Do you wonder how companies like Amazon know exactly what product recommendations to show you? It’s not magic; the answer lies in segmentation (a concept in marketing and product marketing). Companies use this to group people based on things like where they live, their age, what they like, and how they shop. This helps them show ads that feel personal to you.
Table of Contents
For example, if you own a clothing store, selling winter coats to people in hot places won’t work. But if you target people in colder areas, you’ll sell more. That’s what segmentation does—it helps businesses reach the right people with the right products.
Instead of treating everyone the same, businesses divide customers into smaller groups. This way, they can create ads and offers that feel special to each group. Companies that use segmentation do better because they understand their customers. It makes marketing smarter and more effective. Segmentation is like giving the right gift to the right person—it just works! Let’s see how segmentation works and why it’s so effective.
What is Segmentation in Marketing?
Segmentation in marketing is the process of dividing a large group of potential customers into smaller, more specific groups. Each group or segment shares similar characteristics, such as age, income, location, or buying habits.
By doing this, businesses can create targeted marketing campaigns that speak directly to each group’s needs and interests. Instead of wasting money on generic ads, companies can craft messages that truly connect with their target audience. This approach makes marketing more efficient, cost-effective, and customer-friendly.
Now, let’s explore the different types of segmentation that businesses use to better understand their customers.
Also read: Retargeting vs Remarketing
Types of Segmentation in Marketing
There isn’t just one way to segment a market. Businesses use different methods based on their goals and industry. The five most common types of segmentation in marketing are:
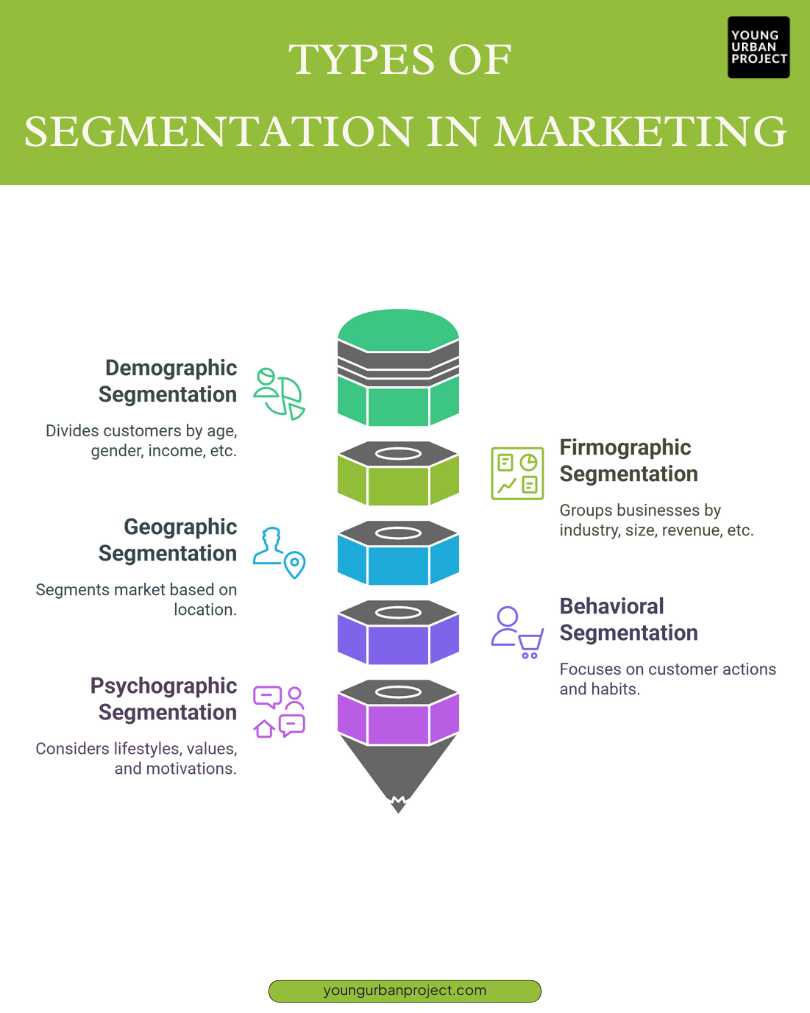
1. Demographic Segmentation
Demographic segmentation divides customers based on factors like age, gender, income, education, and occupation. For example, a luxury car brand may target high-income individuals, while a toy company focuses on parents with young children. This is one of the easiest and most commonly used segmentation methods because demographic data is widely available and easy to analyze.
