Imagine a customer is about to purchase a basic smartphone online. As they check out, they see a prompt encouraging them to upgrade to a model with a better camera and faster processor. This suggestion nudges them to consider a better version of what they were already set on buying. However, before completing the transaction, they also encounter related recommendations: a phone case, a screen protector, and wireless earbuds that complement the purchase.
Table of Contents
This simple scenario exemplifies two powerful sales tactics used by businesses worldwide: up-selling and cross-selling. While both techniques aim to increase sales, they serve distinct purposes and require different approaches. Mastering the difference between upselling and cross-selling enables businesses to boost revenue, improve customer experience, and build long-term loyalty. In this guide, we’ll dive deep into each concept, providing examples, strategies, and tips to help you effectively apply these techniques in your business.

What is Upselling?
Before understanding the difference between upselling and cross-selling, let’s look at what both of these exactly mean.
Upselling encourages customers to purchase a higher-end version or premium model of their chosen product or service. It’s a way of helping customers see the value in a more feature-rich product that might better meet their needs, providing a win-win scenario when executed well.
Why Upselling Matters
Upselling is a powerful tactic that allows businesses to increase the average order value and strengthen customer relationships by meeting their needs in a more comprehensive way. When upselling emphasizes real benefits, it can boost customer satisfaction as people leave with a product that adds value to their life or business.
For instance, if someone buys a mid-range laptop for work, an effective upsell could be a premium laptop with enhanced processing speed and additional features that support better multitasking. Customers may realize the added functionality can benefit them long-term, making the upsell feel worthwhile.
Examples of Upselling
- Tech and Gadgets: When a customer selects a basic laptop model, they’re encouraged to choose a version with upgraded specifications, like extra memory or faster processing power.
- Travel and Hospitality: Airlines often upsell by promoting seat upgrades from economy to business class, emphasizing perks like more legroom, priority boarding, and premium meals.
- Food and Beverage: In a fast-food chain, customers ordering a small meal may be offered a larger combo with additional items or a premium drink.
- Subscription Services: Streaming platforms or software providers frequently encourage users to switch from free or basic tiers to premium versions, highlighting features such as ad-free browsing, exclusive content, or multi-device support.
- Retail: Clothing stores often recommend designer or higher-quality versions of clothing items as an upsell, showcasing the added benefits in terms of fabric quality, fit, and durability.

What is Cross-Selling?
Cross-selling, unlike upselling, suggests products that complement the main purchase. The intent is to create a more complete shopping experience by recommending items that might enhance the value or usability of the primary purchase. Cross-selling helps businesses increase their average order value while fulfilling a broader set of customer needs.
Why Cross-Selling is Important
Cross-selling not only boosts the total sale amount but also enhances the customer experience by making thoughtful suggestions. When cross-sell items are chosen well, customers feel that their needs have been anticipated, which can lead to a stronger sense of loyalty.
For instance, when someone buys a digital camera, cross-selling related items like memory cards, camera bags, and tripods helps provide a complete solution. Cross-selling saves the customer time and effort by showing all the accessories they may need to get the most from their purchase.
Examples of Cross-Selling
- Tech and Electronics: Customers buying a laptop are shown complementary items like laptop bags, mice, or external hard drives.
- E-commerce: Online retailers suggest accessories like scarves, belts, or jewelry to customers who purchase clothing items.
- Automotive: Car dealerships might cross-sell extended warranties, seat covers, or GPS systems to customers buying a new vehicle.
- Financial Services: When opening a bank account, customers might be offered credit cards, savings accounts, or insurance options to build a complete financial plan.
- Retail Stores: Grocery stores often cross-sell by suggesting recipe-based items together. For example, someone buying pasta might be shown sauce, cheese, or salad ingredients.
