Growth marketing has become a famous term currently, especially among marketers aiming for rapid business success. Unlike conventional marketing, which often seeks immediate outcomes, growth marketing takes a more holistic approach. It’s centered on sustainable growth through ongoing experimentation, analysis, and optimization of every stage in the customer journey.
It focuses on long-term growth through continuous experimentation, data-driven analysis, and optimization across all stages of the customer journey. Whether you’re an established marketing professional or just beginning your career, understanding the principles of growth marketing is crucial for remaining competitive and achieving success in today’s dynamic market.
Table of Contents
What is Growth Marketing?
Growth marketing is a strategic approach that integrates data analytics with creative techniques to accelerate user acquisition, boost retention, and fuel overall business growth.
Unlike traditional marketing, which often focuses on top-of-the-funnel objectives like brand awareness or lead generation, growth marketing takes a holistic view of the entire customer lifecycle. This includes stages such as acquisition, activation, retention, revenue, and referral, commonly known as the AARRR funnel.
Growth marketers leverage a variety of methods, including A/B testing, content marketing, SEO, email campaigns, and paid advertising. Through continuous experimentation and refinement, they identify the most effective tactics for sustained growth.
Why is Growth Marketing Important?
Data-Driven Decision Making: Growth marketing places a strong emphasis on data analysis, enabling marketers to make well-informed decisions. This reliance on data minimizes uncertainty, resulting in more effective strategies and improved outcomes.
Customer-Centric Approach: By examining the complete customer journey, growth marketing optimizes the customer experience at every interaction. This focus on the customer not only enhances satisfaction but also increases retention and lifetime value.
Scalability: Growth marketing strategies are designed to be scalable. Once successful tactics are identified, they can be replicated and expanded to achieve even greater results.
Long-Term Growth: In contrast to traditional marketing, which often seeks immediate gains, growth marketing is aimed at achieving sustained long-term success. By continuously refining their strategies and tactics, businesses can maintain growth over time.
Also Read: Skimming Pricing Strategy: A Comprehensive Guide to Maximizing Early Profits
The Six Stages of Growth Marketing
1. Awareness
The awareness stage is the foundation of the growth marketing process, where the primary goal is to generate interest in your product or service among potential customers.
Strategies:
- Content Marketing: Creating valuable and informative content such as blog posts, infographics, and videos that address common pain points or questions within your target audience. For example, a software company might produce a series of blog articles on productivity tips that incorporate their product as a solution.
- Social Media Marketing: Leveraging platforms like Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn, and Twitter to share engaging content and interact with your audience. For instance, a fitness brand might post-workout tips and user testimonials to engage users on social media.
- Paid Advertising: Utilizing pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns and social media ads to reach a wider audience quickly. A new app could run Facebook ads targeting specific demographics based on interests and behaviors to drive traffic to their landing page.
2. Acquisition
In this stage, the focus shifts from simply creating awareness to converting that interest into leads or customers. This involves capturing contact information and encouraging users to take a specific action.
Strategies:
- Landing Pages: Designing dedicated landing pages that provide a clear value proposition and strong calls-to-action (CTAs) to convert visitors. For example, an online course platform might create a landing page offering a free trial to entice users to sign up.
- Lead Magnets: Offering free resources such as eBooks, webinars, or templates in exchange for email addresses. For instance, a digital marketing agency might offer a free eBook on SEO strategies to attract potential clients.
- Email Sign-Ups: Encouraging visitors to subscribe to newsletters or updates for exclusive content or discounts. A retail website might offer a discount code for signing up, thereby increasing their email list.
3. Activation
The activation stage focuses on ensuring that newly acquired users have a positive experience that encourages them to engage fully with the product or service.
Strategies:
- Onboarding Process: Implementing a smooth onboarding experience that guides users through the initial setup and features of the product. For example, a SaaS company may use interactive tutorials that highlight key functionalities.
- Personalized Communication: Sending tailored emails or notifications that guide users through their first interactions with the product. An app might send personalized onboarding emails based on user preferences gathered during sign-up.
- Trial Periods: Offering free trials or limited-time offers to allow users to explore the product without risk. A subscription service might provide a month of free access to entice users to experience its full value.
