How do businesses figure out if an investment is worth the money? The Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) is one tool they use. It’s a simple way to measure how much return a business can expect from an investment based on profits rather than cash flow. ARR helps companies quickly decide whether a project is a good financial decision. It compares the return on investment to the cost of that investment.
Table of Contents
However, while ARR is easy to use, it doesn’t consider the time value of money, which means it might not fully capture how a project will perform in the long run. Still, it remains a popular metric for businesses that want a quick, straightforward way to assess the potential profitability of their investments. In this blog, we’ll explain what ARR is, how to calculate it using the accounting rate of return formula, and why it’s an important factor in making smart investment choices.
What is ARR (Accounting Rate of Return)?
The Accounting Rate of Return is a straightforward tool businesses use to check how profitable an investment could be. Unlike other methods that focus on cash flow or market value, ARR looks at accounting profits, making it easier to calculate. ARR measures the return an investment can generate compared to its initial cost.
This helps businesses quickly compare different investment options and pick the ones likely to bring the best returns. However, ARR has some drawbacks. It doesn’t consider the time value of money, so it might not fully show an investment’s potential over time. While ARR gives a useful snapshot of a project’s profitability, it’s best to use it with other tools to get a clearer picture of an investment’s long-term value.
Accounting Rate of Return Formula
To calculate the Accounting Rate of Return, you use the following formula:

Where:
- Average Annual Accounting Profit is the average annual profit expected from the investment.
- Initial Investment is the total cost of the investment.
To calculate the ARR, you first estimate the average annual profit the project is expected to generate over its lifespan. Then, divide this by the initial investment cost and multiply by 100 to get the percentage return on the investment.
ARR Calculation: An Example
Let’s say a company is considering investing in new equipment that costs ₹1,00,000. The equipment is expected to generate an average annual accounting profit of ₹20,000 over 5 years.
Using the formula:
ARR = (₹20,000 / ₹1,00,000) × 100
ARR = 20%
So, the Accounting Rate of Return for this investment is 20%, meaning the business expects a 20% return on its initial investment each year.
Also read: Product-Led Marketing
Components of Accounting Rate of Return
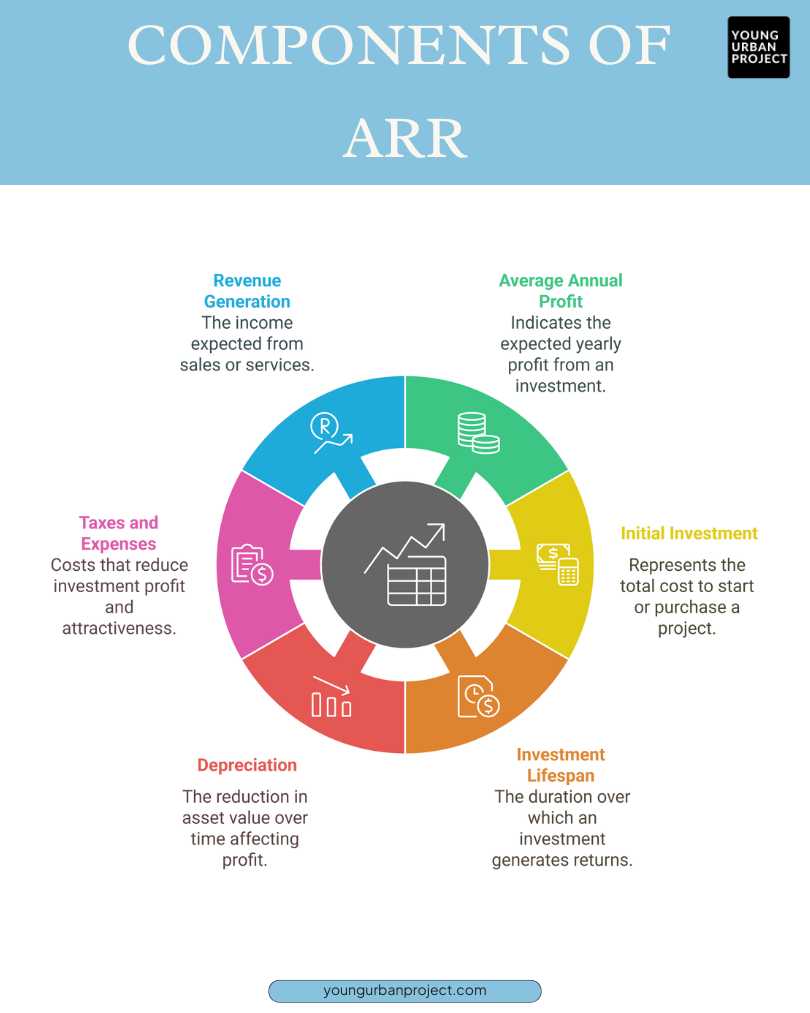
1. Average Annual Accounting Profit
This is the average profit an investment is expected to make yearly. It’s found by subtracting costs like operating expenses and taxes from the revenue. This shows how much money the business can expect to earn annually from the investment. It helps measure the investment’s potential return and gives a clear idea of its yearly profitability.