2. Firmographic Segmentation
Firmographic segmentation in marketing is similar to demographic segmentation but applies to businesses instead of individuals. Companies are grouped based on industry, company size, revenue, or location. Market research helps B2B companies understand which businesses are likely to need their product or service. For instance, a software company may use market segmentation to target startups differently from large enterprises.
3. Geographic Segmentation
This type of segmentation divides the target market based on their location, such as country, city, climate, or urban vs. rural areas. A company selling winter jackets will focus on colder regions, while a surfboard brand will target coastal areas. Geographic segmentation is crucial for businesses offering location-specific products and services, ensuring their marketing efforts reach the right audience.

Checkout our Product Marketing Course
4. Behavioral Segmentation
Behavioral segmentation focuses on customer actions, such as purchasing habits, brand loyalty, and product usage. For example, a coffee shop may offer discounts to frequent buyers or create special promotions for first-time customers. Understanding customer behavior allows businesses to tailor offers, improve customer experiences, and boost sales by targeting the right audience at the right time.
5. Psychographic Segmentation
Psychographic segmentation dives deeper into customer lifestyles, interests, values, and personality traits. Unlike demographics, which focus on external factors, psychographics look at what motivates people to buy. It helps businesses craft marketing messages that appeal to customer motivation. For example, a fitness brand might target health-conscious individuals, while a luxury brand appeals to people who value exclusivity. This type of segmentation helps brands connect emotionally with their audience.
Process of Segmentation in Marketing
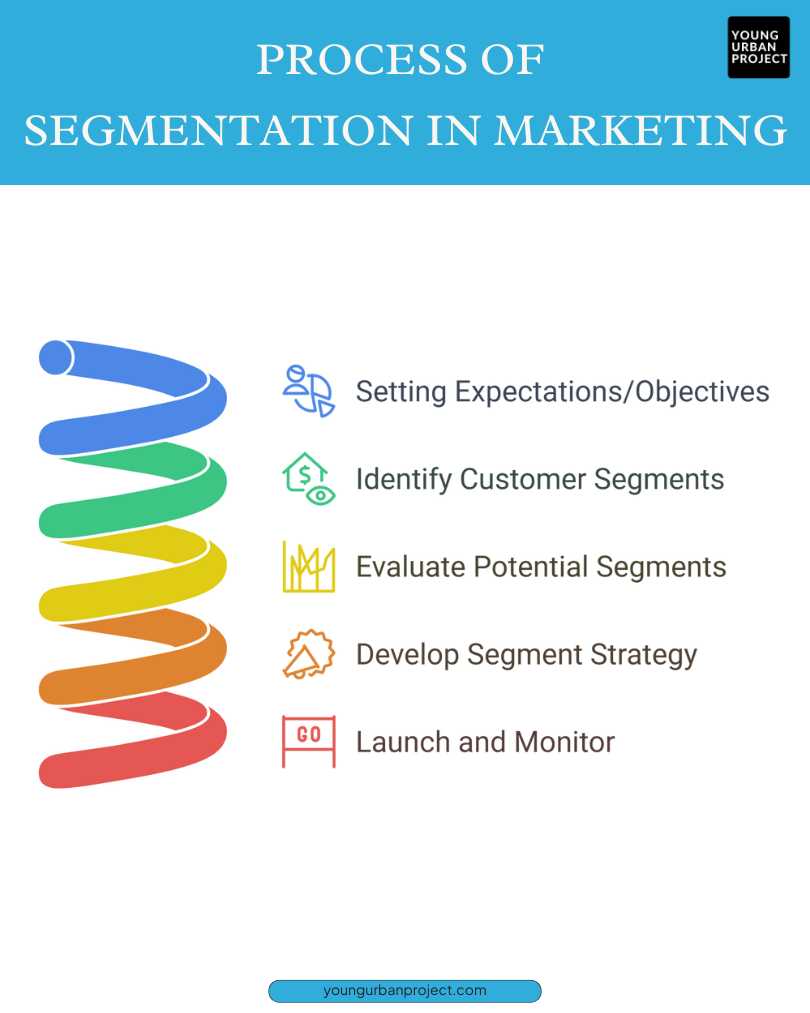
Segmentation in marketing is not just dividing customers into groups. It’s a step-by-step process to help businesses target the right people. The process includes setting goals, identifying groups, evaluating them, creating strategies, and launching campaigns. By following these steps, businesses can make their marketing more effective and reach the right audience.
