Developing a new product is one of the most exciting and rewarding challenges for businesses. However, it’s also one of the most complex. The new product development process (NPD) involves various stages that require strategic thinking, market analysis, and precise execution. Whether you’re building a software product, a tangible consumer good, or even an innovative service, the NPD process is essential to ensuring success in the market.
Table of Contents
So, let’s break down the NPD process.
What is a New Product Development Process (NPD)?
New Product Development refers to the process of conceptualizing, designing, creating, and bringing a new product to the market. The NPD process is not just about inventing something new but about solving real problems that your target audience faces while ensuring that the product aligns with business goals.
From simple product ideas to a final product that resonates with consumers, the NPD process is integral to building successful businesses. Whether you’re looking to develop a new product or improve existing products, this systematic approach can help guide you through the complexities of market demand, cost analysis, and competition.
Types of Product Development
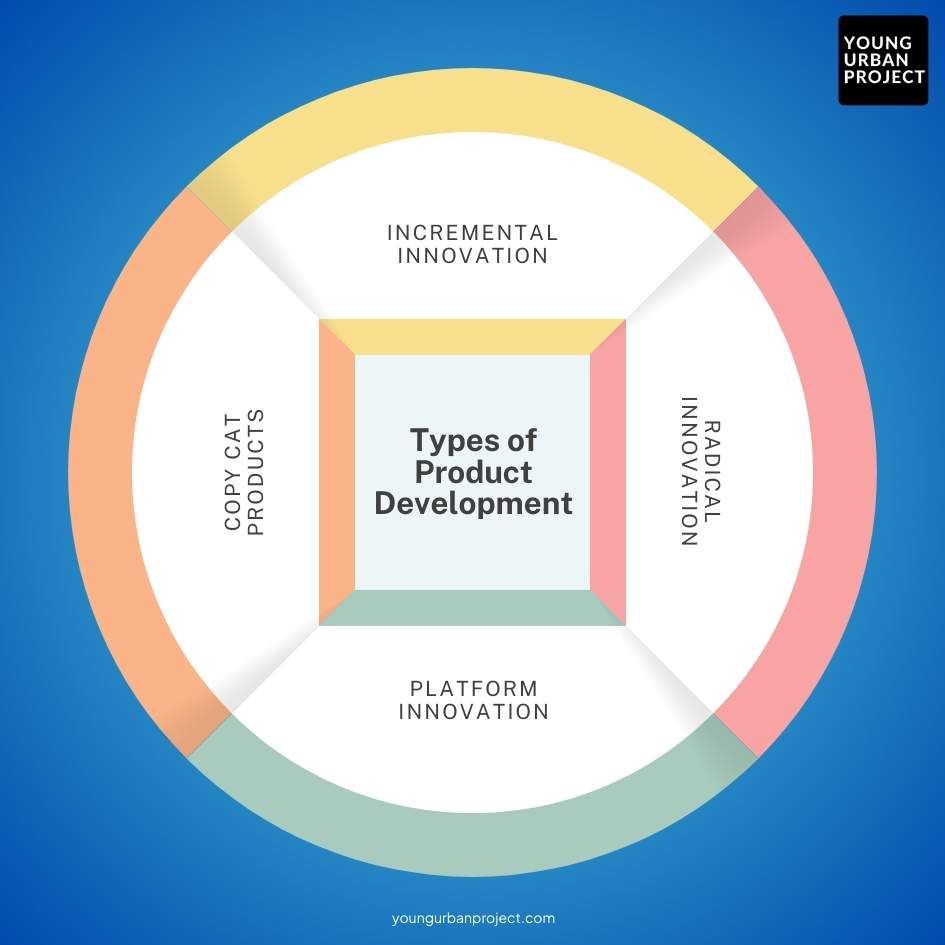
1. Incremental Innovation
Incremental innovation involves small, iterative improvements to existing products. This approach is common in industries like consumer electronics or SaaS platforms, where companies frequently update products with new features or performance upgrades. Take Zoho, which consistently adds new features to its CRM suite, ensuring it remains competitive and aligns with customer needs.
2. Radical Innovation
Radical innovation refers to the creation of entirely new products or technologies that drastically change the market. Blinkit, for instance, transformed the grocery shopping experience by offering ultra-fast delivery services. This was a radical departure from traditional brick-and-mortar retail, capitalizing on a clear market gap for fast, on-demand grocery delivery.
3. Platform Innovation
Platform innovation focuses on building ecosystems around products, often involving complementary goods or services. This approach enhances the customer experience and drives higher user adoption.
4. Copycat Products
Some businesses replicate successful ideas in new markets or tweak them for different consumer segments. This is common in industries where market leaders are already established. For instance, several Indian food delivery startups like Zomato and Swiggy have mirrored the business models of global giants like Uber Eats, adapting them to local preferences.