2. Initial Investment
This is the total money spent to start or buy a project. It includes the cost of the asset, setup, and any extra expenses to get it running. This amount is compared to yearly profits to calculate the return. Knowing the initial investment helps determine if the project is worth the cost and effort.
3. Investment Lifespan
This is the time a business expects to earn money from the investment. It could be a few years or many decades, depending on the project. A longer lifespan means steady profits but may also come with more risks. The lifespan is important because it helps calculate the average yearly profit over time.
4. Depreciation
Depreciation is when an asset loses value over time due to age or becoming outdated. It’s treated as an expense, which reduces the overall profit. When calculating Accounting Rate of Return, businesses include depreciation expense to get a more accurate profit figure. This helps show how much money the investment is truly making after accounting for the asset’s declining value.
5. Taxes and Other Expenses
Taxes and costs like maintenance or insurance reduce the profit from an investment. These are subtracted from the total revenue when calculating ARR. Higher expenses or taxes mean lower profits and a lower ARR, making the investment less attractive. Keeping these costs low can help improve the ARR and make the investment more appealing.
6. Revenue Generation
This is the money an investment is expected to earn over time, like from sales or services. Higher and more stable revenue leads to better profits, which can increase the ARR. This makes the investment more attractive to businesses. Strong revenue generation is key to ensuring the investment is profitable and worth the effort.
Also read: What is the Difference Between Goods and Services?
Why is the ARR growth rate important?
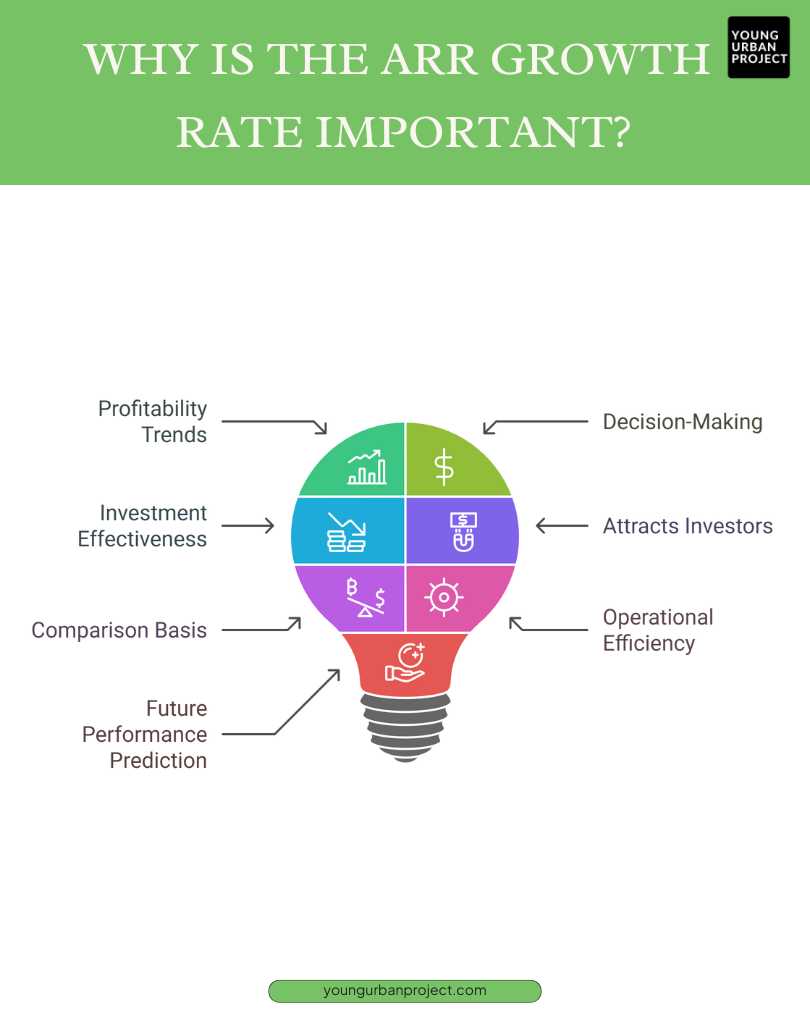
1. Indicates Profitability Trends
The ARR growth rate shows if an investment is becoming more profitable over time. If the ARR keeps rising, it means the investment is earning more money yearly, which is a positive sign. This helps businesses see if their investment is on the right path for future growth and higher profits, making it easier to plan ahead.
