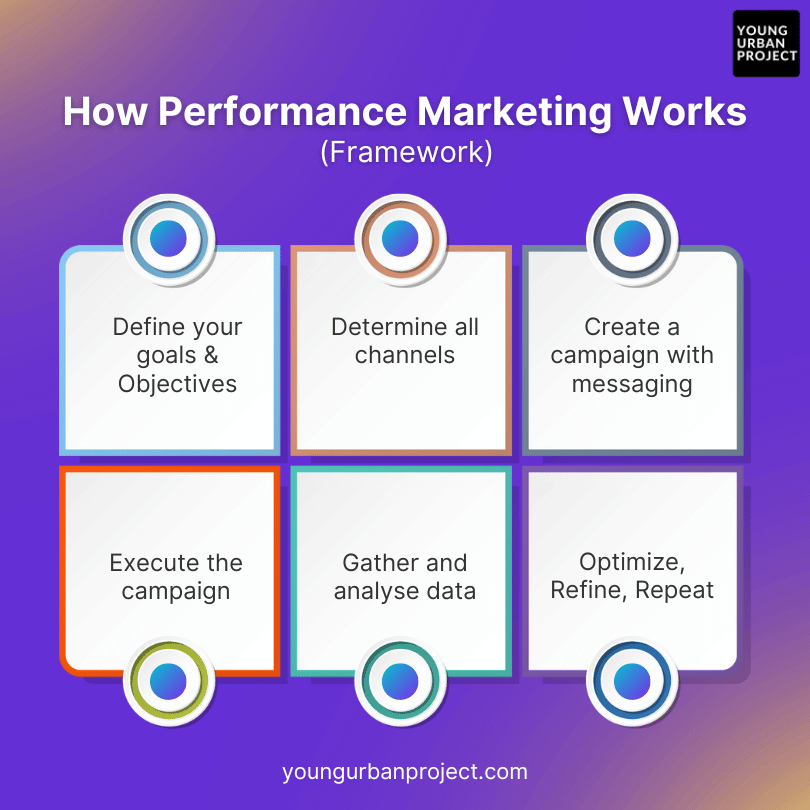
Define Your Goals and Objectives
The first step in any performance marketing strategy is to define clear goals and objectives. These should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Your goals will guide every subsequent decision, from choosing channels to creating campaigns.
Importance of Goal Setting
Setting goals provides a clear direction and focus. Without defined objectives, marketing efforts can become scattered and inefficient. Goals help in prioritizing tasks, allocating resources, and measuring success. Moreover, having clear objectives ensures that all team members are aligned and working towards the same outcomes.
Example:
A fitness app aiming to increase its user base might set a goal of acquiring 10,000 new users in three months. This goal is specific (new users), measurable (10,000), achievable (given proper resources), relevant (growth-oriented), and time-bound (three months).
Determine Your Channels
Choosing the right channels is crucial to reaching your target audience effectively. The choice of channels will depend on your goals, target audience, and budget. Common channels for performance marketing include:
- Search Engine Marketing (SEM): Platforms like Google Ads allow you to target users based on search queries. SEM is highly effective for capturing intent-driven traffic, where users are actively searching for solutions.
- Social Media Advertising: Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and other platforms offer targeted advertising options. Social media ads are excellent for audience segmentation based on interests, behaviors, and demographics.
- Affiliate Marketing: Collaborating with partners who promote your products for a commission on sales. Affiliates can expand your reach and tap into new customer bases.
- Email Marketing: Targeted email campaigns to drive conversions. Personalized email marketing can nurture leads and build long-term customer relationships.
- Display Advertising: Banner ads on relevant websites to reach a wider audience. Display ads can boost brand awareness and retarget potential customers.
Read more: Difference Between ROAS and Blended ROAS
Example:
A B2B software company might focus on LinkedIn and Google Ads to target professionals actively searching for solutions in their industry. LinkedIn offers precise targeting based on job titles, industries, and company sizes, making it ideal for B2B marketing.
Create a Campaign with Messaging

Once you’ve chosen your channels, the next step is to create compelling campaigns with clear messaging. Your campaigns should resonate with your target audience and communicate the value of your product or service. Effective campaigns often include:
- Ad Copy: Craft concise, engaging, and action-oriented copy. The copy should highlight key benefits and include a strong call to action (CTA).
- Visuals: Use high-quality images or videos that capture attention. Visual content should be relevant, professional, and aligned with your brand.