Also Read: Product Classification in Marketing
The 7 Stages of New Product Development Process
New Product Development (NPD) is a structured process used to transform an idea into a market-ready product. It involves several distinct stages, each focusing on refining the product and aligning it with customer needs, technical feasibility, and business goals. Here’s a detailed look at the seven stages of the new product development process:
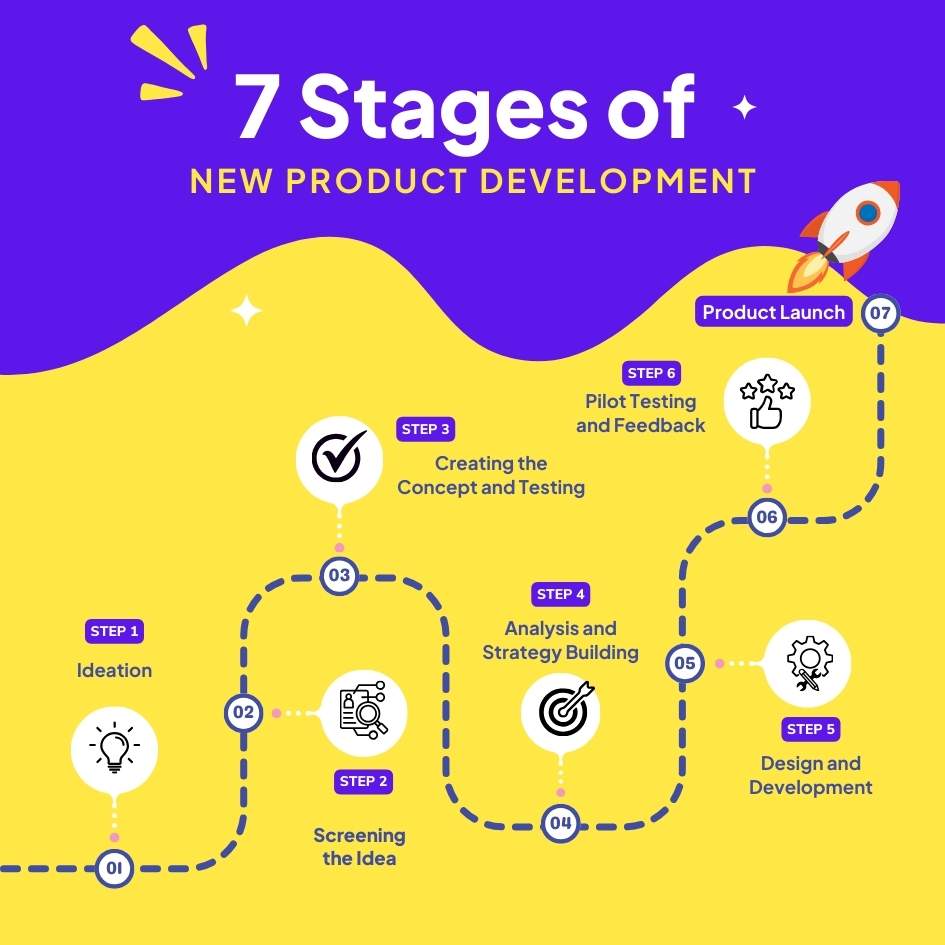
1. Ideation
The first stage of the new product development process is idea generation, where creativity and innovation take center stage. This stage involves brainstorming and gathering as many potential product ideas as possible. These ideas can stem from various sources, including internal teams, customers, and market research. The goal here is to generate a broad range of ideas—whether entirely new products, new features for existing products, or solutions to unmet market needs.
Key Activities:
- Brainstorming sessions
- Market and customer research
- Competitor analysis
2. Screening the Idea
Once a large pool of ideas is generated, the next stage is idea screening. In this phase, businesses evaluate the viability of each idea by filtering out those that are not feasible due to reasons like technical limitations, lack of market demand, or high production costs. The goal is to select the most promising ideas that are worth pursuing further.
For instance, a SaaS startup might come up with multiple new features for their platform, but after screening, they may focus only on the ideas that address the largest pain points of their target users, like improving the user interface or integrating with other popular tools.
Key Activities:
- Feasibility analysis
- Technical assessments
- Cost and market demand evaluation
3. Creating the Concept and Testing
In this stage, the selected idea is transformed into a detailed product concept, which serves as a refined version of the initial idea. Prototypes or Minimum Viable Products (MVPs) are created and tested with potential customers to evaluate their interests and gather feedback.
Spotify is a prime example of how focusing on a single core feature rather than getting sidetracked by additional features can lead to success. The company aimed to create the best music streaming service, and, for their MVP, they focused solely on music streaming. They developed a desktop app and launched a closed beta to test the market. As the MVP and freemium pricing model gained traction with users, Spotify’s team dedicated efforts to signing more artists, developing mobile apps, and expanding into the US market.
Key Activities:
- Development of product concepts and prototypes
- Customer testing and feedback collection
- Iterative refinement of the product
4. Analysis and Strategy Building
After the concept has been tested and validated, the next stage is creating a marketing strategy and business analysis. At this point, businesses must develop a solid market strategy that aligns the product with the target audience. This includes defining the value proposition, establishing pricing strategies, setting business goals, and analyzing the financial feasibility of the product.
Key Activities:
- Market segmentation and positioning
- Competitor analysis
- Pricing strategy development
- Financial viability assessment
5. Design and Development
This stage involves the actual design and development of the product, including both its physical aspects (if applicable) and software development (in the case of digital products). Prototypes are created and refined, and various tests are carried out to ensure the product meets both functional and quality standards.