2. Helps in Decision-Making
Tracking the ARR growth rate helps businesses make smarter decisions. If the ARR keeps growing, it means the investment is doing well and should be continued. If the ARR stops growing or falls, the business might need to rethink the investment or even stop it. This helps avoid losses and focus on better opportunities.
3. Measures Investment Effectiveness
ARR growth shows how well an investment is performing in terms of profit. A rising Accounting Rate of Return means the business is earning more returns from the investment. This helps businesses see which projects are most effective and profitable, allowing them to focus on the ones that bring the best results and avoid less successful ones.
4. Attracts Investors
Investors like projects with strong growth potential. A rising ARR growth rate makes an investment more attractive because it shows the project is generating higher profits. This can help businesses bring in investors who want to support projects that will grow and provide good returns in the future, boosting the business’s financial strength.
5. Provides a Basis for Comparisons
Businesses often have many investment options, and Accounting Rate of Return growth helps compare them. By looking at which projects have the highest ARR growth, businesses can focus on the ones with the best chances of success. This helps them use resources wisely and invest in the most profitable opportunities, ensuring better returns for the business.
6. Reflects Operational Efficiency
A rising ARR growth rate shows the company is managing resources well and keeping costs low. This could mean the business is improving efficiency, keeping customers longer, or earning more per unit. All of this leads to higher profits and shows the business is improving its operations and financial health, making it stronger overall.
7. Predicts Future Performance
The ARR growth rate helps predict how an investment will perform in the future. If the ARR keeps growing steadily, it suggests the investment will continue to provide profits. This gives businesses a clearer idea of what to expect, helping them plan better and make smarter decisions for long-term success.
Also read: What Is the Service Marketing Triangle and How Does It Work?
What is a Good ARR Growth Rate?
A good ARR growth rate depends on the industry, the type of investment, and the goals of the business. Generally, an annual growth rate of 10-20% is considered healthy for most businesses. However, some industries, like tech or startups, may see higher growth rates due to rapid changes or innovation. In more stable or mature industries, the growth might be slower.
The most important thing is to have steady and consistent growth. If the ARR keeps growing at a stable rate year after year, it shows that the investment is on the right track and can continue to bring profits. Businesses should set realistic growth targets based on their past performance and the current market conditions. Trying to grow too fast without proper planning can lead to risks. Overall, a steady and achievable ARR growth rate indicates that the business is making smart, profitable decisions for the long term.
