Why did Blockbuster fail while Netflix thrived? It wasn’t just about DVDs turning into streams. It was about business research(or a lack of it). Netflix saw a shift in how people consumed entertainment. They gathered data, analyzed behavior, and used business research methods to forecast trends. Blockbuster? They stuck to what they thought worked.
Table of Contents
In business, gut feelings can only get you so far. To make informed decisions, businesses need to ask questions, collect data, and analyze insights using both qualitative research and quantitative methods. That’s where business research steps in.
Let’s understand what business research is, explore its methods, and see why it’s the secret weapon for companies aiming to succeed in competitive markets.
What is Business Research?
Business research is the systematic process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting data to solve business problems. It involves exploring market research, assessing customer satisfaction, or testing a product or service.
Whether it’s understanding your target audience, testing a new ad campaign, or improving customer experiences, business research helps companies make informed decisions based on facts, not assumptions.
In other words, business research provides the “what,” “why,” and “how” behind every business challenge.
Also read: What is Business Research?
Methods and Types of Business Research
Business research can be broadly categorized into two main approaches: quantitative research methods and qualitative research methods. Each method serves a distinct purpose and is chosen based on the types of business research in question, the type of data needed, and the overall objectives of the study. To fully understand the scope of business research and the utility of these methods, let’s explore them in detail, along with real-world examples.
1. Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research focuses on gathering numerical data that can be statistically analyzed. It helps businesses identify patterns, measure variables, and test hypotheses to draw objective conclusions. Quantitative research is ideal when you need precise, measurable, and generalizable data.
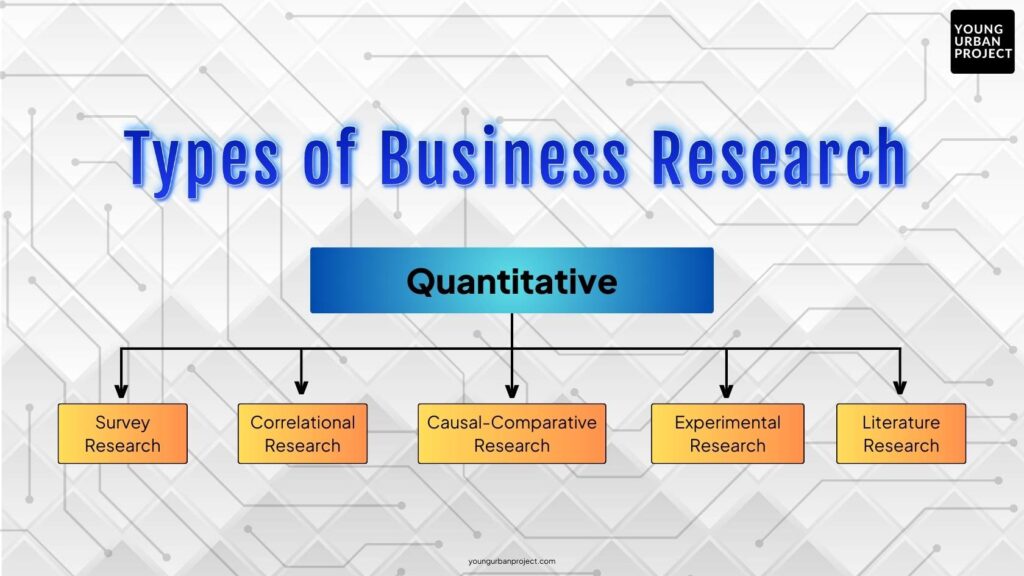
1. Survey Research
Surveys are one of the most commonly used business research methods to collect data from a large population. A survey consists of structured questionnaires with both closed-ended and open-ended questions designed to collect targeted responses.
- Example: A clothing retailer wants to assess customer satisfaction after launching a new collection. They send out an online survey asking customers to rate their satisfaction level, the design, and pricing. The numerical data collected helps the retailer determine which products performed well and which didn’t.
