When was the last time you went shopping for something big—say, a new phone or a car? If you think about it, the process wasn’t as simple as just picking an item and paying for it. First, there was the realization that you needed (or wanted) a new phone, then a deep dive into the latest models, endless comparisons, maybe some trial runs at a store, and finally, that exhilarating decision to buy. But even after your purchase, you likely evaluated whether you’d made the right choice.
This multi-step journey is known as the consumer buying process, a sequence of steps consumers go through before and after making a purchase. Let’s explore each stage of this journey, why understanding it is crucial for businesses, and how real-world brands successfully navigate this process to connect with consumers on a deeper level.
Table of Contents
What is the Consumer Buying Process?
The consumer buying process is the journey a consumer undertakes when deciding to purchase a product or service. It encompasses everything from the initial recognition of a need to post-purchase reflections, and it’s shaped by various personal, psychological, and social influences.
The process isn’t linear; it’s a dynamic, feedback-driven sequence that helps marketers predict consumer actions. For example, when someone decides they want a new smartphone, they’ll often consider factors like budget, brand, and features before purchasing. But this decision-making process isn’t only relevant for high-ticket items—consumers go through it for all kinds of purchases, big or small.
This process helps marketers understand how consumers think, what factors drive their decisions, and how they can influence these choices. With this insight, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to create better consumer experiences and, ultimately, boost sales.
The Importance of Consumer Buying Behavior
Understanding consumer buying behavior isn’t just a “nice-to-have” for brands—it’s essential. Here’s why it matters:
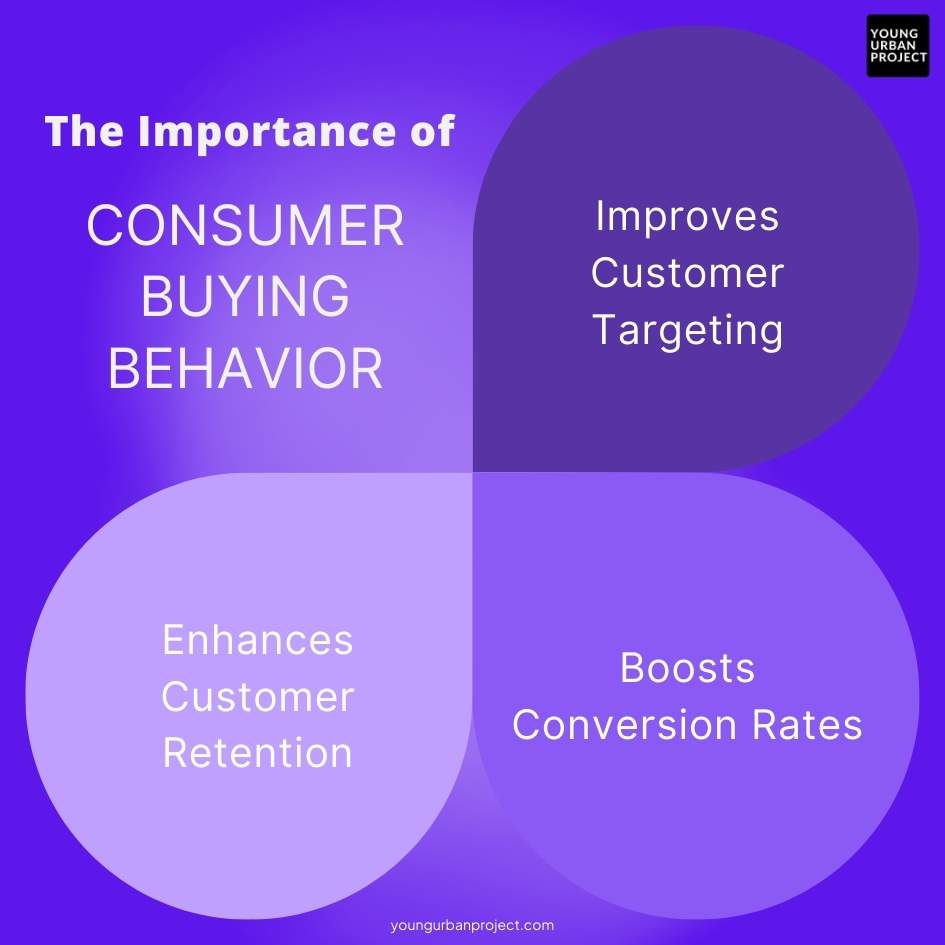
Improves Customer Targeting
When brands understand what drives their consumers, they can refine their targeting efforts and deliver tailored messaging that speaks directly to consumer needs. For example, a skincare brand aware that customers often seek products for specific skin issues, such as dryness or acne, can create ads or content addressing these pain points specifically.