How to Boost Your ARR Growth Rate
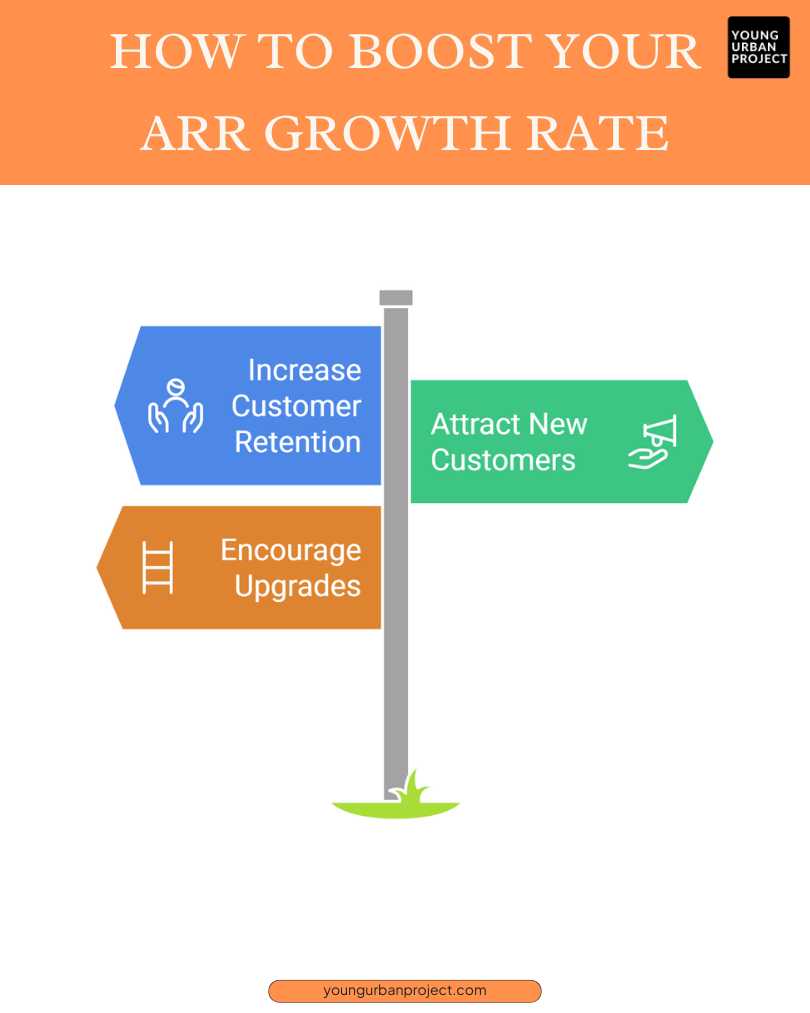
1. Increase Your Customer Retention Rates
Improving customer retention is one of the most effective ways to boost ARR growth. Satisfied customers are more likely to continue purchasing, renew subscriptions, or stay engaged with your services over time. By offering exceptional customer service, building strong relationships, and regularly adding value, businesses can reduce churn rates and increase the lifetime value of each customer, thus contributing to a healthy ARR growth rate.
2. Attract New Customers
Expanding your customer base is essential for increasing ARR. Attracting new customers through effective marketing strategies, such as targeted ads, promotions, or content marketing, helps to boost revenue. The more customers you bring in, the higher your Accounting Rate of Return can grow. It’s important to tailor your marketing efforts to the right audience and ensure that your value proposition aligns with their needs and preferences.
3. Get Existing Customers to Upgrade
Encouraging existing customers to upgrade their purchases or subscribe to premium services is a great way to grow ARR. Offering upsell opportunities, such as higher-tier plans, additional features, or exclusive services, can generate additional revenue from your current customer base. Businesses can implement loyalty programs, personalized offers, or incentives to motivate customers to upgrade, which can lead to a significant increase in ARR without the need to acquire new customers.
Also read: What Is Digital Marketing ROI?
Advantages of ARR
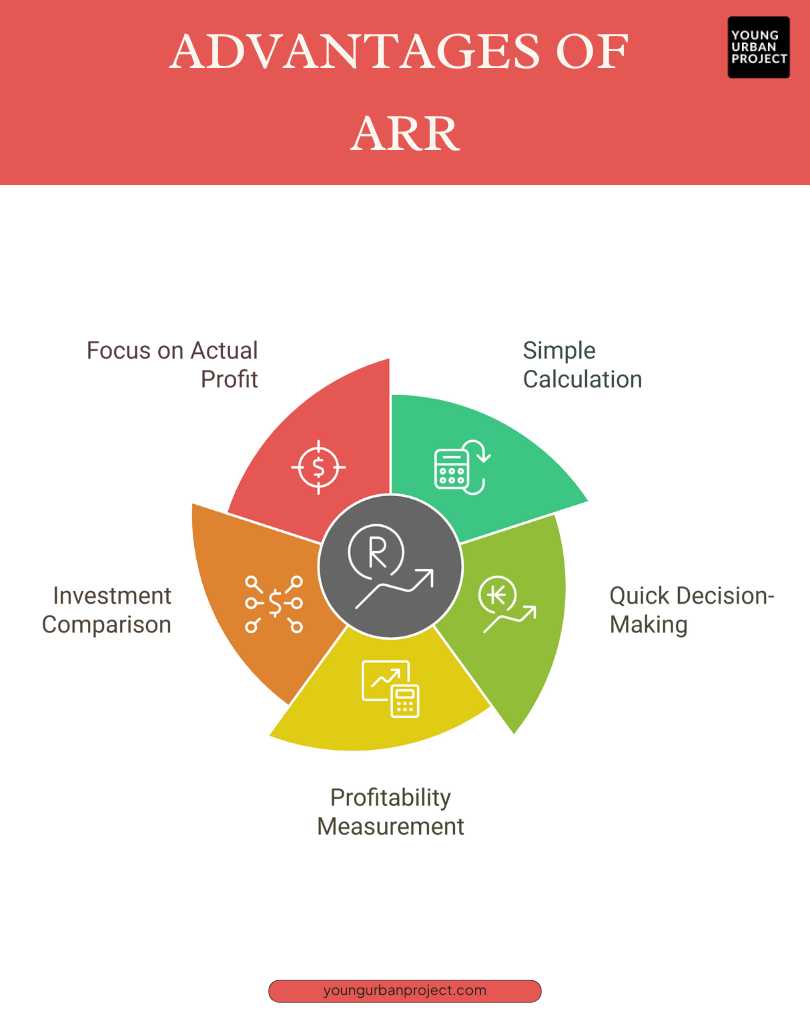
1. Simple and Easy to Calculate
ARR is very simple to calculate. You only need the average yearly profit from the investment and its total cost. This makes ARR an easy tool for all businesses, whether they have a big finance team or not. It doesn’t need complex math or formulas, so anyone can use Accounting Rate of Return to check an investment’s potential return.