- Tools Used: Google Forms, SurveyMonkey, Typeform.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, scalable, and allows for quick data collection from a broad target audience.
- Disadvantages: Low response rates and potential for superficial answers if surveys are too lengthy or unclear.
2. Correlational Research
Correlational research is used to study the relationship between two or more variables without manipulating them. It answers questions like: “Is there a relationship between X and Y?”
- Example: A fitness app wants to know whether users who engage with notifications are more likely to achieve their fitness goals. By comparing the interaction data (engagement with notifications) and goal completion rates, the business finds a positive correlation. This insight helps them improve app notifications for better outcomes.
- Advantages: Helps identify connections between variables; uses existing data for analysis.
- Disadvantages: Correlation does not equal causation, meaning other factors might influence the relationship.
3. Causal-Comparative Research
Also known as ex post facto research, this method identifies cause-and-effect relationships by comparing two or more groups. Unlike experiments, researchers do not manipulate variables but analyze existing differences.
- Example: A company compares two regional branches—one with a flexible work-from-home policy and the other with traditional office work. The research reveals that employee productivity is higher in the flexible branch. Though causation cannot be fully established, this comparison highlights important patterns.
- Advantages: Helps identify possible causes; works well when experiments are impractical.
- Disadvantages: Cannot control external variables that might influence the outcome.
Also Read: Objectives of Marketing Research
4. Experimental Research
Experimental research involves manipulating one variable (independent variable) to observe its impact on another variable (dependent variable). It’s the most reliable method for establishing causation.
- Example: An e-commerce website conducts A/B testing to evaluate two product page designs. One design includes customer reviews prominently, while the other highlights a discount banner. After tracking conversion rates, the team finds the design featuring reviews performs 25% better.
- Advantages: Provides clear cause-and-effect results; variables can be controlled for precision.
- Disadvantages: Expensive and time-consuming; may not always represent real-world conditions.
5. Online Research / Literature Research
This method involves gathering and analyzing existing information from online sources, academic journals, reports, or case studies. It provides secondary data to inform business decisions or support other research methods.
- Example: A startup entering the electric vehicle (EV) market conducts literature research to analyze government policies, competitor pricing, and consumer adoption rates. Existing industry reports help them identify gaps and market opportunities.
- Advantages: Access to vast resources; cost-effective compared to primary research.
- Disadvantages: Requires critical evaluation of data accuracy and relevance. Outdated or biased information can impact conclusions.
Also Read: Marketing Research Process
2. Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research focuses on understanding people’s perceptions, experiences, and motivations. Unlike quantitative research, it deals with non-numerical data and explores the “why” behind behaviors. This method is especially valuable when exploring new ideas, understanding complex issues, or forming hypotheses for future quantitative studies.
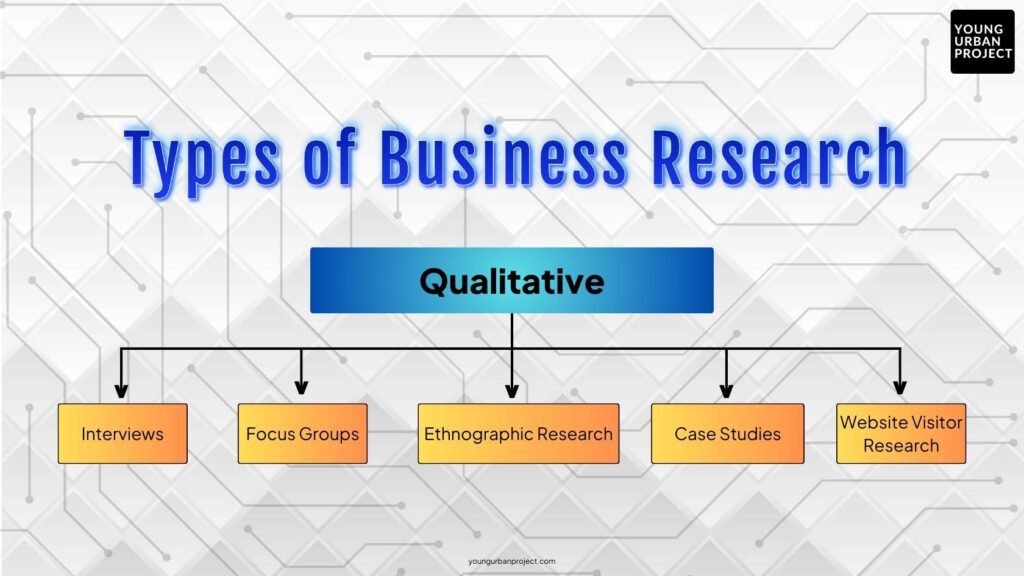
1. Interviews
Interviews involve one-on-one conversations where a researcher asks open-ended questions to gather detailed insights.
