If you are someone who is constantly looking to buy stuff online, you would know how e-commerce has changed life for you and around you. From getting groceries in 10 minutes to starting a business from the comfort of your living room, electronic commerce has transformed traditional commerce in ways beyond imagination. But while it’s a playground for innovation and convenience, it’s not without its pitfalls. So, let’s look at the advantages and disadvantages of e-commerce to understand its true impact on businesses and consumers alike.
Table of Contents
What is E-commerce?
Well, e-commerce or electronic commerce is the buying and selling goods or services using the internet. It includes financial transactions, product exchanges, and services through e-commerce websites or apps. Some examples are Amazon, Etsy, and Shopify.
E-commerce isn’t limited to large-scale companies. Even small e-commerce businesses are using its potential to reach customers worldwide. With AI and mobile commerce leading the way, the scope of e-commerce for businesses continues to expand rapidly.
💡 Fun fact: The E-Commerce market is expected to generate $4,791 billion in revenue by 2025.
Types of E-commerce
E-commerce is far more than just selling and buying online. It’s a dynamic ecosystem with different models that cater to specific needs and interactions. Let’s look at these types in greater detail to understand the versatility of electronic commerce better.
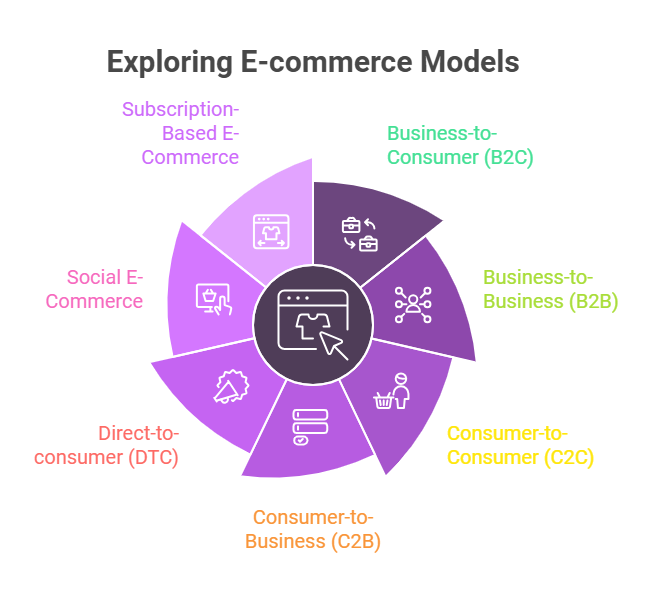
1. Business-to-Consumer (B2C)
The B2C model is the most recognizable type of e-commerce, where businesses sell products or services directly to consumers through platforms like Amazon or Myntra.
- Examples: Online clothing stores, digital product platforms, and subscription services.
- Key Features:
- Customer-centric experience
- Fast transaction times
- High volume but lower value per transaction
This model thrives on personalized experiences, discounts, and direct interaction with end users.
2. Business-to-Business (B2B)
In the B2B model, businesses sell products or services to other businesses. Think wholesale suppliers, software providers, and manufacturers.
- Examples: Alibaba, Oracle, and raw material suppliers.
- Key Features:
- Large order sizes
- Longer sales cycles
- Focus on relationships and contracts
This type of e-commerce business often involves customized pricing and complex supply chains, making it ideal for industries like manufacturing and IT.
Also read: Mastering B2B Lead Generation
3. Consumer-to-Consumer (C2C)
C2C is a peer-to-peer model where individuals sell goods or services to one another. Platforms act as intermediaries, ensuring secure transactions.
- Examples: eBay, OLX, Facebook Marketplace.
- Key Features:
- Direct seller-to-buyer interaction
- Often used for second-hand goods or collectibles
- Minimal business infrastructure
While it’s cost-effective for sellers, building trust between buyers and sellers can be challenging.
4. Consumer-to-Business (C2B)
The C2B model flips the traditional selling process, allowing individuals to offer products or services to businesses.
- Examples: Upwork (freelance services) and stock photography platforms.
- Key Features:
- User-driven pricing
- Flexible service offerings
- Businesses benefit from diverse talent pools
This model empowers individuals to monetize their skills, often catering to specific, short-term business needs.