Also Read: B2C vs D2C: Key Differences between e-commerce models and which is better
Difference Between Upselling and Cross-Selling
While both upselling and cross-selling aim to increase sales and improve customer satisfaction, they operate with distinct goals and require different approaches.
| Aspect | Up-selling | Cross-selling |
| Primary Goal | Encourage customers to purchase a more expensive or premium version of the selected item. | Suggest complementary items that enhance the primary purchase. |
| Focus | Enhances the main product by offering a better, upgraded version. | Provides a complete solution by suggesting related products. |
| Customer Benefit | Provides improved features or higher quality in the primary item. | Creates added value by offering additional functionalities or accessories. |
| Sales Timing | Often suggested during the product selection or pre-checkout stage. | Frequently presented post-selection or during checkout. |
| Product Scope | Typically focuses on one primary product that the customer initially considered. | Broadens the scope by introducing related items from different categories. |
| Example | Suggesting a higher-capacity smartphone with better specifications. | Recommending a phone case, screen protector, or earbuds with the phone purchase. |
| Typical Industries | Common in tech, electronics, software, travel, and luxury retail. | Common in retail, food & beverage, e-commerce, and automotive. |
| Customer Perception | Seen as an opportunity to get a superior version that fits their needs better. | Viewed as helpful suggestions for accessories they may have overlooked. |
| Impact on AOV (Average Order Value) | Increases AOV by offering higher-priced product alternatives. | Increases AOV by adding multiple related, usually lower-priced items. |
| Sales Strategy | Uses comparative benefits to highlight features and advantages of a premium option. | Uses bundling and recommendations to show how additional items complement the purchase. |
In essence, upselling adds value by suggesting a better version, while cross-selling enhances the customer experience with complementary items.
Also Read: 101 Guide: Start an E-Commerce Business in India
Best Strategies for Cross-Selling
Now that you’ve understood the difference between upselling and cross-selling, it’s time to see what strategies to use while applying these to your business.
Cross-selling can be extremely effective when done thoughtfully and strategically. Here are some tips to maximize its effectiveness:
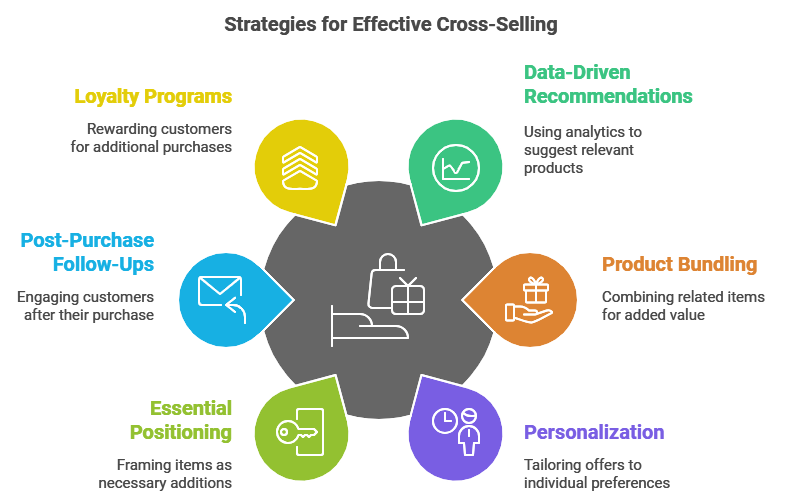
1. Use Data-Driven Recommendations
With the help of data analytics, businesses can use purchase history and browsing patterns to make targeted recommendations. Amazon’s “Customers who bought this item also bought…” is a prime example of this data-driven cross-selling. By suggesting popular add-ons, you enhance relevance and increase conversion rates.
2. Bundle Products
Create bundles of related products to provide convenience and added value. For example, a bookstore might bundle books by the same author or within the same genre, giving customers an easy way to discover similar reads.
3. Leverage Personalization
Personalized cross-selling ensures that recommendations are highly relevant. Retailers can use machine learning to analyze individual customer preferences, creating a sense of a custom-curated experience.
4. Position Cross-Sells as Essential Additions
By positioning cross-sell items as essential accessories, you can make customers feel that they’re purchasing a complete package. For instance, a gym might suggest a range of health supplements or fitness equipment, framing them as key to an effective workout plan.