- Example: A tech company interviews its top customers to understand why they choose their software over competitors. The feedback helps the company improve messaging and highlight customer-preferred features.
- Advantages: Provides in-depth, personalized information.
- Disadvantages: Time-consuming and can introduce interviewer bias.
2. Focus Groups
A focus group brings together a small group of people (6–10) to discuss a specific topic, product, or idea under the guidance of a moderator.
- Example: A beverage company uses focus groups to test reactions to a new flavor. Participants share their opinions on taste, packaging, and pricing, giving the company rich qualitative insights.
- Advantages: Encourages dynamic discussions and varied perspectives.
- Disadvantages: Dominant participants may influence others; responses may not represent the entire target audience.
3. Ethnographic Research
This method involves observing participants in their natural environment to understand their behaviors and interactions.
- Example: A retail brand observes how shoppers navigate its store layout. Findings show customers often miss new arrivals placed at the back, prompting the store to adjust product placements for better visibility.
- Advantages: Captures real-life, contextual insights.
- Disadvantages: Requires significant time and can be influenced by researcher bias.
4. Case Study Research
Case study research involves an in-depth examination of a specific subject, such as a company, event, or project, to uncover key insights.
- Example: A streaming service conducts a case study on Netflix to analyze its successful strategies for subscriber retention. Findings inform the streaming service’s business strategy.
- Advantages: Provides comprehensive, real-world insights.
- Disadvantages: Findings may not be generalizable to other situations.
5. Website Visitor Profiling/Research
This method involves analyzing website data to understand user demographics, behaviors, and preferences.
- Example: An online retailer uses website analytics to track visitor activity, such as page views, session duration, and purchase patterns. Insights help optimize the user experience and increase conversions.
- Advantages: Provides concrete behavioral data; easily accessible.
- Disadvantages: Limited to online behavior; cannot capture offline influences.
Also Read: Advantages and Disadvantages of Marketing Research
Importance of Business Research
Business research is more than just a tool—it is the backbone of strategic decision-making and business success. In a world driven by data, businesses that fail to conduct thorough research risk falling behind their competitors, missing opportunities, or making costly missteps. Below, we explore why business research is indispensable and how it helps organizations navigate today’s dynamic environment.

1. Informed Decision-Making
One of the primary reasons businesses invest in research is to move away from intuition or gut feelings and make decisions grounded in facts and data. Business research provides quantitative and qualitative insights that empower leaders to evaluate situations objectively and reduce uncertainty. Whether launching a new product, entering a market, or adjusting pricing strategies, businesses need reliable data to determine the most effective course of action.
Without business research, decision-making becomes speculative, which can lead to wasted resources, missed opportunities, and poor performance. With robust research, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their goals, customer expectations, and market realities.
2. Identifying Opportunities
Market dynamics are constantly shifting, and staying ahead requires identifying opportunities before competitors do. Business research helps uncover:
- Untapped markets that hold potential for expansion.
- Emerging customer needs or preferences that businesses can address.
- Gaps in current product offerings that can be filled with innovative solutions.