5. Direct-to-consumer (DTC)
DTC e-commerce eliminates the middleman, enabling brands to sell directly to their customers through their own e-commerce website or store.
- Examples: Warby Parker, Dollar Shave Club, Glossier.
- Key Features:
- Greater control over brand image and customer experience
- Higher profit margins by cutting out intermediaries
- Strong emphasis on brand loyalty
DTC is gaining traction due to its ability to create a direct relationship between brands and customers, supported by effective marketing strategies.
6. Social E-Commerce
An emerging trend in e-commerce for businesses, social commerce integrates shopping directly into social media platforms.
- Examples: Instagram Shops and Facebook Marketplace.
- Key Features:
- Seamless integration of browsing and buying
- Social proof through reviews and influencer collaborations
- Targeted marketing based on user data
This model capitalizes on the heavy social media usage among consumers, especially younger demographics.
7. Subscription-Based E-Commerce
This type offers recurring products or services for a set price. Customers benefit from convenience, and businesses enjoy predictable revenue streams.
- Examples: Netflix, meal kits like Blue Apron, beauty boxes like Birchbox.
- Key Features:
- High customer retention if managed well
- Opportunities for upselling
- Relies on excellent customer service
Also read: B2C vs D2C: Key Differences between e-commerce models and which is better
Advantages and Disadvantages of E-commerce

Advantages of E-commerce
E-commerce has dramatically changed the way businesses operate and how consumers shop, offering a range of transformative benefits. Here’s a deep dive into the advantages of running an e-commerce business:
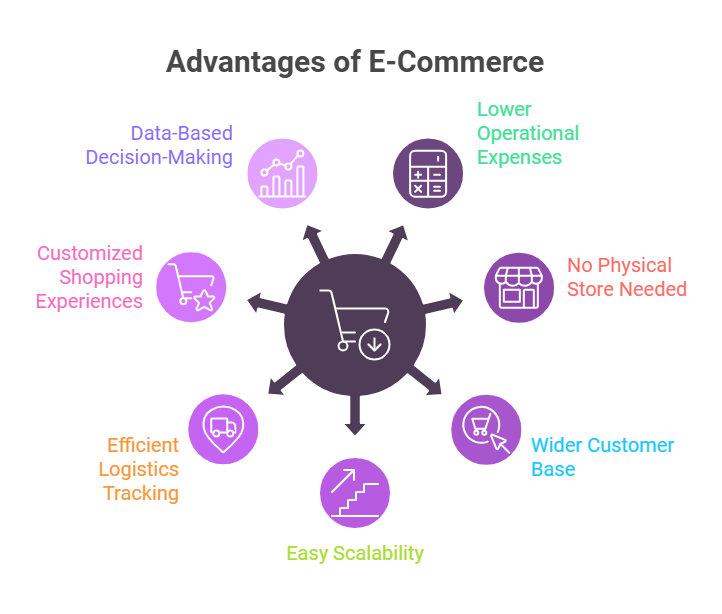
1. Lower operational expenses
Traditional brick-and-mortar stores face significant fixed costs—rent, utilities, and staff salaries are just the tip of the iceberg. E-commerce eliminates many of these expenses, providing a cost-efficient alternative.
- Credible Data: According to the U.S. Small Business Administration, operating an online store can save businesses up to 30% in overhead costs.
- Application: Startups and small businesses leverage this advantage to enter markets with lower capital investment.
E-commerce platforms like Shopify and WooCommerce further simplify entry by reducing the technical costs of building an e-commerce website.
2. Elimination of the need for a physical store
Running an e-commerce business eliminates the need for a traditional retail space, freeing up resources for product development, marketing, or inventory management.
- 24/7 Accessibility: Unlike physical stores with set operating hours, an e-commerce store operates round the clock, accommodating customers in different time zones.
- Customer Convenience: According to a PwC survey 60% out of the total people surveyed preferred shopping from online stores.
By skipping the storefront, businesses can reinvest savings into customer acquisition strategies, such as targeted online advertising.
3. Access to a wider customer base
One of the most transformative aspects of e-commerce is its global reach. With an online store, geographic boundaries become irrelevant.
- Global Markets: Platforms like Amazon and Alibaba demonstrate how even small businesses can cater to international customers.