4. Retention
Retaining customers is critical for sustainable growth, as it is generally more cost-effective to keep existing customers than to acquire new ones.
Strategies:
- Customer Engagement: Regularly communicating with customers through newsletters, updates, and personalized recommendations based on their usage. For instance, a streaming service may send tailored movie recommendations based on viewing history.
- Loyalty Programs: Implementing programs that reward repeat customers with points, discounts, or exclusive access. A coffee shop chain could create a loyalty card system where customers earn free drinks after a certain number of purchases.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Actively seeking customer feedback to identify pain points and improve the product or service. A software company might use surveys or feedback forms to understand user satisfaction and areas for improvement.
5. Revenue
At this stage, the goal is to maximize revenue from existing customers through various monetization strategies.
Strategies:
- Upselling and Cross-Selling: Encouraging customers to purchase additional features or products that complement their original purchase. For example, an online software provider might offer advanced features at a premium rate.
- Subscription Models: Implementing subscription-based pricing to ensure recurring revenue. A content platform may offer tiered subscription levels, each providing different access levels to content.
- Limited-Time Offers: Using scarcity and urgency in marketing campaigns to encourage quick purchases. A retailer might run flash sales or limited-time discounts on select items to drive immediate revenue.
6. Referral
The final stage leverages satisfied customers to generate new leads through referrals, capitalizing on existing relationships and trust.
Strategies:
- Referral Programs: Creating programs that incentivize current customers to refer new users, often by providing rewards or discounts for successful referrals. For example, a ride-sharing service may offer ride credits for both the referrer and the new user.
- Shareable Content: Producing engaging and shareable content that encourages users to spread the word. An online quiz or interactive printable poster can entice users to share results on social media.
- Testimonials and Reviews: Actively encouraging satisfied customers to leave reviews or share their experiences online. A product might prompt users to write reviews in exchange for future discounts or free trials.
Successful Growth Marketing Case Studies
Tinder

Tinder’s journey, despite being clouded by controversy and rumors, is undeniably intriguing. Its growth has been fueled by both media attention and innovation within a crowded and stagnant market.
Since its launch in late 2012, Tinder has amassed 75 million monthly active users.
While there may be uncertainty around its financial valuation and controversies, the most compelling aspect of Tinder’s story lies in its impressive growth.
Here’s a brief breakdown:
Tinder’s Strategy: Online dating is notoriously challenging, but Tinder understood the key to success. The platform focused on getting a substantial number of women to join first, knowing this would encourage men to follow. They tackled this by targeting sorority houses and recruiting female users dorm by dorm. Once enough women were on board, it was easy to draw in male users with the promise of potential dates.
Gamifying the Experience: Tinder’s need for a large user base in each location led to a gamification strategy. The app’s “swiping” feature creates a sense of anticipation, keeping users engaged as they hope to match with someone new. This gamified experience has been a critical factor in its widespread appeal.
Improving the Experience: In a saturated market, Tinder didn’t just create another dating app — it addressed common user frustrations. Features designed to protect women from unwanted attention made the platform more inviting and enjoyable for them, which contributed to increased female participation and overall growth.
Continuous Innovation: To keep users engaged, Tinder consistently adds new features, evolving the app into a more social experience while maintaining its core function. Add-ons like “Matchmaker,” which allows friends to introduce each other, and “Moments,” which lets users share edited photos with matches, keep the platform dynamic and fresh.
Canva

In the past, creating a flyer, banner, or any design without design expertise meant either hiring a professional or enduring the frustrating process of using PowerPoint or, even worse, Word Art. Today, however, Canva has transformed the landscape of basic graphic design, making it accessible to everyone.
Here’s a look at their growth strategy:
User-Friendly Design: Although various tools existed for quick design creation, they often fell short in user interface, cost, or ease of use. Canva addressed these issues right from its inception. The platform features an intuitive interface with easy-to-use templates and is web-based, eliminating the need for downloads or installations. Most importantly, the free version offers significant functionality, quickly establishing Canva as the go-to tool for anyone needing quick design solutions.
Transparent Pricing and Value Proposition: Canva has simplified the upgrade process for users considering the paid version. The free version allows newcomers to explore the platform, integrating it into their workflow. Once users become accustomed to its benefits, upgrading to the paid version for added features becomes an easy decision. Notably, Canva’s pricing was strategically positioned within a “Goldilocks zone,” appealing to its target audience compared to competitors.