By systematically analyzing market trends, industry data, and consumer behavior, businesses can discover opportunities they may have overlooked. For example, this is especially critical. Pairing research insights with the right tools—such as a Social Media Management Tool for Startups that enables them to position themselves competitively, identify trends early, and act with precision in dynamic markets.
This ability to proactively spot opportunities leads to better product development, smarter resource allocation, and stronger business growth.
3. Risk Mitigation
Every business decision carries some degree of risk. Whether it’s launching a new product, entering a foreign market, or investing in a marketing campaign, unforeseen challenges can derail progress. Business research acts as a safety net by anticipating risks and providing strategies to manage or avoid them.
For example, conducting thorough market research before entering a new region can reveal cultural differences, regulatory hurdles, or competitive landscapes that pose risks. With this knowledge, businesses can develop contingency plans, adjust strategies, and proceed with confidence.
By identifying potential obstacles early, business research reduces uncertainty, minimizes losses, and ensures resources are invested wisely. This foresight makes businesses more resilient and adaptable in the face of challenges.
4. Competitive Advantage
In highly competitive industries, maintaining an edge over competitors is critical for long-term success. Business research equips organizations with insights into:
- Competitor strategies, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Market trends, such as changes in technology or consumer behavior.
- Industry benchmarks that highlight areas for improvement.
By understanding what competitors are doing and where the market is heading, businesses can craft unique strategies that set them apart. For instance, research may reveal that competitors are falling short in customer service, providing an opportunity for a business to differentiate itself by delivering exceptional support.
Business research also helps companies innovate. By analyzing market gaps, customer pain points, and technological advancements, businesses can introduce unique solutions that give them a competitive advantage.
5. Customer Understanding
Customers are at the heart of every business, and understanding them is essential for delivering value and ensuring long-term success. Business research helps organizations gather insights into:
- Customer preferences and buying behaviors.
- Pain points and challenges that need addressing.
- Satisfaction levels and areas for improvement.
Through survey research, focus groups, and interviews, businesses can learn what customers truly want and need. This understanding enables companies to develop products or services that meet those needs, create targeted marketing campaigns, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Moreover, business research helps businesses track customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are key indicators of success. Happy customers not only make repeat purchases but also become advocates for a brand, driving growth through word-of-mouth recommendations.
By continuously researching and staying attuned to customer needs, businesses can build stronger relationships, increase retention, and adapt to changing preferences over time.

CheckOut: Product Marketing Course
7 Steps of a Business Research Process
The business research process is a systematic approach that guides businesses in solving problems, making informed decisions, and exploring new opportunities. This process is often structured in seven key steps that ensure data is collected, analyzed, and used effectively. Let’s break down each step in the process and explore the specific strategies businesses can use to achieve success at every stage.
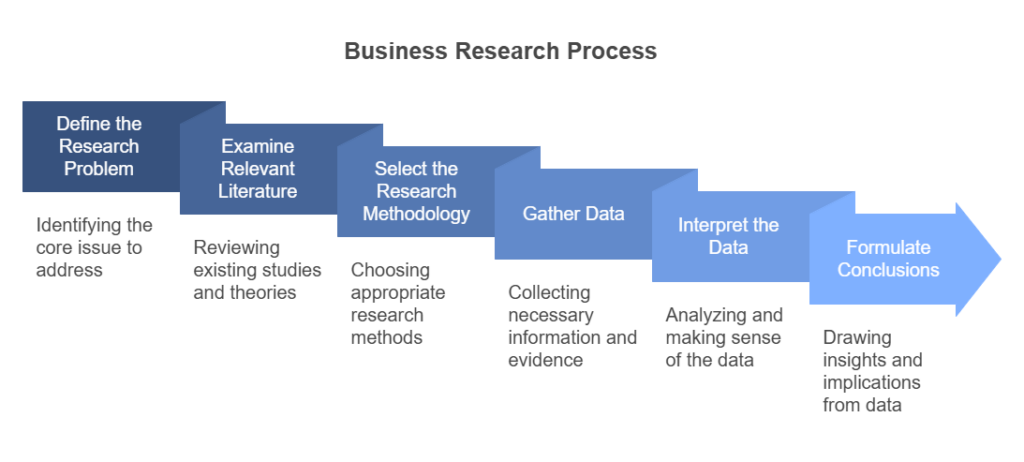
1. Define the Problem
The first and most crucial step in any business research process is identifying the problem or opportunity that needs to be addressed. This involves recognizing a gap or challenge within the business, such as customer dissatisfaction, declining sales, or the need for market expansion. Clear problem identification ensures that the research will be focused and relevant to the needs of the business.