Key Activities:
- Design and software development
- Prototype creation and iteration
- Testing and quality control
6. Pilot Testing and Feedback
Before launching a product on a large scale, companies often conduct Test Marketing. This stage involves introducing the product in a limited market or demographic to evaluate its performance, collect additional feedback, and make necessary adjustments to both the product and marketing strategies.
Key Activities:
- Limited market release
- Performance tracking
- Gathering customer feedback for final improvements
7. Product Launch
Finally, the product reaches the Product Launch stage. This is where the product is introduced to the broader market. A comprehensive launch strategy is essential, which includes a well-planned marketing campaign, distribution, and sales strategies to ensure the product reaches its target audience effectively.
Key Activities:
- Customer support and post-launch analysis
- Full-scale market release
- Marketing campaign execution
Key Roles in the Product Development Team
The success of any new product relies heavily on the collaboration of various professionals working together in a well-defined product development team. These roles span multiple disciplines—ranging from idea generation to final product launch—and each member contributes their expertise to ensure the new product meets both customer expectations and business objectives. Below are the key roles that are crucial in the NPD process.
1. Product Manager
The Product Manager (PM) is the strategic leader of the product development team. They are responsible for guiding the product from concept to launch, ensuring that all stakeholders are aligned with the vision, goals, and timelines. The PM works closely with both the business and development teams to make critical decisions about product features, pricing, and positioning. They are also responsible for maintaining the product roadmap, a strategic plan that defines the product’s journey through its lifecycle.
The product manager’s primary responsibility is balancing customer needs with business objectives, ensuring the product delivers value while maintaining profitability.
Key Responsibilities:
- Define the product vision and align it with business goals.
- Develop and prioritize the product roadmap.
- Coordinate with stakeholders across design, engineering, marketing, and sales teams.
- Ensure that the product meets market demands and customer pain points.
2. Product Designer
The Product Designer focuses on the user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design of the product. They translate the product concept into intuitive, functional, and aesthetically pleasing designs. This role requires an understanding of human-centered design principles, user behavior, and technological constraints.
In software development, the Product Designer may create wireframes, prototypes, and interactive designs. They also test design concepts with real users and iterate based on feedback. The designer ensures that the product features are both usable and visually appealing.
Key Responsibilities:
- Conduct user research to understand customer needs.
- Develop wireframes, mockups, and prototypes.
- Collaborate with developers to ensure design feasibility.
- Iterate on designs based on user feedback and testing.
3. Software Engineers / Developers
Software Engineers or Developers are at the heart of turning the product idea into a working product. They bring the product design to life through coding, testing, and debugging. In the case of SaaS products, the engineering team ensures that the software is scalable, secure, and capable of delivering the promised features.
Depending on the size of the company, software engineers may specialize in front-end development (focused on the user interface) or back-end development (focused on databases and servers). In some cases, engineers may be full-stack developers, skilled in both areas.
Key Responsibilities:
- Write code to implement product features.
- Build and maintain the product’s architecture.
- Ensure the product is scalable, secure, and efficient.
- Collaborate with product managers and designers to implement features.

4. Marketing and Sales Teams
The Marketing and Sales teams play pivotal roles in both the product’s development and launch phases. While they may not be involved in creating the final product, their insights into customer needs, market trends, and competitive analysis help guide product decisions.
The Marketing team creates the product’s market strategy, defining how to position it in the market and communicating its benefits to potential customers. They are also responsible for brand messaging and promotional campaigns.
The Sales team gathers customer feedback, often acting as a bridge between customers and product managers. They provide insights into customer pain points, needs, and how well the product resonates with the target market.
Key Responsibilities:
- Develop marketing campaigns to build awareness.
- Conduct market research and competitive analysis.
- Provide feedback from potential customers and early users.
- Promote the product through various sales channels.
Also Read: Scope of Marketing Research
5. Quality Assurance (QA) Engineers
QA Engineers are essential to ensuring the final product meets quality standards. They test the product for bugs, usability issues, and functionality flaws. The QA team conducts various testing, including manual and automated testing, performance testing, and user acceptance testing (UAT) to ensure the product meets all required specifications before launch.
In a software development environment, QA engineers work closely with developers to test the product features, ensuring that the product performs as expected under various scenarios. QA engineers are crucial for minimizing the risk of issues after launch.
Key Responsibilities:
- Write and execute test cases to identify product defects.
- Perform stress and performance testing.
- Ensure that the product meets customer expectations and quality standards.
- Collaborate with product designers and developers to resolve issues.
6. Operations and Logistics Teams
For physical products, the operations and logistics teams are essential for the manufacturing, distribution, and scaling of the product. They manage the production process, ensuring that the final product meets specifications and is delivered on time. This involves working closely with manufacturers and vendors to source materials, overseeing the production process, and ensuring efficient distribution channels.
For tech-based products, these teams may focus on infrastructure, hosting, and scaling to handle user traffic effectively once the product is launched. They play a critical role in ensuring the product-to-market strategy runs smoothly.
Key Responsibilities:
- Manage supply chain, inventory, and manufacturing processes (for physical products).
- Ensure the infrastructure is scalable for tech products.