- Mobile Commerce Growth: Statista reports mobile e-commerce sales reached $2.2 trillion in 2023, making up 60% of global e-commerce revenue. By 2027, mobile commerce is projected to comprise 62% of the e-commerce sector, up from 56% in 2018. So, businesses can target an audience beyond desktop users.
By employing multilingual websites and localized marketing, companies can appeal to diverse demographics, creating a truly borderless e-commerce business.
4. Easy scalability
Scaling a traditional business is often expensive and time-intensive, requiring additional physical space, staffing, and logistics. E-commerce offers unparalleled scalability.
- Examples: During peak seasons like Black Friday, businesses can increase inventory, expand server capacity, and introduce promotions without major infrastructure changes.
- Tools for Growth: Cloud-based platforms such as BigCommerce and Magento provide flexible tools for scaling operations.
Scalability allows businesses to adapt to demand fluctuations with minimal downtime or disruption.
5. Efficient logistics tracking
E-commerce platforms enable seamless integration of logistics tools, allowing businesses to monitor orders, manage inventory, and provide real-time updates to customers.
- Customer Trust: Transparency in shipping updates builds credibility. For instance, companies using automated tracking tools report 32% higher customer satisfaction (Zendesk, 2023).
- Inventory Management: Advanced tools like AI-driven demand forecasting optimize stock levels, reducing storage costs and preventing overstocking.
Efficient logistics enhance both operational efficiency and the overall customer experience, a cornerstone of successful electronic commerce.
6. Customized shopping experiences for customers
Ecommerce enables businesses to harness customer data to create highly personalized shopping experiences.
- Data Utilization: Tools like Google Analytics and CRM platforms collect valuable data on customer preferences, allowing businesses to offer personalized product recommendations, targeted emails, and retargeting ads.
- Customer Loyalty: According to McKinsey, personalization drives a 20% increase in customer satisfaction and a 10-15% boost in revenue.
This tailored approach fosters loyalty and encourages repeat purchases, key for sustainable growth in the e-commerce business.
7. Data-Driven Decision Making
E-commerce provides businesses with a wealth of actionable data, enabling smarter, faster decision-making.
- Customer Insights: With tools like heatmaps, businesses can analyze user behavior on their e-commerce website, identifying pain points and optimizing navigation.
- Performance Metrics: Sales funnels, conversion rates, and customer lifetime value (CLV) are just a few metrics businesses can monitor.
Using data, companies can fine-tune pricing strategies, launch targeted campaigns, and identify new opportunities, staying competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
💡 Did you know: Asia dominates as the world’s largest e-commerce market. In 2024, online retail sales across Asian nations totaled close to two trillion U.S. dollars, surpassing the Americas by approximately 500 million U.S. dollars. In contrast, e-commerce revenues in Australia, Oceania, and Africa remained significantly lower, staying under 50 billion U.S. dollars. Asia’s top position is primarily driven by China, which alone generated over 1.4 billion U.S. dollars in revenue that year. (Statista)
Also read: What is Quick Commerce?
Disadvantages of E-commerce
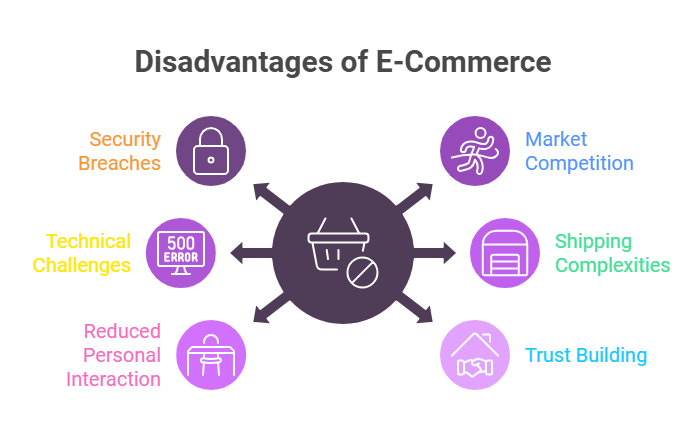
1. Risk of Security Breaches
The digital nature of e-commerce businesses makes them vulnerable to cyberattacks, data breaches, and fraud.