What to do:
- Clarify the Research Objective: Begin by defining what you hope to achieve with the research. Are you solving a specific problem (e.g., low customer retention) or looking for new opportunities (e.g., identifying underserved markets)?
- Set Clear Research Questions: Frame the research around specific questions that need answering. For example, “What factors contribute to our declining sales?” or “What unmet needs do customers have in our target market?”
- Consult Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders such as managers, product teams, and customers to ensure the problem is well-defined and everyone’s perspectives are considered.
- Use a SWOT Analysis: Perform a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats) to fully understand the problem from all angles.
Strategies to use:
- Problem Definition Workshops: Organize brainstorming sessions with relevant stakeholders.
- Customer Feedback: Use surveys or focus groups to directly understand the issues customers face.
- Competitive Analysis: Study competitors to see if they have already solved similar problems or if they present opportunities you can capitalize on.
2. Examine Relevant Literature
Once the problem is clearly defined, it’s essential to review existing literature. This means looking at past research, reports, articles, and case studies that relate to your topic. By reviewing what has already been discovered, businesses can gain valuable insights, identify gaps, and avoid duplicating efforts.
What to do:
- Search Academic and Industry Research: Use resources like academic journals, industry reports, and market analysis to gather background information on your research topic.
- Identify Gaps in Knowledge: Assess the existing research to find areas that haven’t been explored in detail or where your business’s unique circumstances might differ from existing studies.
- Create a Literature Review Summary: Summarize key findings from the existing literature and use them to inform your own research objectives.
Strategies to use:
- Use Online Databases: Platforms like Google Scholar, JSTOR, or industry-specific databases are great for finding relevant literature.
- Review Market Research Reports: Many market research firms publish free executive summaries or offer paid reports with in-depth information.
- Competitive Intelligence: Look at what your competitors have published or what insights their case studies provide.
3. Select the Research Methodology
The research design is the blueprint for how the research will be conducted. It involves deciding which research methods and strategies will be used to collect data and ensure that the findings are reliable and valid. This stage determines whether the research will be qualitative, quantitative, or a combination of both.
What to do:
- Decide on the Research Type: Determine whether your research will be qualitative (focused on understanding opinions, experiences, or motivations) or quantitative (focused on measurable data, statistics, and numerical analysis).
- Select Research Methods: Choose the appropriate research methods, such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, experiments, or case studies.
- Design Sampling Strategy: Identify the target audience and how you will select participants. This can involve random sampling, stratified sampling, or convenience sampling based on the research’s needs.
- Set Variables and Parameters: Define the variables you will examine (e.g., customer satisfaction, employee engagement) and how they will be measured.
Strategies to use:
- Use Mixed Methods: In many cases, combining qualitative and quantitative research methods (mixed-methods design) can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the problem.
- Pilot Testing: Run a small pilot of your chosen research design to iron out any potential issues with the process, such as unclear survey questions or unreliable data collection methods.
4. Gather Data
Data collection is the process of gathering relevant information based on your research design. This can be done through various methods depending on the type of research and the research questions. The quality of data collected directly impacts the quality of the conclusions drawn.
What to do:
- Choose Your Data Collection Tools: Depending on your design, you may need tools such as online survey platforms (e.g., SurveyMonkey, Google Forms), interview scripts, or observation checklists.