5. Utilize Post-Purchase Follow-Ups
Cross-selling doesn’t have to be limited to the checkout phase. Email marketing can be a powerful way to recommend items post-purchase. A clothing brand, for example, could follow up with emails suggesting matching accessories or seasonal items based on previous purchases.
6. Create a Loyalty Program to Encourage Cross-Selling
Loyalty programs can be structured to reward customers for purchasing complementary items. For example, a beauty retailer could offer points for buying skincare products that work well together, encouraging customers to try additional products.
7. Highlight Customer Reviews for Cross-Sell Products
Displaying reviews of cross-sell products can reassure customers of their value and quality. A retailer selling laptops could showcase positive feedback for laptop bags and accessories, increasing the credibility of the cross-sell items.
Best Strategies for UpSelling
Upselling requires subtlety and insight into customer preferences. Here are the most effective ways to approach upselling:
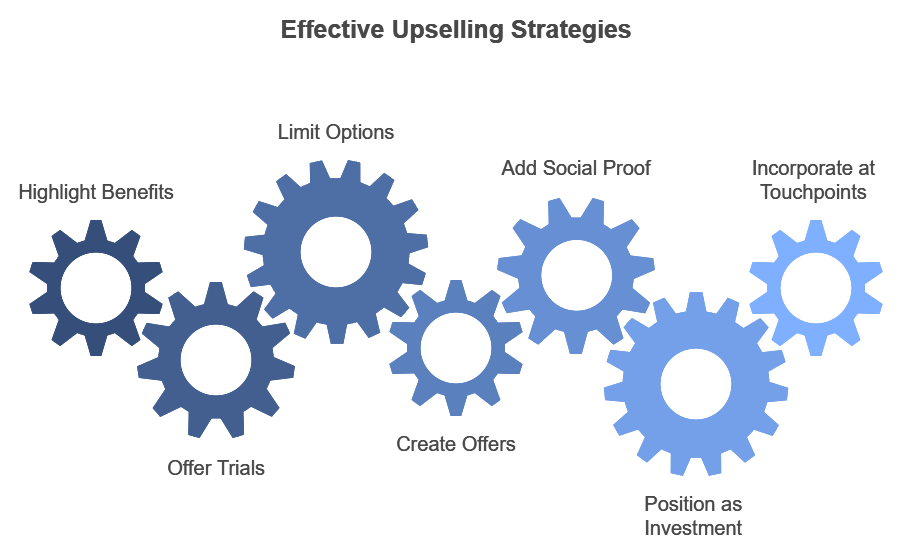
1. Highlight Comparative Benefits
When presenting a more expensive option, make sure to showcase its unique features and benefits. Comparison charts that illustrate differences can help customers understand why the premium version might be a better choice.
2. Offer a Trial of Premium Versions
Allowing customers to try premium products helps them experience the added value. A SaaS company offering a 30-day trial of a premium version can encourage users to explore advanced features, which they may find essential by the end of the trial.
3. Limit Upsell Options to Avoid Overwhelm
Instead of displaying too many upgrade choices, limit the options to one or two recommendations that align with customer needs. For example, a fashion brand might only suggest one high-end version of a basic clothing item, helping customers make faster decisions.
4. Create Limited-Time Offers for Premium Products
Time-sensitive offers encourage quick decision-making, which can lead to higher conversion rates. A food delivery service offering a limited-time discount for an upgraded meal plan encourages customers to act quickly to get the premium experience.
5. Add Social Proof with Testimonials
Display testimonials from customers who’ve chosen the premium product to showcase its value. A tech company might display reviews of users who upgraded to the pro version, helping new buyers feel confident in choosing the upgrade.
6. Position Upsell Items as Investments
Upselling works best when customers see the upgrade as a long-term investment. A car dealership could position a premium model as a safer, longer-lasting choice, helping customers justify the higher cost.