Boosts Conversion Rates
By understanding consumer behavior, brands can remove friction points from the buying journey, guiding customers smoothly from one stage to the next. Apple, for instance, simplifies its purchase experience by offering comprehensive in-store support and an easy-to-use website that ensures customers find the information they need at each stage.
Enhances Customer Retention
By focusing on the post-purchase experience, brands can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty. Amazon excels in this area with its hassle-free return policy and proactive customer service, creating a post-purchase experience that encourages repeat buying.
Understanding consumer buying behavior gives businesses the power to meet customers where they are—through awareness, education, or support—at every step of their journey.
The Five Stages of the Consumer Buying Process
Let’s break down each step in the consumer buying process, from the initial spark of interest to the final post-purchase reflection.
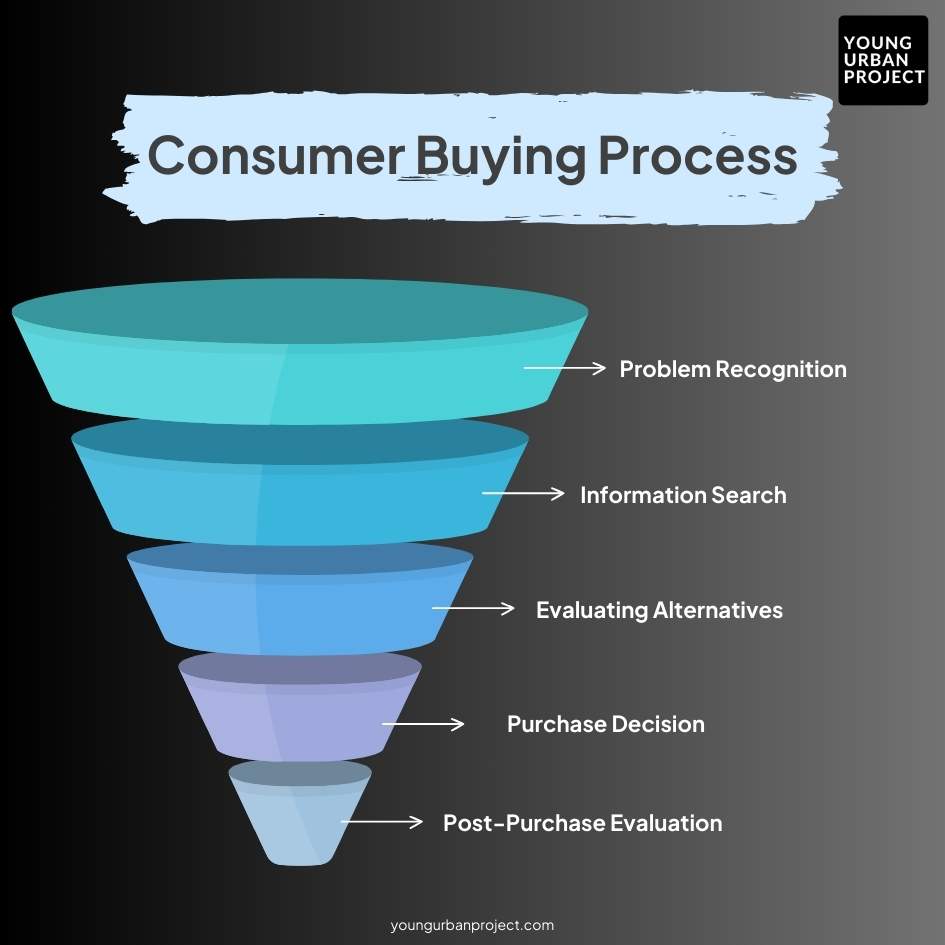
Stage 1: Problem Recognition
The first step is when a consumer recognizes a need or a problem they want to solve. This need might arise from a gap in their current lifestyle (like realizing they need a faster laptop) or external influences (like seeing a friend’s new watch and feeling inspired).
Example: Imagine you’re on a road trip, and halfway through, you realize your car’s AC isn’t working well. This discomfort creates a need for an upgrade or repair. Marketers can capitalize on this stage by addressing specific “pain points.” A car repair brand, for instance, might run targeted ads focusing on quick and affordable AC repair services, hoping to capture consumers’ attention when they’re facing issues.