- Coordinate product distribution and fulfillment.
7. Customer Support and Feedback Teams
After the product is launched, Customer Support and Feedback teams become critical in ensuring product success. These teams handle post-launch customer queries, troubleshooting, and feedback collection. They are on the front lines, directly interacting with customers and reporting on their experience with the product.
Their insights into customer challenges, issues, and suggestions help the product team iterate and improve the product after its release. This feedback loop is crucial for long-term product success.
Key Responsibilities:
- Address customer inquiries and technical issues.
- Collect and report on user feedback.
- Monitor customer satisfaction and retention.
Also Read: Customer-Centric Product Development
Challenges in the New Product Development Process
The product development stage is critical in transforming an initial concept into a tangible, market-ready product. While it’s a phase full of potential, it also brings a number of challenges that can hinder progress and affect the overall success of the product. From resource constraints to market unpredictability, companies face various obstacles that can delay or derail the development process. Below are some of the key challenges encountered during this stage:
1. Resource Constraints
One of the most common challenges during the product development stage is a lack of resources—be it time, budget, or personnel. Development teams may struggle with having enough financial backing or the necessary skill sets within the organization. Tight budgets can force companies to cut corners or prioritize certain features over others, which can negatively affect the product’s quality. Additionally, insufficient staffing or lack of specialized talent, such as software engineers or product designers, can impede the speed and quality of development.
Impact: Limited resources can delay timelines, increase development costs, or compromise the quality of the product, all of which can affect its market success.
2. Technological Constraints
Many products, especially in technology-driven industries, face challenges related to the available technology during the product development process. The chosen technology may not be compatible with other parts of the product, or it may be unable to meet performance requirements. Technological limitations can also arise when a product team attempts to use cutting-edge innovations that have not yet matured, leading to bugs, security issues, or scalability concerns.
Impact: These technological roadblocks can lead to significant delays, higher development costs, and the need for rework or redesign. In severe cases, the product may need to be abandoned or heavily modified.
3. Unclear Product Vision or Market Fit
An unclear product vision or lack of clarity regarding product-market fit is another major challenge in the product development stage. If the development team does not have a clearly defined vision, or if they misunderstand the customer needs, the product may fail to resonate with the target audience. Without proper market research, a product can end up being poorly aligned with customer demands, which increases the risk of failure post-launch.
Impact: A misaligned product vision leads to wasted time and resources, resulting in products that do not meet market demands and ultimately fail to generate sales or gain traction.
4. Scope Creep
Scope creep refers to the gradual expansion of a project’s scope beyond its initial goals. This can occur when stakeholders, often due to changing business priorities or new ideas, request additional features or modifications to the original product concept. While adapting the product to new insights can be beneficial, it often leads to delays and budget overruns.
Impact: Scope creep can result in a product that is launched late, over budget, or overcomplicated, which may dilute the product’s value or make it harder to market effectively.
5. Inadequate Testing and Quality Assurance
Quality assurance (QA) plays a significant role in the product development stage, but the challenge lies in adequately testing the product. In the rush to meet deadlines, some teams may overlook comprehensive testing, either due to time constraints or a belief that the product is “good enough.” As a result, defects, bugs, and performance issues may go unnoticed until after launch, when they can have far-reaching consequences.
Impact: Inadequate testing leads to a poor user experience, which damages the product’s reputation, increases customer support costs, and may require costly post-launch fixes.
6. Managing Stakeholder Expectations
During the product development process, multiple stakeholders—including internal teams, external partners, and investors—may have differing expectations regarding timelines, features, and the final product. Balancing these sometimes competing demands while maintaining the integrity of the product can be challenging. Miscommunication or misunderstanding between stakeholders can lead to delays or changes that undermine the product’s development.
Impact: Poorly managed stakeholder expectations can cause frustration, misalignment of goals, and unnecessary modifications, which can ultimately derail the project.
7. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
For products, particularly in regulated industries (like healthcare, finance, or food and beverage), adhering to regulatory requirements is a critical challenge. Navigating complex rules, standards, and certifications can significantly delay product development. Ensuring compliance from the initial concept through the product testing stage requires dedicated resources and careful planning, which can complicate the development process.
Impact: Regulatory hurdles add time and cost to the development process, and non-compliance can result in legal issues or even product recalls, severely harming the brand.
8. Market Uncertainty and Changing Consumer Preferences
The market and consumer preferences are dynamic and can shift rapidly. During the product development stage, companies can encounter difficulty predicting trends or changes in customer expectations. A product that was originally conceived to meet a particular market need may lose relevance if consumer behavior changes or if new competitors emerge with innovative solutions.
Impact: Shifting market conditions can render a product obsolete or irrelevant, leading to wasted investment in development and a lack of customer interest post-launch.
9. Integration with Existing Systems
One common challenge for tech products is integrating the new product with existing systems or third-party software. Whether it’s compatibility with legacy systems or smooth integration with other technologies, ensuring the product functions well with other tools or platforms is crucial for customer satisfaction and usability. Integration issues can also arise when the development team overlooks the complexity of working with other systems.
Impact: Poor integration can lead to functional issues, dissatisfied users, and the need for additional development to fix these problems.