7. Incorporate Upsell Offers at Key Touchpoints
The timing of upsell recommendations can greatly impact their effectiveness. Displaying the option to upgrade at strategic points—like right after a customer has committed to the initial purchase—can boost conversions. For example, an e-commerce website might recommend an upgraded version on the checkout page as a “last chance” offer.
Industry-Specific Applications for Up-Selling and Cross-Selling
Different industries adapt upselling and cross-selling tactics based on customer expectations, product types, and typical purchase journeys.
E-commerce
Upselling: Online stores frequently use data to make upsell suggestions. An e-commerce fashion retailer, for instance, might recommend a high-end clothing line to shoppers who frequently browse luxury brands.
Cross-selling: E-commerce platforms are known for “frequently bought together” sections, which entice customers to add related items to their cart.
Travel and Hospitality
Upselling: Airlines and hotels excel at upselling, often suggesting seat or room upgrades with added amenities that enhance the travel experience.
Cross-selling: The travel industry excels at offering experiences like excursions, car rentals, or dining packages that enhance the overall trip.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Upselling: SaaS companies often encourage customers to move up to premium tiers by highlighting advanced features that solve more complex business needs.
Cross-selling: They cross-sell by offering add-ons, integrations, or companion tools that make the software even more effective.
Which is Better, Upsell vs Cross Sell?
Ultimately, the best strategy for any business is likely a combination of both up-selling and cross-selling, applied thoughtfully based on customer needs, industry, and buying behavior. Emphasizing the difference between upselling and cross-selling allows businesses to design sales strategies that cater to various customer segments effectively. A data-driven approach—backed by testing and insights—will reveal which combination yields the best results in terms of revenue and customer satisfaction.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between upselling and cross-selling allows businesses to strategically enhance customer value, build loyalty, and boost revenue. By refining these techniques to fit your specific industry and customer needs, you can deliver a richer shopping experience, turning one-time buyers into repeat customers and loyal advocates.
FAQs: Difference Between Upselling and Cross-selling
What is the difference between upselling and cross-selling?
The difference between upselling and cross-selling lies in their objectives. Upselling encourages customers to purchase a more expensive version of a product they are already considering, while cross-selling suggests related products that complement the original item. For example, upselling might involve recommending a premium laptop model, whereas cross-selling could involve suggesting a laptop bag or software.
Can you provide examples of upselling and cross-selling?
In a restaurant, upselling may occur when a server suggests a more expensive wine to pair with a meal. On the other hand, cross-selling happens when the same server recommends appetizers or desserts that complement the main course.
Why is understanding the difference between upselling and cross-selling important for businesses?
Understanding the difference between upselling and cross-selling helps businesses tailor their sales strategies effectively. By recognizing when to use each technique, companies can enhance customer satisfaction, increase average order value (AOV), and ultimately boost revenue.
Are upselling and cross-selling effective in all industries?
While both strategies can be effective in various industries, their success may vary depending on the target market and product types. For instance, tech and luxury retail often see great success with upselling, while e-commerce platforms frequently leverage cross-selling through “frequently bought together” features.
How can businesses implement effective upselling and cross-selling strategies?
To implement effective upselling and cross-selling strategies, businesses should analyze customer behavior, train sales staff to identify opportunities, and use data-driven insights to make personalized recommendations. Understanding the difference between upselling and cross-selling can guide businesses in developing targeted approaches for their customers.
What role does customer experience play in upselling and cross-selling?
Customer experience is crucial in both upselling and cross-selling. If done correctly, these techniques can enhance customer satisfaction by offering relevant and helpful suggestions. However, aggressive or pushy tactics can lead to a negative experience, so it’s important to approach both strategies thoughtfully.
Can upselling and cross-selling lead to customer loyalty?
Yes, when executed well, upselling and cross-selling can foster customer loyalty. By providing customers with valuable options that genuinely meet their needs, businesses can build trust and encourage repeat purchases. Understanding the difference between upselling and cross-selling is essential in creating a cohesive and satisfying shopping experience.