Phase 1: Setting Expectations/Objectives
The first step is to set clear goals. Businesses need to know why they are segmenting their audience. Are they trying to increase sales, personalize marketing, or enter new markets? Clear goals help create a focused strategy. Without them, segmentation can become unclear, leading to wasted time and money.
Phase 2: Identify Customer Segments
Next, businesses analyze data to group customers with similar traits. This can be based on age, behavior, location, or interests. For example, a sportswear brand may group customers into casual gym-goers and professional athletes. Identifying the right groups ensures marketing efforts are directed at the most relevant audience, making them more effective.
Phase 3: Evaluate Potential Segments
Not all customer segments are equally valuable. Businesses must check each group’s size, profitability, and growth potential. A group should be big enough to target and easy to reach. If a group is too small or hard to serve, it may not be worth the effort. This step helps businesses focus on the best opportunities.
Phase 4: Develop Segment Strategy
After choosing the right groups, businesses create tailored marketing strategies. This includes messaging, pricing, and promotions that fit each group. For example, a luxury watch brand may target rich professionals with high-end ads, while a budget brand focuses on discounts. A good strategy ensures the right message reaches the right people.
Phase 5: Launch and Monitor
Finally, businesses launch their marketing campaigns and track results. They use data, customer feedback, and sales to measure success. If a group doesn’t respond well, they can make changes. Monitoring helps businesses stay flexible and improve their approach over time, making their marketing more effective and impactful.
Benefits of Segmentation in Marketing
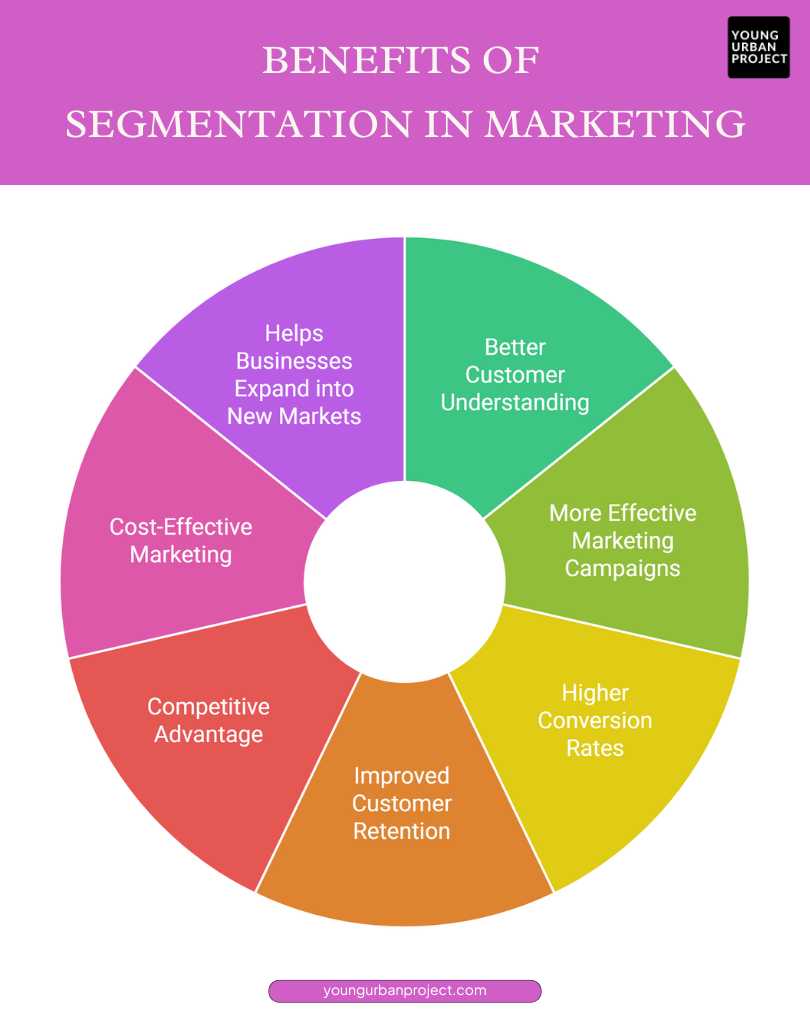
1. Better Customer Understanding
Segmentation helps businesses know what customers like, need, and expect. By studying different groups, companies learn about buying habits, preferences, and problems. This helps them create personalized experiences, making customers happier and more loyal. Without segmentation, businesses might treat everyone the same, which can make customers feel ignored or misunderstood.
2. More Effective Marketing Campaigns
Businesses can send the right message to the right people with segmentation. Instead of wasting money on ads that don’t fit everyone, they can create campaigns that match each group’s interests. For example, a clothing store can promote winter coats only to people in cold areas, making the ads more relevant and increasing interest.
3. Higher Conversion Rates
Segmentation helps turn potential customers into buyers. When messages and offers match what people want, they are more likely to buy. For example, sending emails with product suggestions based on past purchases works better than sending the same email to everyone. This makes customers feel understood and increases sales.