10. Speed to Market
In today’s fast-paced business environment, companies are under increasing pressure to accelerate time to market. However, speeding up the product development process often means sacrificing thorough testing, quality assurance, or comprehensive feature sets. Balancing the need to release the product quickly while maintaaining a high standard of quality can be a difficult challenge.
Rushed product development may lead to a subpar product, which could lead to poor user adoption, negative reviews, and missed business objectives.
Also Read : Product Marketing Strategies Examples
Benefits of New Product Development (NPD)
New Product Development (NPD) is essential for a business’s growth and long-term success. By continuously developing innovative products, companies not only meet consumer demands but also differentiate themselves in the marketplace. The process offers numerous advantages that can lead to increased profitability, brand loyalty, and competitive positioning. Below are some key benefits of investing in NPD:
1. Market Differentiation
Developing new products allows businesses to differentiate themselves from competitors. In a competitive marketplace, offering innovative products that solve customer pain points can set a company apart from its competitors. Whether through improved features, new technologies, or unique solutions, a fresh product offering helps a brand stand out, gaining customer attention and loyalty. By continuously evolving product lines, companies can keep their brand fresh, and customers are more likely to stay engaged with the brand over time.
Market differentiation increases brand visibility and helps build a loyal customer base. This becomes a powerful tool to fend off competition and establish a unique identity in the marketplace.
2. Revenue Growth and Profitability
NPD is a major driver of revenue growth. Launching new products can open up new revenue streams and tap into previously unexplored markets. With a successful launch, businesses can expand their product portfolio, thus broadening their customer base and increasing sales. When companies introduce products that meet specific customer needs, they have the potential to generate higher margins and greater profitability. This is particularly true when the new products are positioned as premium options or address emerging trends.
By diversifying product offerings, companies can reach more customers and generate more sales, ultimately leading to increased profitability.
3. Adaptation to Market Changes
Consumer preferences, technological advancements, and market conditions are constantly evolving. NPD allows businesses to stay relevant by adapting to these changes. New product development ensures that companies can quickly respond to shifts in consumer demand, such as changes in technology or evolving tastes. For instance, companies that introduce products addressing environmental sustainability or advancements in AI technology can capture the attention of a growing segment of environmentally conscious consumers or tech-savvy buyers.
Adaptation to market changes helps businesses remain competitive and resilient, ensuring they stay ahead of industry trends and continue to serve their target audience effectively.
4. Increased Brand Equity
Successful product innovation can significantly enhance a brand’s reputation and brand equity. When a company introduces a product that resonates with customers and exceeds their expectations, it builds trust and credibility. Positive experiences with new products contribute to stronger emotional connections with the brand. Customers who are loyal to a brand are more likely to spread positive word-of-mouth, which can further boost the company’s image and customer loyalty. Over time, consistent innovation helps establish the brand as a leader in its industry.
A strong reputation for innovation and quality enhances brand equity, making the company more attractive to investors, customers, and potential business partners.
5. Competitive Advantage
Innovative products often give companies a competitive edge, especially in saturated markets. Through differentiation and the ability to offer exclusive features, companies can outperform competitors. Products that offer unique solutions, better usability, or superior quality can gain market share, leading to a more dominant position. Moreover, having a pipeline of innovative products means a company can stay ahead of the competition by consistently releasing new offerings that appeal to evolving consumer needs.
Competitive advantage ensures that a business has a stronger hold on the market, making it harder for competitors to replicate or surpass its success.
6. Improved Customer Satisfaction
New products can enhance the overall customer experience by addressing customer needs or improving existing solutions. When a company introduces products that solve specific problems or enhance user convenience, it leads to higher levels of customer satisfaction. By listening to customer feedback and developing products based on their preferences, companies can strengthen relationships with their existing customer base. This feedback loop not only drives product development but also nurtures customer loyalty.
Higher customer satisfaction translates to increased retention, reduced churn, and a stronger brand-customer relationship.
7. Risk Diversification
Relying on a single product or service can be risky, especially in industries where trends shift rapidly or market demand fluctuates. By investing in NPD, companies can diversify their risk across multiple product lines. This allows businesses to cushion the impact of market downturns or other unexpected disruptions. A diversified product portfolio increases the chances of maintaining steady revenue even if one product faces challenges or becomes obsolete.
Risk diversification minimizes the financial impact of market changes or failures, allowing businesses to better withstand market volatility.
8. Entry into New Markets
Developing new products often opens doors to new geographical or demographic markets. For instance, a product that performs well in one region may be tailored for a different cultural context and sold in new international markets. Similarly, a business can introduce products designed for a different customer segment, expanding its reach. This expansion can increase the overall footprint of the brand and offer new growth opportunities, especially when the product is adapted to meet local needs or regulations.
NPD can help businesses enter new markets, expanding their footprint and creating additional revenue streams from untapped customer bases.
9. Enhancement of Operational Efficiency
Throughout the product development stage, companies often streamline their processes, improving overall operational efficiency. The creation of new products may require reevaluating supply chains, refining production methods, and adopting advanced technologies. These changes can have ripple effects across the organization, resulting in reduced costs and optimized resource management. For example, developing products using more sustainable materials may lead to more efficient manufacturing processes and lower operational costs in the long run.