- Landing Pages: Ensure your landing pages are optimized for conversions, with clear calls-to-action (CTAs). A seamless user experience on landing pages can significantly impact conversion rates.
Example:
An online course provider could create a Facebook ad campaign highlighting a limited-time discount, paired with a landing page that includes testimonials and a simple sign-up form. The ad copy might say, “Limited Time Offer! Enroll in Our Digital Marketing Course and Save 30%. Learn from Industry Experts. Sign Up Now!” The landing page would feature student testimonials, course highlights, and a straightforward enrollment form.
Read More: What is Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) & How to calculate it
Execute Your Campaign
With your campaign assets ready, it’s time to execute. This involves setting up your campaigns on the chosen platforms, configuring targeting options, and launching your ads. Key considerations during execution include:
- Budget Allocation: Distribute your budget based on expected performance and channel potential. Allocate more budget to high-performing channels.
- Targeting: Use demographics, interests, and behaviors to reach your ideal audience. Refine targeting criteria to ensure relevance.
- Bidding Strategies: Choose appropriate bidding strategies (e.g., cost-per-click, cost-per-impression) to maximize ROI. Experiment with different bidding options to find the most cost-effective approach.
Example:
A fashion e-commerce store could allocate a larger portion of its budget to Instagram ads, targeting users based on interests in fashion and recent purchase behaviors. The campaign might include a mix of photo ads, video ads, and carousel ads to showcase different products.
Gather and Analyze Data
Data collection and analysis are critical components of performance marketing. Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, cost-per-acquisition (CPA), and return on ad spend (ROAS). Use analytics tools for Performance marketing provided by ad platforms and third-party software to gather insights.
Read more: Difference Between ROAS and Blended ROAS
Importance of Data Analysis
Analyzing data helps in understanding what’s working and what’s not. It provides insights into customer behavior, campaign performance, and ROI. Data-driven decisions are more likely to succeed because they are based on real-world evidence rather than assumptions.
Example:
A travel agency running a Google Ads campaign could use Google Analytics to track conversions and identify which keywords and ads are driving the most bookings. They might discover that ads targeting affordable vacation packages” have a higher conversion rate than those targeting “luxury travel experiences.
Optimize, Refine, and Repeat
Optimization is an ongoing process in performance marketing. Use the data collected to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments. This might involve tweaking ad copy, adjusting targeting options, reallocating budget, or testing new channels.
Continuous Improvement
The key to successful performance marketing is continuous improvement. By regularly reviewing and refining your campaigns, you can achieve better results over time. Always be on the lookout for new opportunities and stay updated with the latest marketing trends and technologies.
Example:
A subscription box service might notice that their Facebook ads perform better among a certain age group. They could adjust their targeting to focus more on that demographic and create tailored messaging for better engagement.

Checkout: Performance Marketing Bootcamp
Steps for Optimization:
- A/B Testing: Continuously test different ad variations to see which performs best. A/B testing can involve changing headlines, images, CTAs, and more.
- Adjust Bids: Modify bids based on performance data to ensure cost-effectiveness. Lower bids on underperforming keywords and increase bids on high-converting ones.
- Refine Targeting: Narrow or broaden your targeting criteria based on audience behavior. Use remarketing to target users who have previously interacted with your brand.
- Update Creatives: Refresh your ad creatives regularly to avoid ad fatigue. New visuals and copy can re-engage your audience and boost performance.
Example:
A SaaS company might find that their email campaigns have higher open rates on Tuesdays. They could shift their email schedule to maximize engagement and conversions. Additionally, they might experiment with different subject lines and email content to see what resonates most with their audience.
Conclusion
Performance marketing is a powerful strategy that focuses on achieving measurable results. By defining clear goals, choosing the right channels, crafting compelling campaigns, executing effectively, gathering data, and optimizing continuously, you can ensure your marketing efforts deliver tangible outcomes. The key to success lies in a data-driven approach, constant testing, and a willingness to adapt based on insights. With these steps, you can create a performance marketing strategy that drives growth and maximizes ROI.
If you are looking to master performance marketing, then Young Urban Project offers the best, and practical performance marketing program in market. This comprehensive program covers all aspects of performance marketing, from strategy to execution, equipping you with the skills and knowledge to excel in this dynamic field. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced marketer, Young Urban Project’s course provides practical insights and real-world examples to help you achieve your marketing goals.