Also read: 20 Types of Email Marketing Every Marketer Must Know
4. Improved Customer Retention
Customers stay loyal to brands that understand them. By personalizing offers and communication, businesses make customers feel special. For example, a beauty brand can give discounts to customers who often buy skincare products. This keeps them coming back and builds a strong relationship between the brand and the customer.
Also read: Retention Marketing 101
5. Competitive Advantage
Businesses that know their customers better than competitors have an edge. Segmentation helps companies stand out by offering tailored experiences. For example, if two brands sell the same product, customers will choose the one that meets their specific needs. This makes the brand more attractive and helps it grow.
6. Cost-Effective Marketing
Segmentation saves money by targeting the right people. Instead of spending on ads that reach everyone, businesses can focus on those most likely to buy. For example, a travel agency can promote luxury vacations to high-income travelers, avoiding wasted ads on people who can’t afford them. This makes marketing more efficient and effective.
7. Helps Businesses Expand into New Markets
Segmentation helps businesses find new opportunities. By studying different groups, companies can spot trends or needs they didn’t know about. For example, a fitness brand targeting gym-goers might discover a demand for home workout products. This allows them to create new products and grow their business in new directions.
Also read: What Is Customer Relationship Marketing?
Limitations of Segmentation in Marketing

1. High Costs Involved
Segmentation can be expensive because it needs a lot of research, data collection, and analysis. Small businesses may not have enough money for tools like surveys or personalized ads. Running many targeted campaigns instead of one big campaign also costs more. If not done carefully, segmentation can make marketing costs much higher than planned.
2. Complexity in Managing Multiple Segments
The more groups a business targets, the harder it is to manage. Companies must create different messages, pricing strategies, and promotions for each group. For example, a clothing brand targeting teens and professionals needs separate strategies, which increases work and makes it harder to stay organized. This can slow down decision-making and create confusion.
3. Risk of Over-Segmentation
If a company divides its audience into too many small segments, it may fail to reach a large enough customer base. Over-segmentation can result in wasted resources, weak marketing impact, and inconsistent branding. For example, if a company selling organic skincare creates highly specific segments, it might end up with groups too small to be profitable.