Innovations in product development not only lead to better products but can also improve the overall operational processes, reducing waste and increasing profitability.
10. Attracting Talent and Investment
A company that consistently develops new products tends to attract top talent and investors. Creative, innovative work is appealing to skilled professionals who want to be part of a forward-thinking organization. Additionally, investors are drawn to companies with a proven track record of successful product development, seeing them as more capable of adapting to changing market conditions and seizing growth opportunities.
Strong NPD practices enhance a company’s reputation, attracting high-quality talent and investment, which is crucial for scaling the business.
Read Also: Product Launch Plan for Product Marketers
💡Tips for a successful product launch?
Launching a new product is a pivotal moment in the new product development process (NPD) process. A well-executed product launch can create buzz, drive sales, and establish your product as a market leader. To achieve this, businesses must carefully plan, test, and refine their strategy. Below are essential components and actionable steps to ensure a successful product launch:
Creating a Winning Market Strategy
A robust market strategy lays the foundation for a successful product launch. Here are the critical elements of a winning strategy:
1. Define Your Target Audience
Understanding your audience is crucial. Identify their demographics, pain points, and preferences. Use tools like customer personas and market segmentation to refine your focus.
2. Position Your Product
Craft a unique value proposition (UVP) that highlights how your product solves specific problems. Your UVP should clearly differentiate your product from competitors and align with your audience’s needs.
Also Read: Types of Positioning
3. Plan Multichannel Marketing
Leverage multiple channels to reach your target audience effectively:
- Social Media Campaigns: Build anticipation through teaser posts, behind-the-scenes content, and influencer collaborations.
- Email Marketing: Use personalized email campaigns to inform existing customers about the launch.
- Content Marketing: Publish blogs, videos, or case studies that showcase your product’s benefits and applications.
4. Set Clear Goals
Define specific, measurable goals for the launch. For example:
- Achieve a specific number of pre-orders.
- Generate a certain amount of website traffic.
- Secure a specific percentage of market share within six months.
5. Align Teams
Ensure that the marketing, sales, and product development teams are aligned on the launch strategy. A cohesive approach ensures consistency in messaging and execution.
Also Read: Consumer Buying Process
Testing Your Minimum Viable Product
Testing your minimum viable product (MVP) is a critical step in validating your product before the official launch. This phase helps identify potential issues and refine the product to meet customer expectations.
1. Identify the Core Features
Focus on delivering your product’s core functionality. Avoid overloading the MVP with features that may dilute its value or delay the testing process.
2. Conduct User Testing
Involve real users in the testing process. This could include:
- Beta testing with a select group of users.
- Usability tests to gauge how easily customers can navigate and use the product.
- A/B testing for specific features or designs.
3. Gather Quantitative and Qualitative Data
Use analytics tools to track key performance indicators (KPIs) like retention rate, engagement time, and conversion rate. Additionally, collect qualitative feedback through surveys or interviews to understand the user experience.
4. Iterate and Improve
Based on the feedback and test results, refine your product. Address issues, enhance usability, and ensure that the product delivers on its promise before scaling for a larger audience.
Importance of Feedback in the Product Development Process
Feedback plays a vital role in shaping a product that resonates with your target audience. It helps businesses make informed decisions and refine their offerings to meet market demands.
1. Collect Feedback from Multiple Sources
Gather insights from a variety of stakeholders, including:
- Customers: Through surveys, reviews, and focus groups.
- Internal Teams: Insights from sales, marketing, and support teams.
- Industry Experts: Recommendations and benchmarks from consultants or thought leaders.
2. Act on Feedback Proactively
Feedback is only valuable if acted upon. Prioritize improvements based on the impact they will have on the product and the business. Addressing critical feedback promptly shows your commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
3. Continuous Feedback Loop
Establish a continuous feedback loop to ensure ongoing product improvements even after the launch. Use tools like:
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) surveys to measure customer satisfaction.
- Real-time analytics to monitor product performance.
4. Prevent Reputational Damage
Acting on feedback pre-launch can help avoid costly mistakes and reputational harm. A well-polished product ensures a positive market reception and builds trust with your audience.
💡 Bonus Tips for a Successful Product Launch:
- Create a Buzz Pre-Launch: For product launch ideas think of countdowns, exclusive previews, or pre-orders to build anticipation.
- Monitor Competitor Activity: Analyze competitors’ recent launches to identify gaps or areas to outperform them.
- Be Ready to Pivot: Stay flexible and ready to adjust your strategy based on market reactions or unforeseen challenges.
- Ensure Scalability: Verify that your operations, supply chain, and customer support are prepared to handle an increase in demand.
Also Read: Product Management vs Product Marketing
The Role of Product Management in the NPD Process?
Product management is a critical function in the New Product Development (NPD) process, acting as the bridge between various teams to ensure a product’s success. From conceptualization to launch, product managers oversee the strategy, execution, and delivery, aligning the product with business objectives and market needs.
Here’s a deep dive into the key roles product management plays in the NPD process:
Defining Roles and Responsibilities in the Product Development Team
Product management plays a pivotal role in clarifying and assigning roles to ensure seamless collaboration. This involves:
1. Aligning Team Objectives
- Product Managers (PMs): Oversee the product vision, strategy, and roadmap.