- Implement Data Collection Methods: Execute the plan by gathering data through the selected methods, whether it’s distributing surveys, conducting interviews, or observing consumer behavior.
- Ensure Ethical Standards: Always follow ethical guidelines, including gaining consent from participants, ensuring anonymity, and protecting privacy.
- Monitor the Process: Keep track of how data is being collected to ensure consistency and address any issues that arise (e.g., low response rates or biased sample groups).
Strategies to use:
- Online Surveys: Utilize platforms that allow easy data collection and analysis.
- Focus Groups and Interviews: For more in-depth qualitative insights, consider semi-structured interviews or focus group discussions.
- Secondary Data: In some cases, secondary data (existing reports, public databases) can be used to supplement primary data collection.
5. Interpret the Data
Once data is collected, the next step is to analyze it. This step involves processing the raw data, applying statistical or qualitative analysis methods, and interpreting the results. Proper analysis allows businesses to uncover trends, patterns, and insights that will drive decisions.
What to do:
- Organize the Data: Ensure that the data is structured in a format that allows easy analysis (e.g., spreadsheets for quantitative data or coding for qualitative responses).
- Select Analysis Techniques: For quantitative data, use statistical tools like regression analysis, correlation analysis, or chi-square tests. For qualitative data, employ thematic analysis or content analysis to identify key themes and insights.
- Validate Findings: Cross-check the data with any existing literature or benchmarks to ensure that the analysis is accurate and valid.
- Interpret the Results: Look for patterns, correlations, or trends that answer your original research questions.
Strategies to use:
- Use Analytical Tools: Data analysis tools can help in precise analysis in a shorter period of time. Software like Excel, Microsoft Power BI, and Tablaeu can help.
- Statistical Significance Testing: Ensure that the results are statistically significant before drawing conclusions.
- Data Visualization: Use charts, graphs, and infographics to present findings in an easily digestible format.
Also read: Best Data Analytics Books to Level Up Your Skills in 2025
6. Formulate Conclusions
Drawing conclusions involves interpreting the data’s implications for the business. At this stage, the researcher synthesizes the findings and translates them into actionable insights. It’s important to link the conclusions back to the original problem and research questions.
What to do:
- Summarize Key Findings: Highlight the most significant findings that directly answer the research questions.
- Make Connections: Relate the conclusions back to the business problem, objectives, and existing literature.
- Assess Limitations: Identify any limitations in the research (e.g., sample size, potential biases) and how they may affect the conclusions.
- Recommend Actions: Provide practical recommendations based on the research findings, guiding decision-makers on the next steps.
Strategies to use:
- Use Clear and Concise Language: Ensure that conclusions are easy to understand and focused on actionable outcomes.
- Link to Business Objectives: Make sure that the conclusions are tied to the overall business goals and strategies.
7. Present the Findings
The final step of the business research process is reporting the results. This step involves presenting the findings in a structured format, such as a research report or presentation, to stakeholders. Clear communication ensures that the research has a lasting impact and drives informed decision-making.
What to do:
- Prepare a Research Report: Write a detailed report that includes an introduction, methodology, results, and conclusions. Ensure that the report is well-organized and easily understandable.
- Create Visual Presentations: For stakeholders who may prefer quick insights, prepare a summary presentation using visuals like charts, graphs, and tables.
- Present Findings to Stakeholders: Hold meetings or presentations to communicate the results to key decision-makers and relevant teams.
- Follow-Up: After presenting the results, follow up with stakeholders to discuss any questions or implementation of the recommendations.
Strategies to use:
- Executive Summary: Start the report with an executive summary that highlights the key findings and recommendations.
- Clear Structure: Organize the report into clearly defined sections—introduction, methodology, analysis, findings, and conclusion—to enhance readability.
Also read: Limitations of Marketing Research
Real Examples of Business Research
1. Salesforce – Product Testing
Methodology: Product testing is a method to test a product or feature on a sample audience to measure its effectiveness before scaling.