4. Limited Data Accuracy
Segmentation depends on customer data, which may not always be correct or updated. People’s preferences and behaviors change over time, making it hard to keep segmentation accurate. For example, a travel agency targeting frequent travelers might struggle if customers stop traveling due to economic problems. This can lead to ineffective marketing strategies.
5. Difficulty in Reaching All Segments Effectively
Even with the right groups, businesses may find it hard to reach everyone. Some customers prefer different ways of communication, like older people liking print ads and younger people liking social media. Managing multiple platforms can be complicated and time-consuming, making it harder to connect with all groups effectively.
6. Increased Competition Within Segments
Popular customer groups often attract many businesses, leading to more competition. If a brand focuses on a high-value group, others may do the same, making it harder to stand out. For example, luxury car brands all target wealthy professionals, so they must offer something unique to win customers. This can make marketing more challenging.
7. Changing Consumer Preferences
Customer preferences and trends change over time, so a group that works today may not work tomorrow. Businesses must keep updating their segmentation strategies, which takes time and money. For example, a phone company targeting users who liked physical keyboards had to change its strategy when touchscreens became popular. This constant change can be stressful and costly.
Examples of Segmentation in Marketing
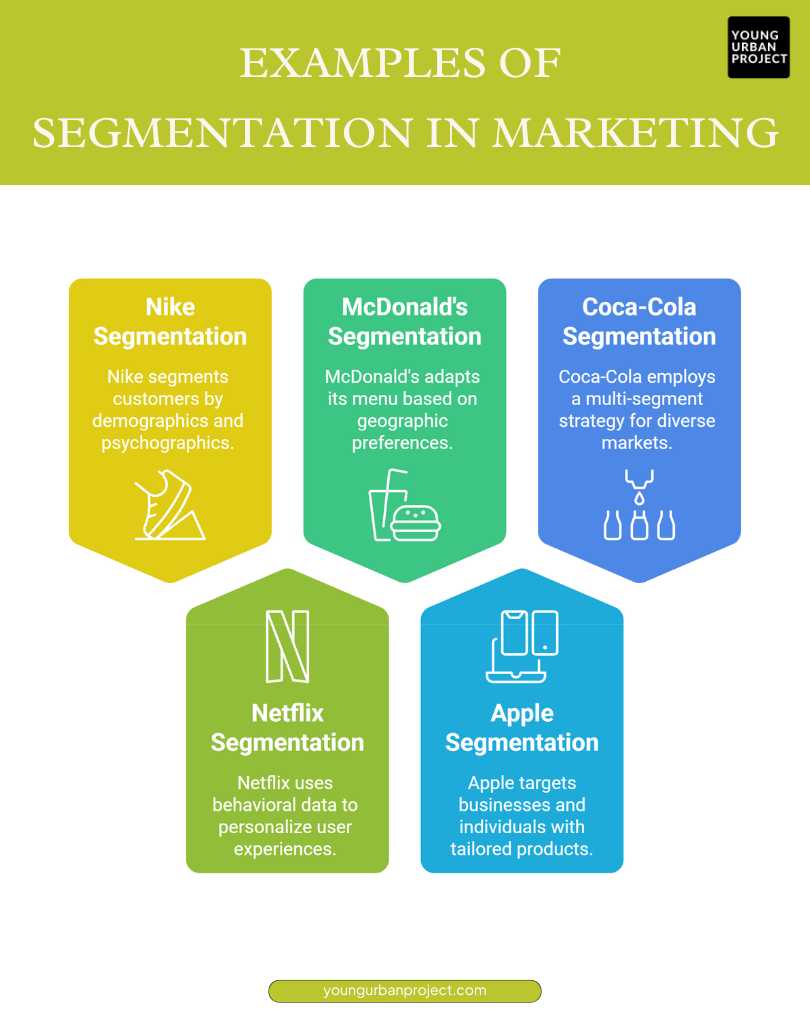
1. Nike – Demographic & Psychographic Segmentation
Nike segments its customers based on age, gender, income level, and lifestyle. It targets young, active individuals, athletes, and fitness enthusiasts who value performance and style. Nike’s messaging varies for different segments—while it promotes professional sports gear to athletes, it markets stylish sneakers as fashion statements to casual buyers, ensuring broader appeal.