- Challenges:
- Hackers can exploit sensitive customer data like payment information.
- Small businesses are particularly at risk, as they may lack advanced cybersecurity measures.
In 2023, global e-commerce losses due to online payment fraud reached $41 billion (Juniper Research).
Here’s what can be done: Implementing strong encryption protocols, two-factor authentication, and compliance with standards like PCI DSS can mitigate these risks. Businesses must also educate customers on safe online practices.
2. Intense Market Competition
The low entry barriers in e-commerce for businesses mean that competition is fierce, especially in saturated markets.
- Challenges:
- Competing against giants like Amazon or Alibaba can be daunting for smaller players.
- Price wars and marketing expenses reduce profit margins.
- This is how it impacts businesses:
Without a unique value proposition, businesses struggle to retain customers in a sea of alternatives.
To combat this, companies need to focus on niche markets, brand differentiation, and superior customer experiences.
3. Technical Challenges
Running an e-commerce website requires ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting to ensure smooth operations.
- Examples of Issues:
- Website downtime during peak shopping seasons, resulting in lost sales.
- Integration problems with third-party tools like payment gateways or inventory management systems.
- Cost Implications:
Businesses must invest in skilled IT professionals or outsourced services, adding to operational costs.
Regular updates, robust hosting solutions, and scalable infrastructure are essential to minimize these challenges.
4. Complex Shipping Processes
Efficient order fulfillment is crucial for customer satisfaction, but it comes with logistical hurdles.
- Challenges:
- Managing inventory across multiple warehouses.
- Dealing with delays caused by third-party shipping providers.
- Handling international shipping regulations and customs processes.
- Impact on Costs:
Shipping expenses, including returns, can significantly erode profit margins.
Implementing automated systems for inventory management and partnering with reliable shipping carriers can simplify logistics, but these solutions require investment.
5. Reduced Personal Interaction with Customers
One of the key drawbacks of e-commerce businesses is the lack of face-to-face interaction, which can affect customer relationships.
- Challenges:
- Customers may miss the personalized assistance they receive in physical stores.
- Resolving complex customer queries online can be time-consuming.
- Customer Perspective:
According to PwC, 82% of consumers value human interaction in their purchasing journey.
To address this, businesses can use live chat, chatbots, and video support to create a more engaging customer experience.
6. Building Customer Trust and Credibility
Trust is a cornerstone of any business, but it’s harder to establish in the digital realm.
- Challenges:
- Customers are wary of scams and counterfeit products.
- Newer businesses face credibility issues due to limited reviews and brand recognition.
- Impact on Customer Retention:
Trust issues can result in abandoned carts and lower customer loyalty.
Transparent policies, secure payment options, and showcasing genuine reviews are effective ways to build credibility. Offering a money-back guarantee or free returns can further ease customer concerns.
Also read: Dropshipping vs Ecommerce: Differences, Similarities, Examples
E-commerce Trends
1. AI and Chatbots
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and chatbots are revolutionizing the way businesses interact with customers.
- Instant Customer Support:
AI-driven chatbots provide 24/7 assistance, resolving customer queries in real time. For instance, tools like ChatGPT or LivePerson streamline customer interactions, improving satisfaction. - Personalization:
AI analyzes customer behavior to offer tailored product recommendations, email campaigns, and pricing. According to McKinsey, companies using AI for personalization see a 30% boost in revenue. - Scalability:
Chatbots can handle multiple inquiries simultaneously, making them cost-effective for scaling customer service.
This trend allows businesses to create efficient, scalable, and personalized e-commerce website experiences.
2. Augmented Reality (AR)
Augmented Reality is closing the gap between physical and digital shopping experiences.
- Product Visualization:
AR enables customers to “try before they buy.” For example, IKEA’s AR app allows users to visualize furniture in their homes before purchasing. - Customer Engagement:
AR features enhance engagement, leading to higher conversion rates. A study by Shopify revealed that products with AR content see a 94% higher conversion rate. - Industries Adopting AR:
Sectors like fashion, beauty, and home decor are leveraging AR to solve common customer pain points.
Here are the top product categories for which people use Augmented Reality (AR) in U.S. online retail, 2024.