- Developers/Engineers: Handle technical implementation and ensure product functionality.
- Designers: Focus on user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design.
- Marketers: Plan and execute go-to-market strategies.
2. Establishing a Communication Framework
PMs ensure consistent communication between departments, acting as the primary point of contact. They facilitate regular meetings, update stakeholders, and maintain transparency throughout the development cycle.
3. Defining Success Metrics
Product management is responsible for setting key performance indicators (KPIs) and tracking them to measure progress, ensuring that the team stays aligned with business goals.
Also Read : Product Management KPIs
PMs Focus on:
Product managers are the linchpin of the NPD process. They contribute to its success in several ways:
1. Customer-Centric Approach
PMs advocate for the customer by focusing on customer-centric product development. They do this by:
- Conducting user research to understand pain points.
- Gathering feedback to ensure the product meets real-world needs.
- Prioritizing features that deliver maximum value to users.
2. Strategic Decision-Making
PMs use data-driven insights to make critical decisions. They analyze market trends, competitor strategies, and performance data to adjust the product direction as needed.
3. Risk Management
PMs identify potential risks early in the process and develop contingency plans. This involves:
- Analyzing project feasibility during the business analysis phase.
- Balancing scope, time, and budget constraints.
4. Driving Collaboration
Product managers foster collaboration across cross-functional teams, ensuring that each team member’s contributions align with the overall product goals.
Using Agile Product Development Methodologies
Incorporating Agile methodologies is a hallmark of modern product management, enabling teams to work iteratively and respond to changing requirements. Here’s how product managers leverage Agile:
1. Iterative Development
PMs break down the NPD process into manageable sprints or iterations, ensuring that the product is developed incrementally. This reduces risk and allows for quicker feedback cycles.
2. Continuous Improvement
Agile encourages frequent retrospectives where teams review what went well and what can be improved. PMs lead these sessions, ensuring learnings are applied in subsequent iterations.
3. Flexibility and Adaptability
By embracing Agile, product managers can quickly pivot in response to market changes or feedback, ensuring that the product remains relevant and competitive.
4. Focus on Collaboration
Agile emphasizes teamwork and communication. PMs use tools like scrum boards and project management software to maintain transparency and track progress.
Product Management in Post-Launch Phases
Even after a product launch, the role of product management continues to be critical:
1. Monitoring Product Performance
PMs track key metrics such as customer acquisition, retention, and satisfaction to evaluate product success.
2. Planning Updates and Enhancements
Based on feedback and analytics, PMs prioritize features or fixes for upcoming versions, ensuring the product evolves to meet user expectations.
3. Driving Market Expansion
PMs explore opportunities to expand the product’s reach, whether through new customer segments, regions, or features that increase usability.
What is the Role of Product Marketing in the NPD Process?
Product marketing plays a pivotal role in ensuring a successful new product development (NPD) process. It acts as the bridge between the development team and the target audience, ensuring that the product aligns with customer needs and market demands while achieving business objectives. Below are the key responsibilities and areas where product marketing contributes to the NPD process:
1. Market Research and Analysis
Product marketers are deeply involved in gathering insights into customer needs, preferences, and market trends. They analyze competitors, assess gaps in the market, and use this data to refine product concepts. Market research ensures that the product idea is viable and aligns with what customers are actively seeking.
2. Positioning and Messaging
Once the product concept is validated, product marketing defines the value proposition, positioning, and core messaging. This step involves answering critical questions such as:
- Who is the target audience?
- What problem does the product solve?
- How is it differentiated from competitors?
The resulting positioning strategy becomes the foundation for marketing and sales efforts.
3. Go-to-Market Strategy
Product marketing leads the go-to-market (GTM) strategy by determining the most effective channels to launch and promote the product. This includes:
- Crafting detailed buyer personas.
- Collaborating with sales teams to create impactful pitches.
- Planning campaigns for product awareness, acquisition, and retention.
4. Driving Cross-Functional Collaboration
Product marketers work closely with product managers, designers, engineers, and sales teams to ensure a cohesive development and marketing strategy. Their input is crucial for aligning the technical aspects of the product with customer-centric messaging.
5. Feedback Loop Creation
Product marketing is instrumental in gathering customer feedback, especially during concept testing and minimum viable product (MVP) stages. This feedback ensures continuous improvement and helps align the product with real-world user needs.
6. Enabling Sales and Customer Success
Product marketers equip sales teams with the tools, training, and content necessary to effectively sell the product. This includes creating demo scripts, FAQs, and objection-handling guides tailored to the product.
Top 10 Product Development Tools

Effective product development requires a blend of creativity, coordination, and data-driven decision-making. Here are the top tools used in the product development lifecycle, their unique selling points (USPs), and key functionalities.
1. Amplitude
USP: Advanced Behavioral Analytics for User-Centric Products
Amplitude excels at tracking user interactions and providing actionable insights through funnel analysis, retention metrics, and product A/B testing. It helps teams understand customer behavior deeply, enabling the optimization of user experiences.
Best For: Analytics and behavior-driven decision-making.