2. Netflix – Behavioral Segmentation
Netflix segments users based on watch history, preferences, and engagement patterns. It uses data to recommend shows, create personalized playlists, and offer tailored subscription plans. For instance, a person who frequently watches action movies will get recommendations for similar content, while a user who prefers documentaries will see a different set of suggestions.
3. McDonald’s – Geographic Segmentation
McDonald’s adjusts its menu based on location. In India, it offers McAloo Tikki and Paneer Wraps to cater to vegetarian customers, while in Japan, it serves Teriyaki Burgers. This geographic ‘segmentation allows’ McDonald’s to respect cultural preferences and local tastes, ensuring its menu resonates with customers in different regions.
4. Apple – Firmographic & Psychographic Segmentation
Apple targets both businesses and individuals using firmographic and ‘psychographic segmentation’. For businesses, it markets MacBooks and iPads as productivity tools. For individuals, it appeals to tech-savvy, premium customers who value design, security, and innovation. By creating an aspirational brand image, Apple attracts loyal customers willing to pay premium prices.
5. Coca-Cola – Multi-Segment Strategy
Coca-Cola segments its market by offering different products for various customer groups. Coca-Cola Zero targets health-conscious consumers, while Sprite appeals to younger audiences. It also uses ‘geographic segmentation’, adjusting sweetness levels based on regional preferences. This strategy ensures Coca-Cola remains relevant across diverse demographics and lifestyles.
Conclusion
Segmentation in marketing is a smart way for businesses to connect with the right customers. By splitting their audience into groups based on things like age, location, or interests, companies can create better marketing campaigns. This helps improve customer engagement, boost sales, and build loyalty. Even though it can be costly and tricky, the benefits of market segmentation are worth it.
Businesses that use market segmentation well can build strong relationships with customers and grow over time. They need to study customer data and update their strategies regularly to stay on track. When done right, segmentation helps businesses understand their customers, make smarter decisions, and create personalized experiences. This makes customers feel valued and keeps them coming back.
Whether it’s a big brand or a small shop, segmentation helps businesses stand out in a competitive market. It’s a key tool for long-term success, helping companies focus on what their customers truly want and need.
FAQs
1. Why is segmentation important in marketing?
Segmentation helps businesses focus on the right people. Instead of advertising to everyone, they can target groups more likely to buy. This makes marketing more effective, increases sales, and improves customer satisfaction. It also saves money by reducing wasted ads. Segmentation ensures businesses reach the right audience with the right message.
2. How do companies collect data for segmentation?
Companies collect data through surveys, website analytics, social media, and purchase history. For example, an online store tracks what products customers view most. They also use feedback and research to understand their audience better. This data helps create accurate customer groups for targeted marketing.
3. What is the difference between segmentation and targeting?
Segmentation divides a large audience into smaller groups based on shared traits like age or behavior. Targeting is choosing which group to focus on and creating campaigns for them. Both steps are important for effective marketing and reaching the right customers.
4. Do small businesses use segmentation?
Yes! Small businesses can use simple strategies like analyzing feedback, tracking purchases, or using social media insights. For example, a bakery can group customers by preferences like cakes or gluten-free products. Segmentation helps small businesses focus their efforts and grow without needing expensive tools.
5. How often should businesses update their segmentation strategy?
Businesses should review their segmentation regularly because customer preferences change. Some update every few months, others yearly. If sales or engagement drops, it’s time to reevaluate. Keeping segments updated ensures marketing stays relevant and effective.
6. What happens if a business targets the wrong segment?
Targeting the wrong group can lead to low sales, poor engagement, and wasted money. Customers may not be interested in the product. To fix this, businesses should analyze feedback, track campaigns, and adjust their strategy to focus on the right audience.
7. Can one product be marketed to multiple segments?
Yes! A product can appeal to different groups with customized messaging. For example, a smartphone can be marketed to professionals for its work features and to gamers for its performance. This helps businesses reach more people while keeping their marketing relevant to each group’s needs.