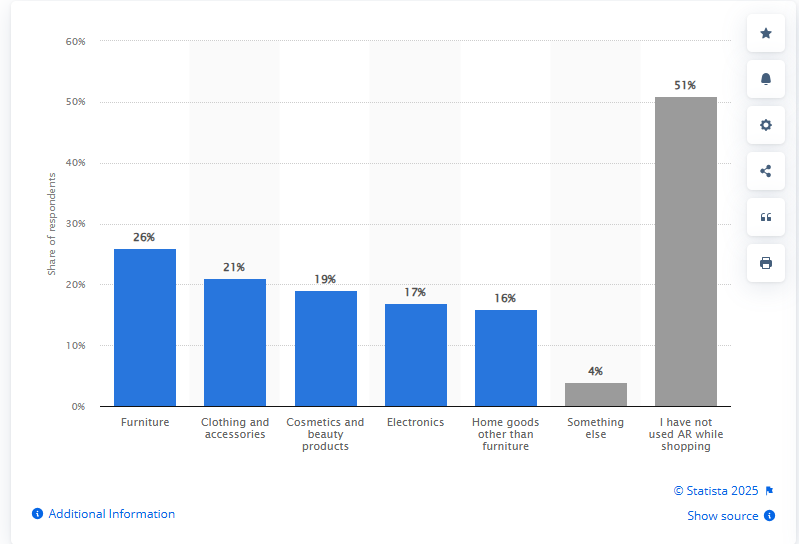
AR is becoming an essential tool for enhancing customer confidence and satisfaction in e-commerce businesses.
3. Subscription Services
Subscription models are transforming the way consumers interact with brands.
- Increased Customer Retention:
Offering products or services on a subscription basis ensures recurring revenue. Examples include Netflix (streaming) and Birchbox (beauty products). - Convenience:
Subscriptions provide convenience, such as automatic replenishment of household items. - Market Growth:
The subscription e-commerce market has seen rapid growth, increasing from $199.41 billion in 2023 to a projected $330.58 billion in 2024, with a CAGR of 65.8%. Although it only went up to $278.0 Billion, that’s still almost a 40% jump.
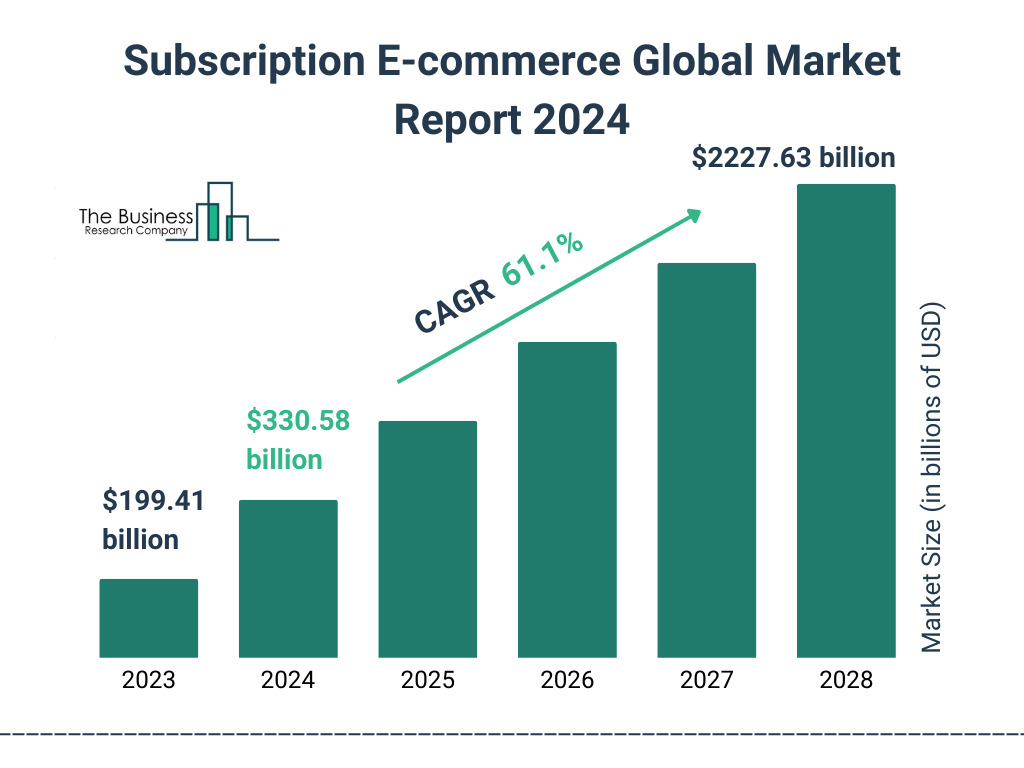
This trend caters to consumers seeking predictability and ease, making it a lucrative model for e-commerce stores.