Rapid User Growth: In its first two years, Canva experienced remarkable growth, expanding from 0 to 2 million monthly users. And now, that number has skyrocketed to 180 million users, including 16 million paying customers, and the company is now valued at $40 billion.
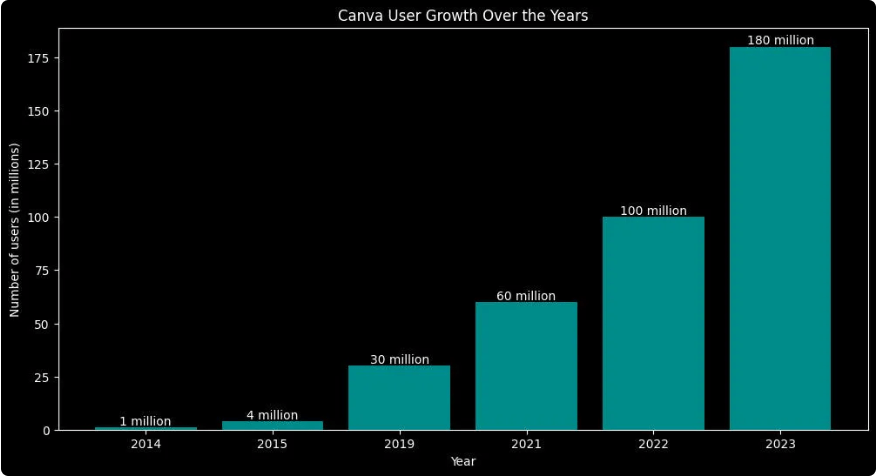
This impressive trajectory resulted from a combination of a product that resonates with its audience and a consistent investment in paid advertising across major social media platforms.

LinkedIn has become a favorite among executives, job seekers, and networking professionals. Launched in 2003, the platform attracted half a million users within its first year, and its growth trajectory has only accelerated since then. Today, it stands as a publicly traded company (LNKD).
Here’s a snapshot of LinkedIn’s growth journey:
Identifying a Need: The demand for high-quality connections among employers and job seekers created an opportunity for LinkedIn. While other platforms existed in the early 2000s, none catered specifically to executives and decision-makers looking for valuable networking opportunities. LinkedIn effectively seized this gap in the market.
Targeting a Niche: Initially, the startup faced challenges due to the tech bubble, but it pivoted its focus toward Silicon Valley. There, it found executives eager to connect with qualified talent and grow their teams. This strategic choice helped establish acceptance within the professional community.
Revenue Diversification: Although LinkedIn maintained a free model for users, its ad revenue was limited. The introduction of paid features, such as job listings and subscriptions, alongside the launch of an advertising platform, significantly boosted their revenue streams.
Leveraging Strengths: By analyzing user engagement data, LinkedIn recognized that while they effectively engaged initial site visitors, they struggled with cold email outreach. This insight prompted a shift in focus towards improving homepage conversions, a challenging yet effective strategy that led to significant growth.
Testing for Virality: Before prioritizing revenue, LinkedIn concentrated on securing its growth through rigorous experimentation, including growth hacking techniques and analytics. This process ultimately led to the development of a viral growth loop.
Community First: By prioritizing the establishment of a large and engaged user community before focusing on monetization, LinkedIn positioned itself to create a business model tailored to its audience. This approach has facilitated strategic acquisitions, such as SlideShare, and the development of content platforms like Pulse, further driving growth.
Conclusion
Growth marketing is a crucial strategy for businesses aiming for sustainable, long-term success. By concentrating on the entire customer journey and utilizing data-driven insights, marketers can create approaches that not only attract new customers but also retain and engage those who are already loyal.
Whether you are an experienced marketer or just beginning your career, adopting the principles of growth marketing can significantly enhance your success in today’s competitive landscape. By implementing the strategies presented in this guide, you can discover new avenues for growth and position your brand for enduring success.
Continue to experiment, maintain a focus on data, and prioritize the customer experience. Growth is not merely a target; it is an ongoing journey.