Marketing Tactics: At this stage, marketers need to raise awareness of their products or services. Brands often run ads, create content, or share user-generated content that emphasizes the problems their offerings solve.
Stage 2: Information Search
Once a need is recognized, consumers seek information to address it. This research phase varies in intensity depending on the purchase’s complexity and importance. For more significant purchases, consumers might read reviews, consult friends, or watch product demos, while for everyday items, they might just check a quick review.
Example: Let’s say someone is looking to buy a fitness tracker. They might start by reading online reviews, watching YouTube comparisons, or asking friends for recommendations. A company like Fitbit might have an advantage here by offering detailed product specs, customer testimonials, and educational resources on their website, helping guide potential customers in their research.
Marketing Tactics: Brands can gain trust at this stage by providing detailed information and comparisons. Creating SEO-optimized blogs, videos, and guides can be highly effective, as consumers often look for content that compares features, prices, and benefits.

Enroll Now: Performance Marketing Training
Stage 3: Evaluating Alternatives
After gathering information, consumers begin comparing different options, assessing the pros and cons. They consider factors like price, quality, brand reputation, and features to determine which option best meets their needs.
Example: If a customer is considering a new smartphone, they may weigh the pros and cons of an iPhone versus a Samsung Galaxy. This is a highly competitive stage as brands try to set themselves apart. Samsung, for instance, might emphasize unique features like its stylus or multi-tasking capabilities to appeal to consumers looking for productivity tools.
Marketing Tactics: At this stage, brands should highlight their unique selling points. Testimonials, case studies, and side-by-side product comparisons can help consumers understand what makes one product superior to another.
Stage 4: Purchase Decision
This is the moment of truth: the consumer has gathered information, evaluated options, and is ready to make a purchase. But it doesn’t mean the decision is set in stone. Factors like last-minute discounts, special offers, or customer service support can tip the balance.
Example: Say someone’s chosen a high-end camera but is still debating whether to buy it. If they visit a store and the salesperson offers a limited-time discount, the consumer may be nudged to purchase immediately. Retailers often capitalize on this moment with special offers, easy financing, and limited-time deals.
Marketing Tactics: Brands can facilitate the purchase decision by offering discounts, convenient payment options, or customer support to address any lingering questions. Making the purchasing experience as seamless and enjoyable as possible is key to closing the sale.
Stage 5: Post-Purchase Evaluation
Once the purchase is made, consumers evaluate whether the product met their expectations. Positive experiences can lead to repeat purchases, while dissatisfaction can deter future buying and lead to negative reviews.
Example: After purchasing a new mattress, a customer might assess how well it improves their sleep quality. Brands like Casper excel at this stage by offering generous return policies, follow-up emails, and tips for product care, reinforcing customer satisfaction and trust.
Marketing Tactics: The post-purchase phase is crucial for customer retention. Brands can reach out with feedback requests, offer loyalty rewards, or provide additional resources to enhance the product experience.
Also Read: Digital Marketing Funnels Explained in Easiest Way with Example
Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Various factors can influence consumer decisions at each stage of the buying process. Here’s a look at the primary influences:
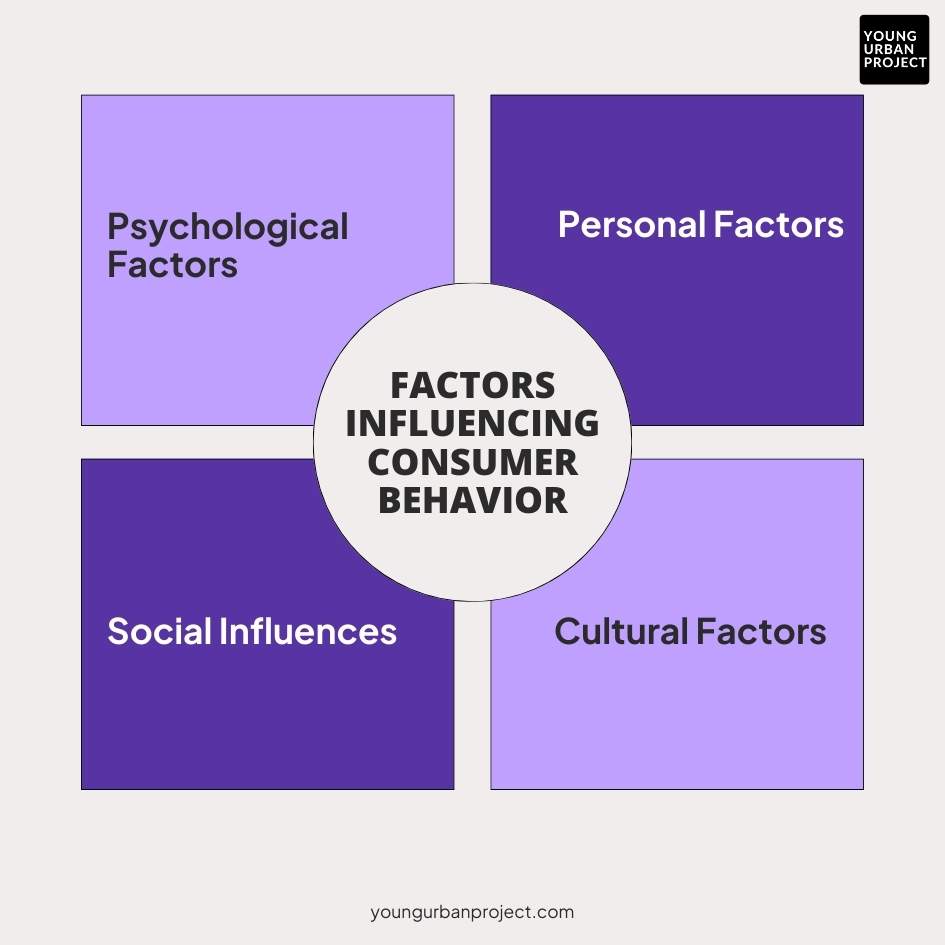
Psychological Factors
Motivation, perception, beliefs, and attitudes are powerful motivators. For example, consumers motivated by health may lean toward organic food products, while environmentally conscious consumers may prefer sustainable brands.
Personal Factors
Age, income, occupation, and lifestyle all shape consumer preferences. Someone with a higher income may prioritize premium products, while younger consumers might be drawn to trend-driven brands.
Social Influences
Family, friends, and societal norms often impact buying decisions. Social proof, like recommendations from friends or influencers, can significantly affect consumer choices.
Cultural Factors
Consumers’ cultural backgrounds influence their values and buying preferences. For instance, in certain cultures, luxury brands may carry more status, influencing consumers’ brand choices.
Understanding the Consumer Buying Process at Every Stage
The key to successful marketing is understanding consumer behavior at every stage. Here’s how brands can meet consumers where they are:
Problem Recognition
Create awareness by showcasing relatable issues or needs that your product can solve. Testimonials or ads depicting real-life scenarios are effective here.
Information Search
Offer valuable resources that educate consumers, such as product guides or comparison articles, to position yourself as a trusted source.
Evaluating Alternatives
Highlight unique benefits that differentiate your brand. Testimonials, endorsements, or product demos can sway decisions at this stage.
Purchase Decision
Simplify the checkout process, offer incentives, and ensure a frictionless buying experience. Clear pricing, payment options, and customer support are vital.
Post-Purchase
Follow up to ensure customer satisfaction. Send thank-you notes, offer support, or encourage feedback. Positive post-purchase interactions can build loyalty and turn customers into advocates.
Also Read: Revealed: How customers prefer to get customer service on digital
Post-Purchase Experience and Customer Satisfaction

The post-purchase experience can make or break customer loyalty. A positive experience ensures repeat business, while negative experiences may lead to lost customers and negative reviews.
Example: Let’s say a customer buys a coffee maker. After using it for a week, they find an issue with the brew strength. If the company has a supportive customer service team that promptly resolves the issue, the customer is more likely to remain loyal, even recommending the product to friends.
Why it Matters: Post-purchase satisfaction is the foundation of brand loyalty. By ensuring that customers feel valued, brands can increase the likelihood of repeat purchases and word-of-mouth referrals.
Strategies to Enhance Post-Purchase Satisfaction:
- Request Feedback: Reach out to customers for feedback and show that their opinions matter.
- Provide Product Tips: Offer resources that help customers get the most from their purchase.
- Offer Support: Ensure customers can quickly access support if they encounter issues.
Also Read: What is Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) and How to calculate it
Conclusion
Understanding the consumer buying process isn’t just about closing a sale; it’s about creating a cohesive experience that guides consumers from awareness to post-purchase satisfaction. By meeting consumers at each stage of their journey, brands can build lasting relationships, increase loyalty, and foster brand advocacy.
Today’s consumers expect more than just a product—they want experiences that solve their problems, add value to their lives, and leave them feeling satisfied. With a strategic approach to the consumer buying process, brands can build meaningful connections that go beyond a single transaction.