2. Quick Decision-Making
ARR helps businesses make decisions fast. By comparing the Accounting Rate of Return of different investments, companies can quickly see which projects are likely to give the best returns. This helps them focus on the most profitable options and make informed choices without wasting time, ensuring they invest in the right opportunities.
3. Helps Measure Profitability
ARR is a good way to measure how profitable an investment is. It shows the profit a business expects to earn compared to the investment’s cost. By using ARR, businesses can understand if an investment is worth it and how much return it might bring over time, helping them make smarter financial decisions.
4. Useful for Comparing Investments
ARR helps businesses compare different investment options to find the most profitable ones. When you calculate ARR for multiple projects, you can easily see which ones will likely bring better returns. This is especially helpful for businesses with many investment choices, as it guides them in picking the best ones to focus on.
5. Focuses on Actual Accounting Profit
ARR looks at accounting profit, which is the money a business actually makes after expenses. This gives a realistic view of expected returns. It helps businesses focus on real profits, making it easier to understand how successful an investment will be without getting distracted by things like market changes or other external factors.
Also read: What is Business Research?
Disadvantages of ARR
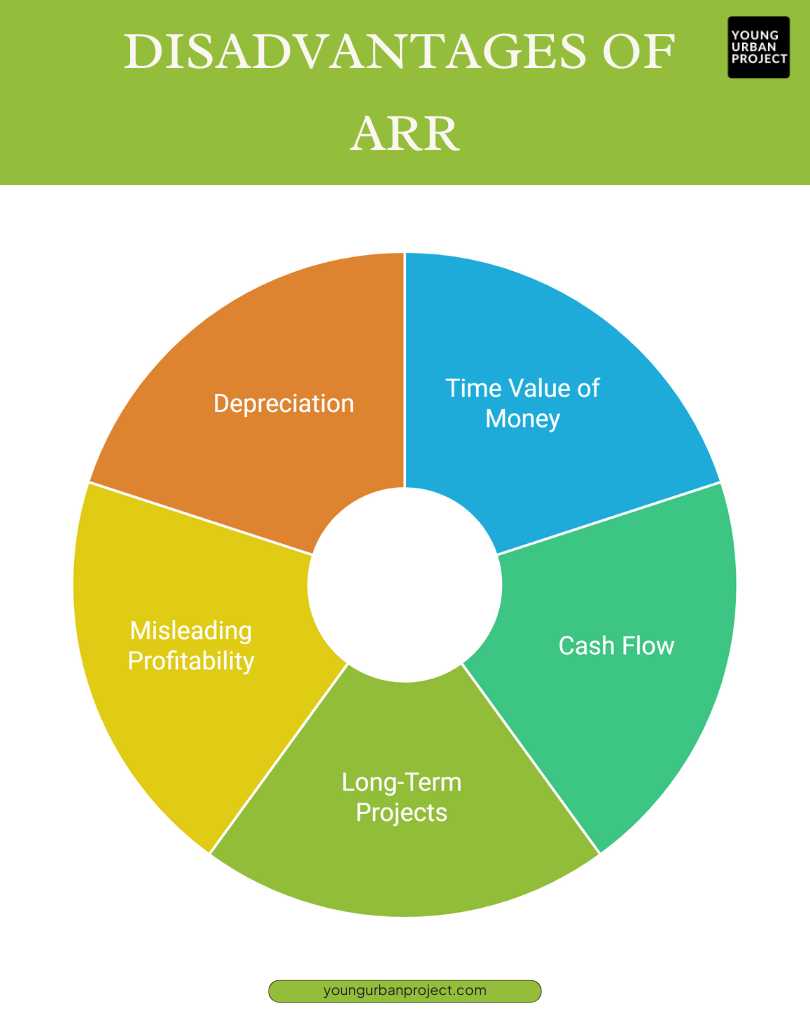
1. Ignores the Time Value of Money
ARR does not consider the time value of money, meaning it treats all profits equally regardless of when they are earned. This can be misleading because money received in the future is worth less than money received today. As a result, ARR may overestimate the attractiveness of investments with returns that come later.