4. Sustainability
As environmental consciousness grows, sustainability is becoming a non-negotiable for e-commerce businesses.
- Consumer Demand:
A survey by Nielsen found that 73% of global consumers are willing to change their consumption habits to reduce environmental impact. - Eco-Friendly Practices:
Businesses are adopting practices like biodegradable packaging, carbon-neutral shipping, and recycling programs. - Brand Differentiation:
Companies embracing sustainability can attract eco-conscious customers, building trust and loyalty.
By prioritizing sustainability, businesses not only contribute positively to the planet but also enhance their brand image.
5. Voice Commerce
Voice-activated shopping is gaining traction as smart home devices become more common.
- Convenience:
Devices like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant allow customers to place orders hands-free. - Adoption Rates:
Insider Intelligence predicts that voice commerce sales will reach $40 billion in the U.S. alone by 2025. - Challenges:
Ensuring accurate product discovery and secure payment methods are critical to widespread adoption.
Voice commerce simplifies the shopping experience, especially for repeat purchases, making it a valuable addition to online business strategies.
6. Social Commerce
Social media platforms are evolving into powerful e-commerce channels.
- Integrated Shopping:
Features like Instagram Shops allow users to purchase products directly within apps. - Influencer Marketing:
Social commerce leverages influencers to promote products, creating authentic connections with audiences. - Market Potential:
The global social commerce market is projected to hit $3.4 trillion by 2028 (Statista, 2024).
Conclusion
Hope you are well aware of the advantages and disadvantages of e-commerce now. While it opens doors to innovation, global reach, and cost-efficiency, it also brings challenges like intense competition and security risks.
For businesses, understanding the advantages of e-commerce and mitigating the disadvantages of e-commerce in 2025 is key to success. By using trends and focusing on customer needs, e-commerce can continue to thrive as a cornerstone of modern commerce.
Whether you’re a new entrepreneur or an established business, choosing into ecommerce for businesses could be your next big step.
FAQs: Advantages and disadvantages of E-commerce
1. What are the main advantages of e-commerce?
E-commerce offers reduced overhead costs, 24/7 availability, global reach, easy scalability, and personalized experiences through data analytics.
2. What are the main disadvantages of e-commerce?
The disadvantages of e-commerce include security risks, intense competition, technical issues, shipping complexities, and lack of personal interaction with customers.
3. Can e-commerce businesses succeed without a physical store?
Yes, e-commerce businesses can succeed by eliminating the need for a physical store, saving costs and offering convenience to customers worldwide.
4. How does e-commerce provide scalability?
E-commerce allows businesses to scale easily by adapting to increasing demand without significant infrastructure changes, making it more cost-efficient.
5. What security measures should e-commerce businesses take?
E-commerce businesses should implement SSL certificates, two-factor authentication, regular software updates, and PCI compliance to protect customer data.
6. How can e-commerce businesses build customer trust without in-person interaction?
By offering clear return policies, secure payment options, positive reviews, excellent customer support, and a strong brand presence online.
7. Are e-commerce businesses more vulnerable to competition?
Yes, the e-commerce marketplace is highly competitive, but businesses can stand out with unique products, excellent customer service, and effective digital marketing.
8. How does e-commerce affect the environment?
E-commerce can be eco-friendly through sustainable packaging and reduced physical stores, but it also contributes to shipping waste and carbon emissions.
9. How do e-commerce businesses handle shipping and returns?
E-commerce businesses manage shipping and returns through third-party fulfillment, clear return policies, multiple shipping options, and real-time tracking.
10. How does AI improve e-commerce?
AI helps by personalizing shopping, automating customer support, optimizing inventory management, and adjusting pricing strategies based on market trends.