Salesforce uses sandbox testing as a controlled environment for customers to try new features.
How it Works:
- Businesses test new updates (like CRM automation tools) in a risk-free environment.
- Research questions include: Does the feature improve workflow efficiency? Are there gaps or bugs?
- Quantitative and qualitative data are collected to refine features.
Outcome: Salesforce ensures its updates align with customer expectations and don’t disrupt existing workflows.
2. Tata Motors: Creating Demand for Affordable Electric Vehicles (EVs)
How Tata Motors uses research:
Tata Motors conducted in-depth business research to gauge Indian consumers’ readiness for electric vehicles. Through surveys and focus groups, they identified key barriers, such as affordability, charging infrastructure, and range anxiety. By understanding these concerns, Tata designed a cost-effective EV, the Tata Nexon EV, and invested in building charging networks across cities.
Impact:
- Tata Nexon EV became the best-selling electric car in India, addressing consumer pain points around pricing and mileage.
- Tata Motors successfully capitalized on the growing demand for eco-friendly mobility solutions by anticipating market trends.
3. Amul: Understanding Local Preferences for Product Diversification
How Amul uses research:
Amul, one of India’s largest dairy cooperatives, conducts qualitative research and surveys to understand evolving consumer tastes and preferences. By analyzing data on regional demands, they diversified their product line to include Amul Lassi, Buttermilk, and various flavored milk products. Their research also highlighted the growing demand for quick snacks, leading to innovations like Amul ice creams and cheese spreads.
Impact:
- Amul successfully positioned itself as a household name with products adjusted to Indian tastes, achieving record-breaking sales.
- Through consistent research, Amul adapted to changing consumer demands, strengthening its market leadership.
4. Canva used business research
Canva used qualitative business research to understand why non-designers struggled with complex tools like Photoshop. They conducted focus groups and usability testing to identify the demand for a simple, drag-and-drop design platform.

Impact:
- Canva simplified design for individuals and businesses, empowering millions to create graphics, presentations, and videos.
- Continuous research allowed Canva to roll out tools like Canva Pro, brand kits, and AI-powered features, catering to business users.
5. McDonald’s
How McDonald’s uses research:
McDonald’s utilizes business research to adapt its menu and strategies for different regions. Through surveys, focus groups, and competitive analysis, McDonald’s learns about local food habits, preferences, and cultural nuances. This research helps the fast-food giant customize its offerings to resonate with diverse markets.

Impact:
- In India, McDonald’s introduced the McAloo Tikki burger to cater to the vegetarian population, which became a best-seller.
- In Japan, seasonal offerings like the Teriyaki Burger appeal to local tastes, helping the company maintain strong market penetration.
FAQs: Business Research Methods
1. What are the 4 stages of business research?
The four stages of business research are defining the problem or opportunity, designing the research, collecting data, and analyzing and interpreting the data. Each stage helps ensure that the research is focused, data is relevant, and the insights gained lead to actionable decisions.
2. What is the purpose of business research?
The purpose of business research is to gather valuable information that helps businesses make informed decisions. It aids in understanding customer needs, assessing market trends, minimizing risks, identifying opportunities, and improving products and services based on data.
3. When to use business research?
Business research should be used whenever a company needs to gather data to make informed decisions. This includes situations like launching new products, entering new markets, assessing customer satisfaction, optimizing marketing strategies, or exploring new business opportunities.
4. What is the best research method for business?
The best research method for a business depends on the goals of the study. Quantitative methods like surveys are ideal for gathering numerical data, while qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups help businesses understand deeper insights into customer attitudes and behaviors. A combination of both, known as mixed-methods research, can also be highly effective.
5. Is business research methodology a reliable source?
Yes, business research methodology is reliable when conducted properly. It follows systematic processes to ensure accuracy and validity. However, the reliability depends on factors such as research design, data quality, and the expertise of the researcher. When these factors are well-managed, business research provides valuable and actionable insights.