2. Does Not Account for Cash Flow
Accounting Rate of Return focuses on accounting profit, but it ignores cash flow, which is the actual money coming in and going out. Even if an investment has a high ARR, it might not have enough cash flow to cover its daily expenses. Without proper cash flow, a business could struggle even with a high ARR.
3. Not Ideal for Long-Term Projects
Accounting Rate of Return is not the best tool for evaluating long-term investments. Since it calculates only average annual profit without considering how profits change over time, it can miss long-term risks or rewards. This makes ARR less useful for projects that need years to generate significant returns.
4. Can Be Misleading
Accounting Rate of Return can sometimes give a false impression of profitability. Since it doesn’t account for factors like inflation, risks, or changing market conditions, it may make an investment seem more attractive than it truly is. This could lead to poor decision-making if ARR is relied on too heavily.
5. Does Not Consider Depreciation
Accounting Rate of Return may not take depreciation into account in some cases. Depreciation represents the decrease in the value of assets over time. Without factoring this in, ARR might show a higher return than is realistic, as it does not reflect the true cost of maintaining or replacing the investment over its useful life.
Bottom Line
To sum it up, the Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) is a helpful tool for businesses to quickly check how profitable an investment might be. Although it has some drawbacks, like not considering the time value of money, it gives a simple way to compare different investment options. A good ARR varies based on the industry and type of investment, but generally, the higher the ARR, the better the chances of making a good profit.
To boost ARR growth, businesses can focus on strategies like keeping customers satisfied, attracting new customers, and encouraging existing ones to upgrade. It’s also important to remember that ARR should not be the only measure used to assess an investment. Combining it with other financial tools can give businesses a clearer and more accurate understanding of how well an investment will perform over time. This way, businesses can make smarter, more informed decisions.
FAQs
1. What does the Accounting Rate of Return (ARR) mean?
ARR is a financial measure that helps businesses understand how much profit an investment could make. It compares the yearly profit of the investment with the money spent to get it started. ARR shows businesses if an investment is likely to bring in good returns and helps decide whether it’s worth going ahead with the project.
2. What is considered a good ARR percentage?
A good ARR percentage can vary depending on the industry, but usually, an ARR of 10-20% each year is considered a good return. A higher ARR means the investment is likely making more profit. However, businesses should also look at other things like risk and how long it will take to see returns before making a decision.
3. How can you calculate ARR?
To calculate ARR, divide the average yearly profit by the total amount spent on the investment, and then multiply the result by 100. The calculation formula is:
ARR = (Average Annual Profit / Initial Investment) × 100.
This formula helps businesses see how much profit an investment could make each year based on the money spent.
4. How does ARR help in making investment decisions?
ARR helps businesses decide if an investment is worth pursuing by showing how much profit it could generate each year. If the ARR is high, it suggests the investment will provide good returns. This helps businesses quickly compare different projects and choose the one that’s most likely to be profitable.
5. Does ARR consider the time value of money?
No, ARR does not consider the time value of money. This means it doesn’t consider that money today is worth more than the same amount in the future. While ARR is a useful tool for quick comparisons, it may not fully reflect the long-term profitability of an investment.