2. Atlassian
USP: Comprehensive Suite for Agile Product Management
Atlassian offers tools like Jira for project tracking, Confluence for collaboration, and Trello for task management. It is ideal for agile workflows, ensuring transparency and team alignment.
Best For: Agile product management and cross-team collaboration.
3. Productboard
USP: Customer-Focused Prioritization
Productboard helps teams centralize customer feedback, prioritize features, and align development roadmaps with business goals. Its simple interface and robust capabilities make it indispensable for customer-driven product planning.
Best For: Building products aligned with user needs.
4. Asana
USP: Streamlined Task and Workflow Management
Asana is known for its user-friendly interface, task prioritization, and automation features. It ensures efficient team coordination, from ideation to execution, with customizable workflows and progress tracking.
Best For: Task management and streamlined workflows.
5. Figma
USP: Real-Time Design Collaboration
Figma is a favorite among designers for creating UI/UX prototypes. It supports collaborative design in real time, offering tools for feedback, prototyping, and exporting designs seamlessly.
Best For: Collaborative design and prototyping.
6. Aha!
USP: Strategic Product Roadmapping
Aha! focuses on visualizing product strategies, collecting feedback, and organizing ideas. It’s particularly useful for teams that need to maintain a clear strategic direction while managing development priorities.
Best For: Strategic planning and roadmapping.
7. Monday.com
USP: Versatile Workflow Customization
Monday.com provides highly customizable templates, integrated communication tools, and resource allocation features. It’s perfect for teams that require flexible workflows for various project types.
Best For: Versatile project and resource management.
8. Notion
USP: All-in-One Workspace for Documentation and Collaboration
Notion combines note-taking, databases, and project management features. It’s ideal for teams that need a central repository for ideas, plans, and documentation.
Best For: Centralized documentation and collaborative planning.
9. Miro
USP: Virtual Whiteboarding for Creative Collaboration
Miro supports brainstorming, wireframing, and strategic planning through an interactive virtual whiteboard. It’s particularly effective for distributed teams to collaborate visually.
Best For: Creative brainstorming and visual planning.
10. Slack
USP: Seamless Team Communication
While Slack is primarily a messaging platform, its integrations with tools like Jira, Asana, and Google Drive make it essential for real-time communication and project updates.
Best For: Team communication and quick updates
FAQs: New Product Development Process
1. What do you mean by the new product development process?
The new product development (NPD) process is a structured approach used by businesses to bring innovative products to market. It involves several stages, such as brainstorming ideas, conducting market research, prototyping, testing, and finally launching the product. Each step is designed to ensure that the product aligns with customer needs and business goals, while minimizing risks and maximizing potential success.
2. How long does it take to develop a new product and get it to market?
The duration of developing and launching a product can vary significantly based on factors such as industry, product complexity, and regulatory requirements. On average, it can take anywhere from a few months for software solutions to several years for highly regulated products like pharmaceuticals or complex machinery. Time is heavily influenced by market research, prototyping cycles, and pre-launch testing phases.
3. Is product development the same as product management?
While product development and product management are interconnected, they serve different purposes. Product development refers to the technical and creative aspects of designing and building a product, involving engineers, designers, and other specialists. Product management, on the other hand, focuses on the strategic planning, market alignment, and lifecycle management of the product to ensure it meets customer needs and achieves business objectives.
4. What are the next steps in the product development process after a new product is launched?
Once a product is launched, businesses shift their focus to monitoring its performance in the market. This involves collecting customer feedback, analyzing sales and engagement data, and identifying areas for improvement. Marketing strategies may be refined to better align with audience responses, and iterative updates or feature enhancements may be implemented to address issues or capitalize on new opportunities. Scaling the product to broader markets often follows a successful initial launch.
5. What role do new products play in a company’s success?
New products are pivotal in driving a company’s growth and sustainability. They open new revenue streams, allow businesses to capture untapped market segments, and strengthen the brand’s competitive edge. Moreover, innovative offerings can enhance customer loyalty by addressing evolving demands and providing fresh solutions, ensuring that the business remains relevant in a dynamic marketplace.
6. What skills do you need to build a repeatable NPD process?
Building a repeatable NPD process requires a combination of analytical and collaborative skills. Market research expertise is essential for identifying trends and consumer needs, while strong project management ensures that timelines and budgets are adhered to. Effective communication and cross-functional collaboration are crucial for aligning diverse teams, and an agile mindset enables adaptability to market feedback and unforeseen challenges.
7. Why do you need a repeatable NPD process?
A repeatable NPD process provides consistency and efficiency in bringing products to market. It reduces risks by standardizing steps like idea evaluation and prototyping, ensuring that resources are optimally utilized. Additionally, having a repeatable framework makes the process scalable, allowing companies to innovate across multiple product lines without reinventing their workflows for each project.
8. What are the next steps in NPD after a product is launched?
After launching a product, the focus should shift toward understanding how it performs in the market. Customer engagement is prioritized to gather valuable insights about their experiences, while sales data and usage metrics help evaluate the product’s impact. Based on these findings, iterative updates may be made to improve features or address shortcomings. Simultaneously, companies may start exploring ways to scale the product to larger or new audiences, further enhancing its market presence.

